|
Robert Horne (virologist)
Robert W. Horne (21 January 1923 – 13 November 2010) was a virologist and expert in electron microscopy. Life and academic career Horne was raised in Montreal and served in the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. He began his scientific career at the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge, where he began working with transmission electron microscopes with Vernon Ellis Cosslett. He received his master's and doctorate from the University of Cambridge. In 1961, Horne moved to what was then the Institute of Animal Physiology (now the Babraham Institute), and in 1968 he moved again to what became the John Innes Centre, directed by Roy Markham. Horne remained there as a department head until retiring in 1982. He continued working after his retirement as an honorary professor at the University of East Anglia. In addition to his scientific interests, Horne was a sailing enthusiast and an artist who focused on marine art. Research Horne specialized in the use of el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virologist
Virology is the scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy. The identification of the causative agent of tobacco mosaic disease (TMV) as a novel pathogen by Martinus Beijerinck (1898) is now acknowledged as being the official beginning of the field of virology as a discipline distinct from bacteriology. He realized the source was neither a bacterial nor a fungal infection, but something completely different. Beijerinck used the word "virus" to describe the mysterious agent in his 'contagium vivum fluidum' ('contagious living fluid'). Rosalind Franklin proposed the full structure of the tobacco mosaic virus in 1955. Virology began whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Staining
In microscopy, negative staining is an established method, often used in diagnostic microscopy, for contrasting a thin specimen with an optically opaque fluid. In this technique, the background is stained, leaving the actual specimen untouched, and thus visible. This contrasts with positive staining, in which the actual specimen is stained. Bright field microscopy For bright-field microscopy, negative staining is typically performed using a black ink fluid such as nigrosin and India ink. The specimen, such as a wet bacterial culture spread on a glass slide, is mixed with the negative stain and allowed to dry. When viewed with the microscope the bacterial cells, and perhaps their spores, appear light against the dark surrounding background. An alternative method has been developed using an ordinary waterproof marking pen to deliver the negative stain. Transmission electron microscopy In the case of transmission electron microscopy, opaqueness to electrons is related to the atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liposome
A liposome is a small artificial vesicle, spherical in shape, having at least one lipid bilayer. Due to their hydrophobicity and/or hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, particle size and many other properties, liposomes can be used as drug delivery vehicles for administration of pharmaceutical drugs and nutrients, such as lipid nanoparticles in mRNA vaccines, and DNA vaccines. Liposomes can be prepared by disrupting biological membranes (such as by sonication). Liposomes are most often composed of phospholipids, especially phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol, but may also include other lipids, such as egg, phosphatidylethanolamine, as long as they are compatible with lipid bilayer structure. A liposome design may employ surface ligands for attaching to unhealthy tissue. The major types of liposomes are the multilamellar vesicle (MLV, with several lamellar phase lipid bilayers), the small unilamellar liposome vesicle (SUV, with one lipid bilayer), the large unilamellar vesicle ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine. Phospholipids are a key component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. In eukaryotes, cell membranes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids. The combination provides fluidity in two dimensions combined with mechanical strength against rupture. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues was lecith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alec Bangham
Alec Douglas Bangham FRS (10 November 1921 Manchester – 9 March 2010 Great Shelford) was a British biophysicist who first studied blood clotting mechanisms but became well known for his research on liposomes and his invention of clinically useful artificial lung surfactants. Life Bangham was the son of Donald Bangham, and Edith Kerby. He studied at the Downs School, and then Bryanston School, and proceeded to earn an MB MS in medicine from University College London. He was appointed to Addenbrooke's Hospital, where he served as a pathologist, in the Royal Army Medical Corps, becoming a captain in 1948. Bangham worked at the Babraham Institute in Cambridge from 1952 to 1982. He is best known for his research on liposomes. Family He was married to Rosalind; they had four children and eleven grandchildren. His brother was Derek Bangham. Awards *1965 doctorate of medicine from London University *1977 Fellow of the Royal Society *1981 Fellow of University College London *199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
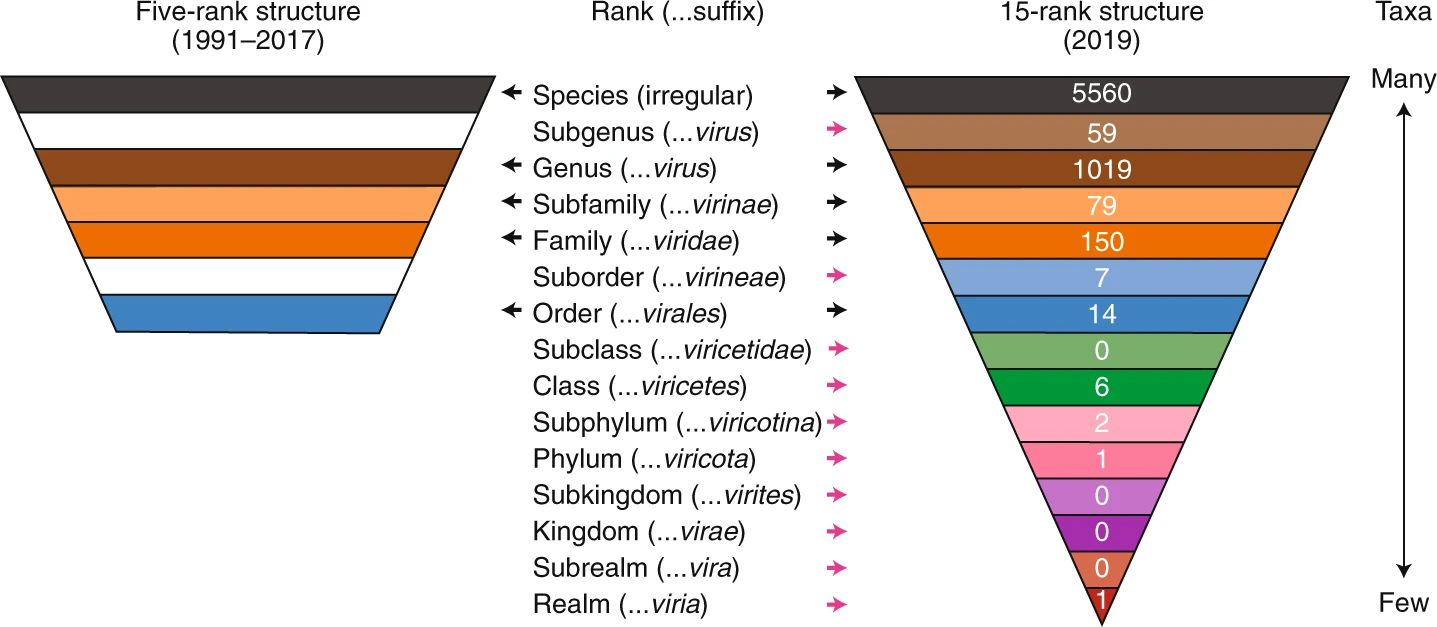
Viral Taxonomy
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a Alpha taxonomy, taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cell (biology), cellular organisms. Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as Virus#Structure, morphology, nucleic acid type, mode of replication, Host (biology), host organisms, and the type of disease they cause. The formal taxonomic classification of viruses is the responsibility of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) system, although the Baltimore classification system can be used to place viruses into one of seven groups based on their manner of mRNA synthesis. Specific naming conventions and further classification guidelines are set out by the ICTV. A catalogue of all the world's known viruses has been proposed and, in 2013, some preliminary efforts were underway. Definitions Species definition Species form the basis for any biological classification system. Before 1982, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Tournier (virologist)
Paul Tournier (12 May 1898 – 7 October 1986) was a Swiss physician and author who had acquired a worldwide audience for his work in pastoral counseling. His ideas had a significant impact on the spiritual and psychosocial aspects of routine patient care, and he has been called the twentieth century's most famous Christian physician.The Christian Psychology of Paul Tournier, by Cary R Collins (1973) book review by H. Newton Malony, Fuller Theological Seminary Life and education Tournier was born in , Switzerland, the son of Pastor Louis Tournier and Alisabeth Ormond. His 70-year-old father, who was a ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Michel Lwoff
André Michel Lwoff (8 May 1902 – 30 September 1994) was a French microbiologist and Nobel laureate of Russian-Polish origin. Education, early life and career Lwoff was born in Ainay-le-Château, Allier, in Auvergne, France, the son of Marie (Siminovitch), an artist, and Solomon Lwoff, a psychiatrist. He joined the Institute Pasteur in Paris when he was 19 years old. In 1932, he finished his PhD and, with the help of a grant from the Rockefeller Foundation, moved with his wife and co-researcher Marguerite Lwoff to the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Medical Research of Heidelberg to Otto Meyerhof, where he did research on the development of flagellates. Another Rockefeller grant allowed him go to the University of Cambridge in 1937. In 1938, he was appointed departmental head at the Institut Pasteur, where he did groundbreaking research on bacteriophages, microbiota and on the poliovirus. Awards and honors He was awarded numerous prizes from the French Académie des Sciences, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The capsid and inner genome is called the nucleocapsid. Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the helical shape resembles the shape of a spring, taking the space of a cylinder but not being a cylinder itself. The capsid faces may consist of one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpes Simplex Virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 are very common and contagious. They can be spread when an infected person begins shedding the virus. As of 2016, about 67% of the world population under the age of 50 had HSV-1. In the United States, about 47.8% and 11.9% are estimated to have HSV-1 and HSV-2, respectively, though actual prevalence may be much higher. Because it can be transmitted through any intimate contact, it is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Symptoms Many of those who are infected ''never'' develop symptoms. Symptoms, when they occur, may include watery blisters in the skin or mucous membranes of the mouth, lips, nose, genitals, or eyes (herpes simplex keratitis). Lesions heal with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willie Russell (virologist)
William Fraser Russell (born 6 December 1901 in Falkirk) was a Scottish professional footballer who played as an inside right. He scored both goals for Airdrieonians in the 1924 Scottish Cup Final. Playing career Airdrieonians He formed part of a potent Airdrie front line including Hughie Gallacher and Bob McPhail. Russell scored both goals for the ''Diamonds'' when they won the 1924 Scottish Cup Final against Hibernian.The Cup Final , Airdrieonians' First Success The Glasgow Herald, 21 April 1924 McPhail said, "The terror-like attitude of Gallacher caused havoc with the Hibs defenders. He and Russell were easily our best forwards". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Wildy
Norman Peter Leete Wildy (31 March 1920 – 10 March 1987) was a 20th-century British virologist who was an expert on the herpes simplex virus. Education and personal life He was born in Tunbridge Wells in Kent on 31 March 1920 the son of Eric Lawrence Wildy (1890–1973) an electrical engineer, and his wife, Gwendolen Leete (1890–1982). He was educated at Eastbourne College. He studied Medicine at Cambridge University graduating MB ChB, and completed his medical training at St Thomas Hospital, London. In 1945 he married Joan Audrey Kenion. They had a son and two daughters.ODNB Prof N P L Wildy He was called up and did his National Service as a medical officer with the Kings West African Rifles, serving in Nigeria, India and Egypt. On his return he worked as a house officer at Greenbank Hospital, Plymouth. Housing was in short supply, so he bought ''Happy Medium'', a retired RAF air-sea rescue launch, which was moored initially on the Cornish side of the Tamar. When he obta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.gif)
