|
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Lodi
The Diocese of Lodi ( la, Dioecesis Laudensis) is an Italian Roman Catholic territorial entity that existed since the 4th century; it is a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Milan."Diocese of Lodi" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved February 29, 2016"Diocese of Lodi" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved February 29, 2016 History Under Diocletian, according to the local legend, 4000 Christians with ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodi, Lombardy
Lodi ( , ; Ludesan: ) is a city and ''comune'' in Lombardy, northern Italy, primarily on the western bank of the River Adda. It is the capital of the province of Lodi. History Lodi was a Celtic village; in Roman times it was called, in Latin, Laus Pompeia (probably in honour of the consul Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo) and was known also because its position allowed many Gauls of ''Gallia Cisalpina'' to obtain Roman citizenship. It was in an important position where a vital Roman road crossed the River Adda. Lodi became the see of a diocese in the 3rd century. Saint Bassianus (San Bassiano) is the patron saint of the town. A free commune around 1000, it fiercely resisted the Milanese, who destroyed it in 1111. The old town corresponds to the modern Lodi Vecchio. Frederick Barbarossa rebuilt it on its current location in 1158. From 1220, the ''Lodigiani'' (inhabitants of Lodi) spent decades in constructing a system of miles of artificial rivers and channels (called ''Consorzio di M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Acre (1291)
The siege of Acre (also called the fall of Acre) took place in 1291 and resulted in the Crusaders losing control of Acre to the Mamluks. It is considered one of the most important battles of the period. Although the crusading movement continued for several more centuries, the capture of the city marked the end of further crusades to the Levant. When Acre fell, the Crusaders lost their last major stronghold of the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem. They still maintained a fortress at the northern city of Tartus (today in north-western Syria), engaged in some coastal raids, and attempted an incursion from the tiny island of Ruad, but when they lost that as well in 1302 in the siege of Ruad, the Crusaders no longer controlled any part of the Holy Land. Background In 1187, Saladin conquered much of the Kingdom of Jerusalem (also called the Latin Kingdom), including Acre and Jerusalem, after winning the Battle of Hattin and inflicting heavy losses on the Crusaders. The Third Crusad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipope Clement III
Guibert or Wibert of Ravenna ( 10298 September 1100) was an Italian prelate, archbishop of Ravenna, who was elected pope in 1080 in opposition to Pope Gregory VII and took the name Clement III. Gregory was the leader of the movement in the church which opposed the traditional claim of European monarchs to control ecclesiastical appointments, and this was opposed by supporters of monarchical rights led by the Holy Roman Emperor. This led to the conflict known as the Investiture Controversy. Gregory was felt by many to have gone too far when he excommunicated the Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV and supported a rival claimant as emperor, and in 1080 the pro-imperial Synod of Brixen pronounced that Gregory was deposed and replaced as pope by Guibert. Consecrated as Pope Clement III in Rome in March 1084, he commanded a significant following in Rome and elsewhere, especially during the first half of his pontificate, and reigned in opposition to four successive popes in the anti-imperial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Stephen V
Pope Stephen V ( la, Stephanus V; died 14 September 891) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from September 885 to his death. In his dealings with Photius I of Constantinople, as in his relations with the young Slavic Orthodox church, he pursued the policy of Pope Nicholas I. Early life His father Hadrian, who belonged to the Roman aristocracy, entrusted his education to his relative, Bishop Zachary, librarian of the Holy See. Stephen was created cardinal-priest of Santi Quattro Coronati by Marinus I. Pontificate Stephen V was elected to succeed Adrian III on the account of his holiness on May 17, 885, but was not accepted by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles III the Fat. However, he was consecrated in September 885 without waiting for the imperial confirmation. The emperor sent a legate to overthrow him, but when he found with what unanimity he had been elected, he let the matter rest. Stephen was called upon to face a famine caused by a drought and by locusts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Marinus I
Pope Marinus I (; died 15 May 884) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 882 until his death. Controversially at the time, he was already a bishop when he became pope, and had served as papal legate to Constantinople. He was also erroneously called Martin II (Martinus II) leading to the second pope named Martin to take the name Martin IV. Ecclesiastical career Born at Gallese, Marinus was the son of a priest. He was ordained as a deacon by Pope Nicholas I. He first served as bishop of Caere. On three separate occasions, he had been employed by the three popes who preceded him as legate to Constantinople, his mission in each case having reference to the controversy started by Patriarch Photios I of Constantinople. In 882, he was sent on behalf of Pope John VIII to Duke Athanasius of Naples to warn him not to trade with the Muslims of southern Italy. Marinus I was elected to succeed John VIII as bishop of Rome from around the end of December 882. This papal el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Council Of Constantinople
The Third Council of Constantinople, counted as the Sixth Ecumenical Council by the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic Churches, as well by certain other Western Churches, met in 680–681 and condemned monoenergism and monothelitism as heretical and defined Jesus Christ as having two energies and two wills (divine and human).George Ostrogorsky, ''History of the Byzantine State'' (Rutgers University Press, 1995), 127. Background The council settled a set of theological controversies that went back to the sixth century but had intensified under the emperors Heraclius () and Constans II (). Heraclius had set out to recover much of the part of his empire lost to the Persians and had attempted to bridge the controversy with monophysitism, which was particularly strong in Syria and Egypt, by proposing a moderate theological position that had as good support in the tradition as any other. The result was first monoenergism, i.e. that Christ, though existing in two natures (divine and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory The Great
Pope Gregory I ( la, Gregorius I; – 12 March 604), commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was the bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 to his death. He is known for instigating the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome, the Gregorian mission, to convert the then largely pagan Anglo-Saxons to Christianity. Gregory is also well known for his writings, which were more prolific than those of any of his predecessors as pope. The epithet Saint Gregory the Dialogist has been attached to him in Eastern Christianity because of his ''Dialogues''. English translations of Eastern texts sometimes list him as Gregory "Dialogos", or the Anglo-Latinate equivalent "Dialogus". A Roman senator's son and himself the prefect of Rome at 30, Gregory lived in a monastery he established on his family estate before becoming a papal ambassador and then pope. Although he was the first pope from a monastic background, his prior political experiences may have helped him to be a talented administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Trent
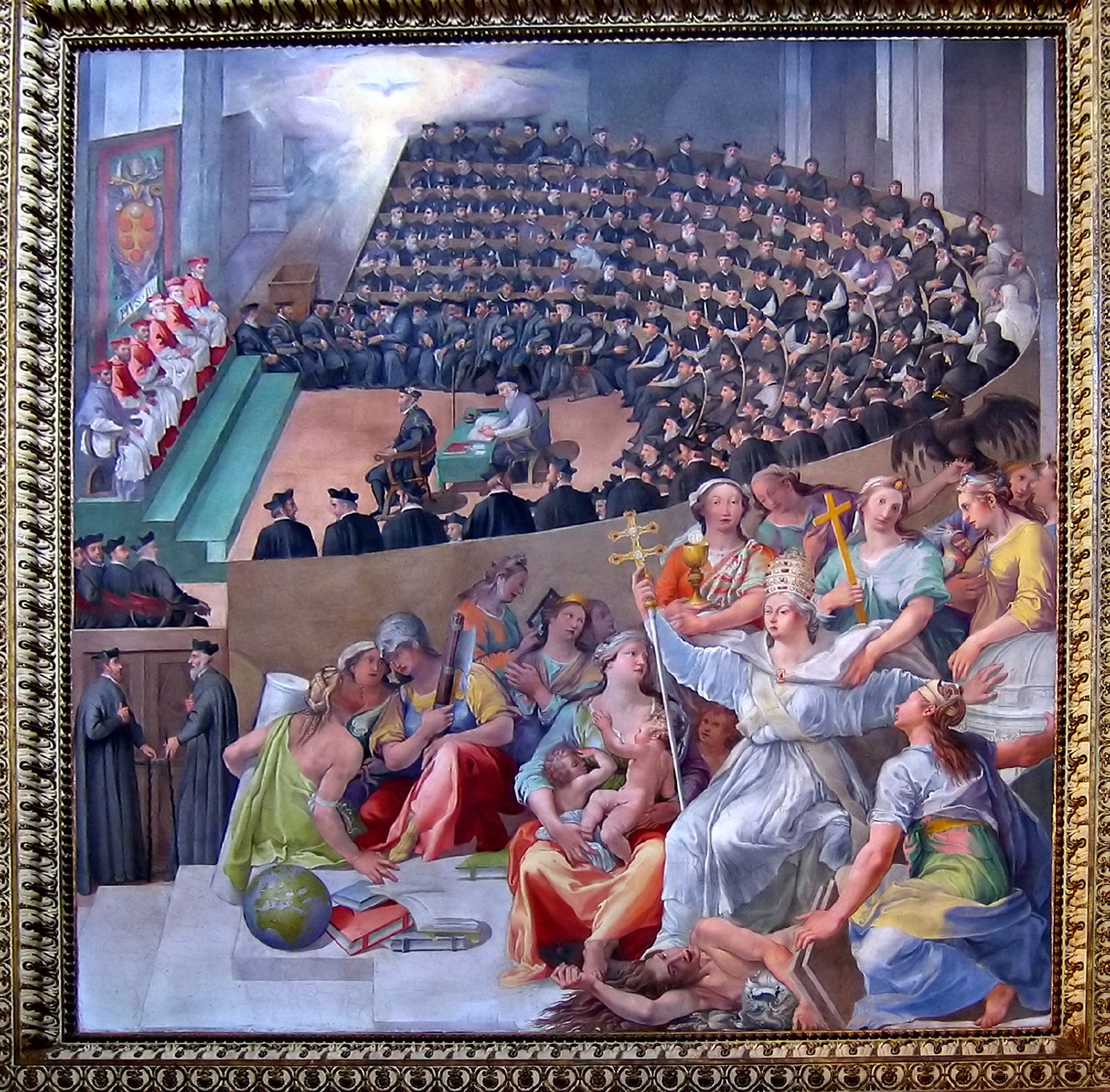
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trento, Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italian Peninsula, Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described as the embodiment of the Counter-Reformation."Trent, Council of" in Cross, F. L. (ed.) ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church'', Oxford University Press, 2005 (). The Council issued condemnations of what it defined to be Heresy, heresies committed by proponents of Protestantism, and also issued key statements and clarifications of the Church's doctrine and teachings, including scripture, the biblical canon, sacred tradition, original sin, Justification (theology), justification, salvation, the Sacraments of the Catholic Church, sacraments, the Mass (liturgy), Mass, and the Veneration, veneration of saints.Wetterau, Bruce. ''World History''. New York: Henry Holt and Company, 1994. The Council met for twenty- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III (c. 1100/1105 – 30 August 1181), born Roland ( it, Rolando), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 September 1159 until his death in 1181. A native of Siena, Alexander became pope after a contested election, but had to spend much of his pontificate outside Rome while several rivals, supported by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa, claimed the papacy. Alexander rejected Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos' offer to end the East–West Schism, sanctioned the Northern Crusades, and held the Third Council of the Lateran. The city of Alessandria in Piedmont is named after him. Early life and career Rolando was born in Siena. From the 14th century, he was referred to as a member of the aristocratic family of Bandinelli, although this has not been proven. He was long thought to be the 12th-century canon lawyer and theologian Master Roland of Bologna, who composed the "Stroma" or "Summa Rolandi"—one of the earliest comment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aachen on 9 March 1152. He was crowned King of Italy on 24 April 1155 in Pavia and emperor by Pope Adrian IV on 18 June 1155 in Rome. Two years later, the term ' ("holy") first appeared in a document in connection with his empire. He was later formally crowned King of Burgundy, at Arles on 30 June 1178. He was named by the northern Italian cities which he attempted to rule: Barbarossa means "red beard" in Italian; in German, he was known as ', which means "Emperor Redbeard" in English. The prevalence of the Italian nickname, even in later German usage, reflects the centrality of the Italian campaigns to his career. Frederick was by inheritance Duke of Swabia (1147–1152, as Frederick III) before his i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipope Victor IV (1159–1164)
Victor IV (born Octavian or Octavianus: ''Ottaviano dei Crescenzi Ottaviani di Monticelli'') (1095 – 20 April 1164) was elected as a Ghibelline antipope in 1159, following the death of Pope Adrian IV and the election of Alexander III. His election was supported by the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. He took the name Victor IV, not accounting for Antipope Victor IV of 1138, whose holding of the papal office was deemed illegitimate. Early life and career Octaviano Monticelli belonged to one of the most powerful counts of Tusculum. He was appointed as rector of Benevento in May 1137, and cardinal priest of San Nicola in Carcere in 1138. In 1151 Octaviano became cardinal priest of Santa Cecilia. He was described by John of Salisbury as eloquent and refined, but petty and parsimonious. When he was sent with Cardinal Jordan of Santa Susanna as a papal legate to summon Conrad III of Germany to Italy to be crowned Holy Roman Emperor, he quarrelled with his co-legate and, in John of Sali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)



.jpg)