|
Roman War Elephants
Due to the Roman focus on infantry and its discipline, war elephants were rarely used. While the Romans did eventually adopt them, and used them occasionally after the Punic wars, especially during the conquest of Greece, they fell out of use by the time of Claudius, after which they were generally used for the purpose of demoralizing enemies instead of being used for tactical purposes. The Romans occasionally used them for transport. History History of elephants and Rome Although the use of war elephants in the Mediterranean is most famously associated with the wars between Carthage and Rome, the introduction of war elephants was primarily the result of the Greek kingdom of Epirus. King Pyrrhus of Epirus brought twenty elephants to attack the Romans at the battle of Heraclea in 280 BC, leaving some fifty additional animals, on loan from Pharaoh Ptolemy II, on the mainland. The Romans were unprepared for fighting elephants, and the Epirot forces routed the Romans. The next year, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velites
''Velites'' (singular: ) were a class of infantry in the Roman army of the mid-Republic from 211 to 107 BC. ''Velites'' were light infantry and skirmishers armed with javelins ( la, hastae velitares), each with a 75cm (30 inch) wooden shaft the diameter of a finger, with a 25cm (10 inch) narrow metal point, to fling at the enemy. They also carried short thrusting swords, or ''gladii'', for use in melee. They rarely wore armour as they were the youngest and poorest soldiers in the legion and could not afford much equipment. They did carry small wooden shields called ''parma'' for protection, and wore headdresses made from wolf skins so their brave deeds could be recognized. The ''velites'' were placed at the front partly for tactical reasons, and also so that they had the opportunity to secure glory for themselves in single combat. ''Velites'' did not form their own units; a number of them were attached to each ''maniple'' of ''hastati'', ''principes'' and ''triarii''. They were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
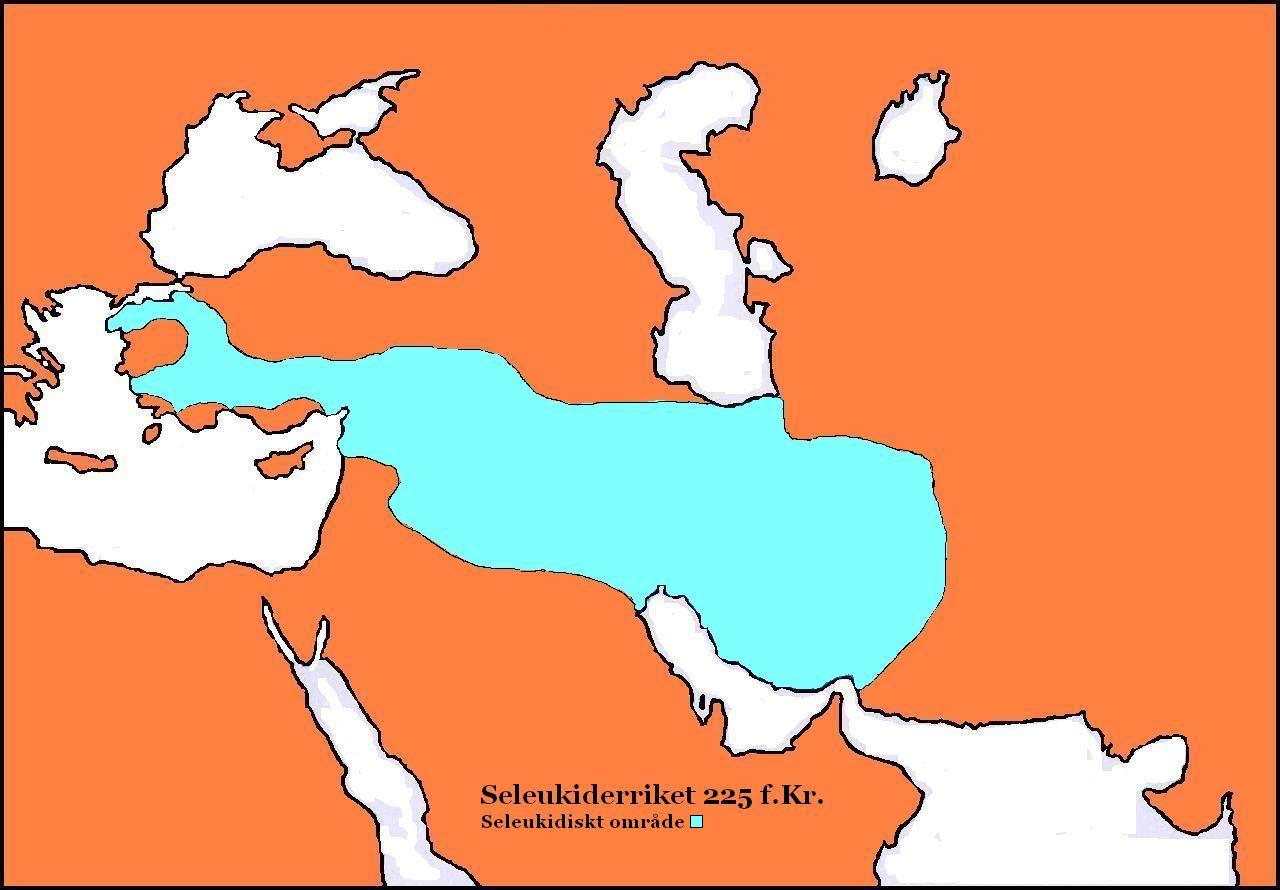
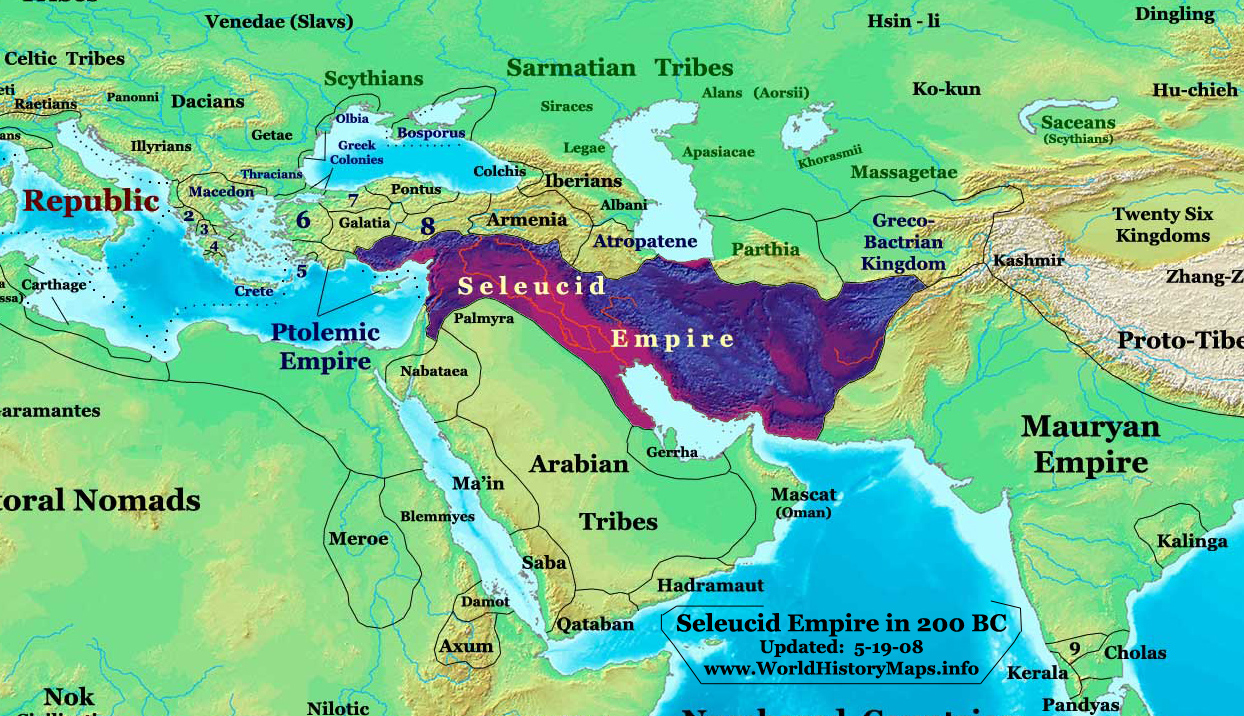
Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman dominat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pergamon under Eumenes II against a Seleucid army of Antiochus III the Great. The two armies initially camped north-east of Magnesia ad Sipylum in Asia Minor (modern-day Manisa, Turkey), attempting to provoke each other into a battle on favorable terrain for several days. When the battle finally began, Eumenes managed to throw the Seleucid left flank into disarray. While Antiochus' cavalry overpowered his adversaries on the right flank of the battlefield, his army's center collapsed before he could reinforce it. Modern estimates give 10,000 dead for the Seleucids and 5,000 killed for the Romans. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman-Pergamene victory, which led to the Treaty of Apamea that ended Seleucid domination in Asia Minor. Backgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Thermopylae (191 BC)
The Battle of Thermopylae took place on 24 April 191 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Manius Acilius Glabrio against a Seleucid-Aetolian army of Antiochus III the Great. When the main bodies of the armies initially clashed at the Thermopylae pass, the Seleucids managed to hold their ground, repulsing multiple Roman assaults. However, a small Roman force under Marcus Porcius Cato managed to outflank the Seleucids from the hillside after surprising the Aetolian garrison of Fort Callidromus. The Seleucids panicked and broke ranks, leading to the destruction of their force. Antiochus managed to escape the battlefield with his cavalry, departing mainland Greece soon afterwards. Background Following his return from his Bactrian (210–209 BC) and Indian (206–205 BC) campaigns, the Seleucid King Antiochus III the Great forged an alliance with Philip V of Macedon, seeking to jointly conquer the territorie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cynoscephalae
The Battle of Cynoscephalae ( el, Μάχη τῶν Κυνὸς Κεφαλῶν) was an encounter battle fought in Thessaly in 197 BC between the Roman army, led by Titus Quinctius Flamininus, and the Antigonid dynasty of Macedon, led by Philip V during the Second Macedonian War. It was a decisive Roman victory and marked the end of the conflict. Prelude In 201 BC, Rome won the Second Punic War against Carthage. Philip V of Macedon had attacked Rome's client states in the Mediterranean for 20 years. The Greek city-states, led by Athens, appealed to Rome for help. In 197 BC the Roman army of Titus Quinctius Flamininus, with his allies from the Aetolian League, marched out towards Pherae in search of Philip, who was at Larissa. Armies Romans Flamininus had about 25,500 men, thus subdivided: 16,000 legionary infantry, 8,400 light infantry, 1,800 cavalry and 20 war elephants; further it included soldiers from the allied Aetolian League, light infantry from Athamania, and mercenar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula,. and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south. Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king PhilipII (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. With a reformed army containing phalanxes wielding the ''sarissa'' pike, PhilipII d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrhic War
The Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC) was largely fought between the Roman Republic and Pyrrhus, the king of Epirus, who had been asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war against the Romans. A skilled commander, with a strong army fortified by war elephants (which the Romans were not experienced in facing), Pyrrhus enjoyed initial success against the Roman legions, but suffered heavy losses even in these victories. Plutarch wrote that Pyrrhus said after the second battle of the war, "If we are victorious in one more battle with the Romans, we shall be utterly ruined." He could not call up more men from home and his allies in Italy were becoming indifferent. The Romans, by contrast, had a very large pool of military manpower and could replenish their legions even if their forces were depleted in many battles. This has led to the expression " Pyrrhic victory", a term for a victory that inflicts losses the victor cannot afford in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maniple (military Unit)
Maniple ( la, manipulus, lit= a handful f soldiers}) was a tactical unit of the Roman Republican armies, adopted during the Samnite Wars (343–290 BC). It was also the name of the military insignia carried by such units. Maniple members, called ''commanipulares'' (singular: ''commanipularis'') were seen as each other's brothers-in-arms, but without the domestic closeness of the eight-man contubernium. Cohorts replaced maniples as organisational units following the Marian reforms of 107 BC. History The manipular system was adopted around 315 BC, during the Second Samnite War. The rugged terrain of Samnium, where the war was fought, was not conducive to the phalanx formation which the Romans had inherited from the Etruscans and Ancient Greeks. The main battle troops of the Etruscans and Latins of this period comprised Greek-style hoplite phalanxes, inherited from the original Greek phalanx military unit. After suffering a series of defeats, culminating in the surrender of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Zama
The Battle of Zama was fought in 202 BC near Zama, now in Tunisia, and marked the end of the Second Punic War. A Roman army led by Publius Cornelius Scipio, with crucial support from Numidian leader Masinissa, defeated the Carthaginian army led by Hannibal. After defeating Carthaginian and Numidian armies at the battles of Utica and the Great Plains, Scipio imposed peace terms on the Carthaginians, who had no choice but to accept them. At the same time, the Carthaginians recalled Hannibal's army from Italy. Confident in Hannibal's forces, the Carthaginians broke the armistice with Rome. Scipio and Hannibal confronted each other near Zama Regia. Hannibal had 36,000 infantry to Scipio's 29,000. One third of Hannibal's army were citizen levies, and the Romans had 6,100 cavalry to Carthage's 4,000, as most of the Numidian cavalry that Hannibal had employed with great success in Italy had defected to the Romans. Hannibal also employed 80 war elephants. The elephants opened t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Trebia
The Battle of the Trebia (or Trebbia) was the first major battle of the Second Punic War, fought between the Carthaginian forces of Hannibal and a Roman army under Sempronius Longus on 22 or 23 December 218 BC. It took place on the flood plain of the west bank of the lower Trebia River, not far from the settlement of Placentia (modern Piacenza), and resulted in a heavy defeat for the Romans. War broke out between Carthage and Rome in 218 BC. The leading Carthaginian general, Hannibal, responded by leading a large army out of Iberia (modern Spain and Portugal), through Gaul, across the Alps and into Cisalpine Gaul (modern northern Italy). The Romans went on the attack against the reduced force which had survived the rigours of the march and Publius Scipio personally led the cavalry and light infantry of the army he commanded against the Carthaginian cavalry at the Battle of Ticinus. He was soundly beaten and personally wounded. The Romans retreated to near Placentia, forti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. The Alpine arch generally extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 128 peaks higher than . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountains, precipitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_p2.342_THERMOPYLAE.jpg)



