|
Rosalind Franklin Institute
The Rosalind Franklin Institute is medical research centre supported by the Government of the United Kingdom located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Oxfordshire, England. It is named after an English chemist Rosalind Franklin, whose discoveries provided the key data for the correct explanation of the helical structure of DNA in 1953. Launched on 6 June 2018, it was officially opened on 29 September 2021. The government approval was announced on 23 February 2017 by Greg Clark, Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy. According to the press release the basis of the name was "in honour of the pioneering British scientist osalind Franklinwhose use of X-rays to study biological structures played a crucial role in the discovery of DNA's 'double helix' structure by Francis Crick and James Watson". The objective was "to develop disruptive new technologies designed to tackle major challenges in health and life sciences, accelerate the discovery of new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Naismith (chemist)
James Henderson Naismith (born 26 July 1968) is Professor of Structural Biology at the University of Oxford, former Director of the Research Complex at Atomic Energy Research Establishment, Harwell and Director of the Rosalind Franklin Institute. He previously served as Henry Wardlaw, Bishop Wardlaw Professor of Chemical Biology at the University of St Andrews. He was a member of Council of the Royal Society (2021-2022). He is currently the Vice-Chair of Council of the European XFEL, European X-ray Free Electron Laser and Vice-President (non-clinical) of Academy of Medical Sciences (United Kingdom), The Academy of Medical Sciences. Education Naismith was educated at Hamilton Grammar School. He went on to study at the University of Edinburgh where he received a British undergraduate degree classification, first class Bachelor of Science degree in chemistry in 1989. He won a Carnegie Trust for the Universities of Scotland, Carnegie Scholarship to work under the supervision of Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affects a person's ability to function and carry out everyday activities. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Consciousness is not affected. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning, and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging. Several diseases and injuries to the brain, such as a stroke, can give rise to dementia. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes In Oxfordshire
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source (or Diamond) is the UK's national synchrotron light source science facility located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire. Its purpose is to produce intense beams of light whose special characteristics are useful in many areas of scientific research. In particular it can be used to investigate the structure and properties of a wide range of materials from proteins (to provide information for designing new and better drugs), and engineering components (such as a fan blade from an aero-engine) to conservation of archeological artifacts (for example Henry VIII's flagship the Mary Rose). There are more than 50 light sources across the world. With an energy of 3 GeV, Diamond is a medium energy synchrotron currently operating with 32 beamlines. Design, construction and finance The Diamond synchrotron is the largest UK-funded scientific facility to be built in the UK since the Nimrod proton synchrotron which was sited at the Rutherfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Research And Innovation
UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) is a non-departmental public body of the Government of the United Kingdom that directs research and innovation funding, funded through the science budget of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy. History and role Established on 1 April 2018 by the Higher Education and Research Act 2017, UKRI brought nine organisations into one unified body. UKRI was created following a report by Sir Paul Nurse, the President of the Royal Society, who recommended the merger in order to increase integrative cross-disciplinary research. Working in partnership with universities, research organisations, businesses, charities and government, its mission is to foster research and development within the United Kingdom and create a positive "impact" – "push the frontiers of human knowledge and understanding", "deliver economic impact" and "create social and cultural impact". The first Chief Executive Officer of UKRI was the immunologist Professo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology Facilities Council
The Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) is a United Kingdom government agency that carries out research in science and engineering, and funds UK research in areas including particle physics, nuclear physics, space science and astronomy (both ground-based and space-based). History STFC was formed in April 2007 when the Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council (PPARC), the Council for the Central Laboratory of the Research Councils (CCLRC), along with the nuclear physics activities of the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) were brought under the one Umbrella organization, umbrella organisation. The organisation's first Chief Executive was Professor Keith Mason, who held the position until 2011, when he was replaced by Professor John Womersley. Womersley servied as CEO until 2016 when he left to become Director General of the European Spallation Source. Dr Brian Bowsher, former CEO of the National Physical Laboratory and member of STFC's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering And Physical Sciences Research Council
The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) is a British Research Council that provides government funding for grants to undertake research and postgraduate degrees in engineering and the physical sciences, mainly to universities in the United Kingdom. EPSRC research areas include mathematics, physics, chemistry, artificial intelligence and computer science, but exclude particle physics, nuclear physics, space science and astronomy (which fall under the remit of the Science and Technology Facilities Council). Since 2018 it has been part of UK Research and Innovation, which is funded through the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy. History EPSRC was created in 1994. At first part of the Science and Engineering Research Council (SERC), in 2018 it was one of nine organisations brought together to form UK Research and Innovation (UKRI). Its head office is in Swindon, Wiltshire in the same building (Polaris House) that houses the AHRC, BBSRC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Walmsley
Ian Alexander Walmsley FRS is Provost of Imperial College London where he is also Chair of Experimental Physics. He was previously pro-vice-chancellor for research and Hooke Professor of Experimental Physics at the University of Oxford, and a professorial fellow at St Hugh's College, Oxford. He is also director of the NQIT (Networked Quantum Information Technologies) hub within the UK National Quantum Technology Programme, which is led by the University of Oxford. He is also a Fellow of the Institute of Physics, the American Physical Society and the Optical Society of America. Walmsley was educated at Imperial College London, and The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester. He received the Joseph F. Keithley Award For Advances in Measurement Science in 2011 and was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in 2012 for his contributions to quantum optics and ultrafast optics, including his development of the spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and Maurice Wilkins were awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". In subsequent years, it has been recognized that Watson and his colleagues did not properly attribute colleague Rosalind Franklin for her contributions to the discovery of the double helix structure. Watson earned degrees at the University of Chicago ( BS, 1947) and Indiana University (PhD, 1950). Following a post-doctoral year at the University of Copenhagen with Herman Kalckar and Ole Maaløe, Watson worked at the University of Cambridge's Cavendish Laboratory in England, where he first met his future collaborator Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivienne Cox
Dame Vivienne Cox, (born May 1959) is a British businesswoman, chairman of the supervisory board of Vallourec, the French multinational steel components company. Cox was born in 1959 and worked for BP for almost three decades before being named as chairperson of the supervisory board of Vallourec, a French multinational steel components company. She is also a non-executive director of Pearson PLC and a commissioner at the UK's Airports Commission. Since July 2016, Cox has been a non-executive director of GlaxoSmithKline. In July 2018, she became the first Chair of the Rosalind Franklin Institute. Honours Cox was appointed Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE) in the 2016 New Year Honours for services to the economy and sustainability and Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire (DBE) in the 2022 New Year Honours The 2022 New Year Honours are appointments by some of the 15 Commonwealth realms to various orders and honours to recognise and reward good work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term " central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to proteins, it cannot flow back to nucleic acids. In other words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
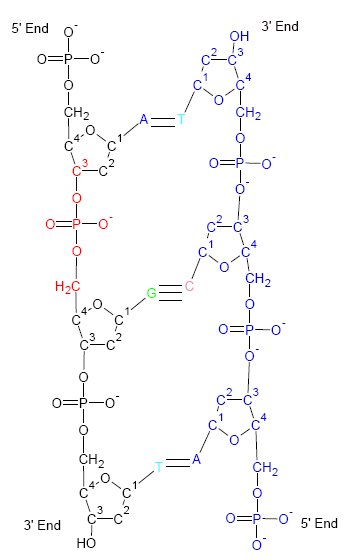
Nucleic Acid Double Helix
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to: *Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom *Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA Nucleus may also refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Astronomy *Active galactic nucleus in astronomy *Comet nucleus, the solid, central part of a comet Biology *Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA *Nucleus (neuroanatomy), a cluster of cell bodies of neurons in the central nervous system *Nucleus that forms in the eye in nuclear sclerosis (early cataracts) *''Nucleus'', a scientific journal concerned with the cell nucleus; published by Taylor & Francis *Nucleus, a small colony of honeybees, induced to raise a new queen by the beekeeper Computer systems * Nucleus (operating system), sometimes a synonym for kernel * Nucleus CMS, a weblog system * Nucleus RTOS, a real-time oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |