|
Robert Koch Institute For Infectious Diseases
The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) is a German federal government agency and research institute responsible for disease control and prevention. It is located in Berlin and Wernigerode. As an upper federal agency, it is subordinate to the Federal Ministry of Health. It was founded in 1891 and is named for its founding director, the founder of modern bacteriology and Nobel laureate Robert Koch. Tasks The Robert Koch Institute monitors public health. Its core tasks include the detection, prevention and combatting of infectious diseases and non-communicable diseases in Germany. The institute advises the specialist public and government, e.g. on preventing and tackling infectious disease outbreaks such as the COVID-19 pandemic, the swine flu pandemic in 2009 and the 2011 Germany E. coli O104:H4 outbreak, EHEC O104:H4 outbreak in 2011. The institute is also in charge of health monitoring and health reporting in Germany, covering non-communicable diseases: in large monitoring studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institute
A research institute, research centre, research center or research organization, is an establishment founded for doing research. Research institutes may specialize in basic research or may be oriented to applied research. Although the term often implies natural science research, there are also many research institutes in the social science as well, especially for sociological and historical research purposes. Famous research institutes In the early medieval period, several astronomical observatories were built in the Islamic world. The first of these was the 9th-century Baghdad observatory built during the time of the Abbasid caliph al-Ma'mun, though the most famous were the 13th-century Maragheh observatory, and the 15th-century Ulugh Beg Observatory. The Kerala School of Astronomy and Mathematics was a school of mathematics and astronomy founded by Madhava of Sangamagrama in Kerala, India. The school flourished between the 14th and 16th centuries and the original discoverie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West African Ebola Virus Epidemic
The 2013–2016 epidemic of Ebola virus disease, centered in Western Africa, was the most widespread outbreak of the disease in history. It caused major loss of life and socioeconomic disruption in the region, mainly in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone. The first cases were recorded in Guinea in December 2013; later, the disease spread to neighbouring Liberia and Sierra Leone, with minor outbreaks occurring in Ebola virus disease in Nigeria, Nigeria and Mali. Secondary infections of medical workers occurred in the United States and Spain. In addition, isolated cases were recorded in Senegal, the United Kingdom and Italy. The number of cases peaked in October 2014 and then began to decline gradually, following the commitment of substantial international resources. It caused significant mortality, with a considerable case fatality rate. By the end of the epidemic, 28,616 people had been infected; of these, 11,310 had died, for a case-fatality rate of 40%. , the World Health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Health Agency
The Federal Health Agency (german: Bundesgesundheitsamt) was a federal government agency and the central research institution for public health in Germany. It was founded in 1876, named the Imperial Health Agency (german: Kaiserliches Gesundheitsamt). It was succeeded by the Reichsgesundheitsamt in 1918 and by the Bundesgesundheitsamt in 1952 (both meaning Federal Health Agency). The agency was dissolved in 1994, and its responsibilities transferred to three institutions, the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices, the Robert Koch Institute The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) is a German federal government agency and research institute responsible for disease control and prevention. It is located in Berlin and Wernigerode. As an upper federal agency, it is subordinate to the Federa ... and the Federal Institute for Health Consumer Protection and Veterinary Medicine.Hans-Joachim Weise, ''Bundesgesundheitsamt – BGA; 100 Jahre Forschung für die Gesundheit'', 1976 Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
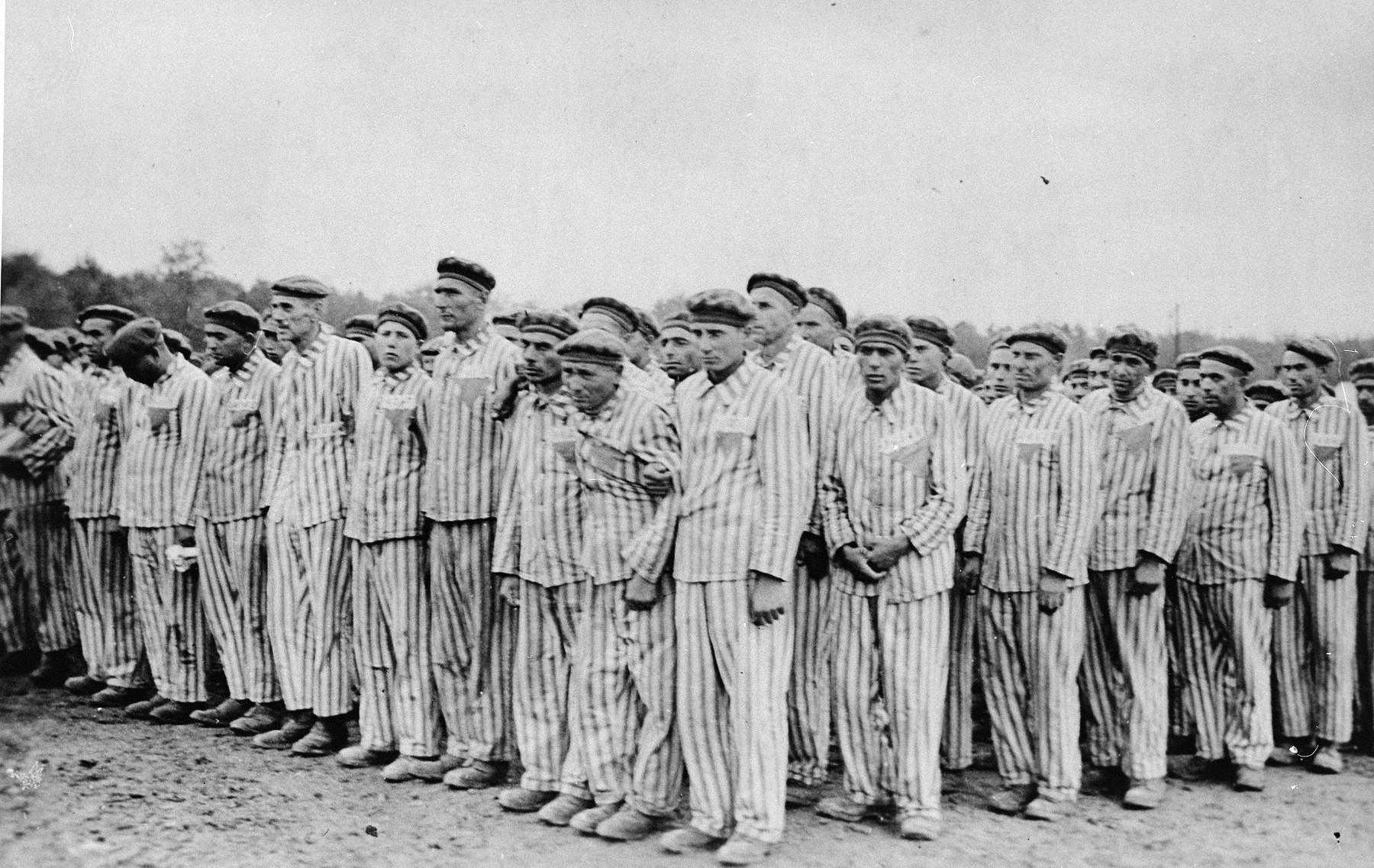
Buchenwald Concentration Camp
Buchenwald (; literally 'beech forest') was a Nazi concentration camp established on hill near Weimar, Germany, in July 1937. It was one of the first and the largest of the concentration camps within Germany's 1937 borders. Many actual or suspected communists were among the first internees. Prisoners came from all over Europe and the Soviet Union—Jews, Poles and other Slavs, the mentally ill and physically disabled, political prisoners, Romani people, Freemasons, and prisoners of war. There were also ordinary criminals and sexual "deviants". All prisoners worked primarily as forced labor in local armaments factories. The insufficient food and poor conditions, as well as deliberate executions, led to 56,545 deaths at Buchenwald of the 280,000 prisoners who passed through the camp and its 139 subcamps. The camp gained notoriety when it was liberated by the United States Army in April 1945; Allied commander Dwight D. Eisenhower visited one of its subcamps. From August 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. The diseases are caused by specific types of bacterial infection. Epidemic typhus is due to ''Rickettsia prowazekii'' spread by body lice, scrub typhus is due to ''Orientia tsutsugamushi'' spread by chiggers, and murine typhus is due to ''Rickettsia typhi'' spread by fleas. Vaccines have been developed, but none are commercially available. Prevention is achieved by reducing exposure to the organisms that spread the disease. Treatment is with the antibiotic doxycycline. Epidemic typhus generally occurs in outbreaks when poor sanitary conditions and crowding are present. While once common, it is now rare. Scrub typhus occurs in Southeast Asia, Japan, and northern Australia. Murine typhus occurs in tropical and subtropical areas of the worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe. On 30 January 1933, Hitler was appointed chancellor of Germany, the head of gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Levinthal
Dr Walter Michel Levinthal FRSE (1886–1963) was a German-born bacteriologist, working in Britain in the 20th century. He gave his name to Levinthal’s Agar. He is known for his work on Psittacosis and the influenza virus. Life He was born in Berlin on 12 April 1886. He studied Medicine at Berlin, Freiburg and Munich graduating in 1909 and later receiving his doctorate (MD) from Munich. His continuing studies allowed him to avoid conscription during the First World War and in 1919 he joined the Robert Koch Institute in Berlin. He quickly rose to the position of Deputy Director of the Research Department. In 1922 working with Fred Neufeld, the Director of the Institute, he made important advances in molecular biology. In 1924 he went to the United States and worked in the Rockefeller Institute in New York City. Here he studied pneumococci and the diphtheria bacilli, and became skilled in the cultivation of single cells. He returned to Berlin where over and above his clinical wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred Neufeld
Fred (Friedrich) Neufeld (17 February 1869 – 18 April 1945) was a physician and bacteriologist who discovered the pneumococcal types. This discovery led Fred Griffith to show that one pneumococcal type could be transformed into another (Griffith's experiment). Subsequently, Oswald Avery demonstrated that the transforming substance was DNA. All modern molecular biology has evolved from this work. Early years Neufeld was the son of a physician. He was musically talented and a gifted pianist. In 1894, Neufeld became assistant to Robert Koch. He worked with Koch on studies of tuberculosis and went to Rhodesia with Koch in 1903 to study rinderpest. Neufeld's discoveries In 1900 Neufeld discovered bile solubility of pneumococci. Addition of a small amount of ox bile to a pneumococcal culture results in complete destruction of the culture after a short incubation. This unique property became widely used to diagnose pneumococcal infections. Then, using immunological techniques, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and last for three days. It usually starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body. The rash is sometimes itchy and is not as bright as that of measles. Swollen lymph nodes are common and may last a few weeks. A fever, sore throat, and fatigue may also occur. Joint pain is common in adults. Complications may include bleeding problems, testicular swelling, encephalitis, and inflammation of nerves. Infection during early pregnancy may result in a miscarriage or a child born with congenital rubella syndrome (CRS). Symptoms of CRS manifest as problems with the eyes such as cataracts, deafness, as well as affecting the heart and brain. Problems are rare after the 20th week of pregnancy. Rubella is usually spread from one person to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur in part due to measles-induced immunosuppression. Less commonly seizures, blindness, or inflammation of the brain may occur. Other names include ''morbilli'', ''rubeola'', ''red measles'', and ''English measles''. Both rubella, also known as ''German measles'', and roseola are different diseases caused by unrelated viruses. Mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |