|
Ritom
__NOTOC__ Lago Ritom is a lake in the Piora valley, Ticino, Switzerland. The natural lake is used as a reservoir by the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB-CFF-FFS) to generate hydro-electric power for the Gotthard line. The first dam was built in 1918 and, in 1950, its height was increased by 23 m. Overview The lake's surface area is 1.49 km² at an elevation of 1850 m. With Lake Cadagno and Lago di Tom, it is one of the main lakes in the Piora valley. Before being used as a reservoir, Lake Ritom was a meromictic lake similar to the nearby Lake Cadagno. Transport The lake can be reached by funicular from Piotta 786 m below. The track with a length of 1,369 m has a maximum inclination of 87.8%, the highest in Europe after the Gelmerbahn funicular (106%). See also *List of lakes of Switzerland *List of mountain lakes of Switzerland This is a list of high-altitude lakes in Switzerland. It includes all significant lakes, natural or artificial, with an area over 4 hectares an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piotta, Switzerland
Piotta is a village in the municipality of Quinto in the Swiss canton of Ticino. Geography The village, located next to the neighbrouring Ambrì, lies in the Leventina Valley, below the Lepontine Alps, and is crossed in the middle by Ticino river. It is 3 km far from Quinto, 5 from Airolo and 52 from Bellinzona. Transport Piotta is the location of the base station of the Ritom funicular, linking the village to Ritom Lake. Along with the neighbouring village of Ambrì, Piotta is served by the infrequently served Ambrì-Piotta railway station on the Gotthard railway, and is located close to Ambri Airport. Sport The village hosts the professional ice hockey team HC Ambrì-Piotta, that plays in indoor sporting arena of "Valascia Valascia was an indoor sporting arena located in Ambrì, Switzerland. The capacity of the arena was 6,500 and was built in 1959. It served as the home arena of the HC Ambri-Piotta ice hockey team of the National League (NL) from 1959 to 2021. The ...", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lakes Of Switzerland
This article contains a sortable table listing all major lakes of Switzerland. The table includes all still water bodies, natural or artificial, that have a surface area of at least , regardless of water volume, maximum depth or other metric. These lakes are ranked by area, the table including also the elevation above sea level and maximum depth. They are either natural (type N), natural but used as reservoirs (NR) or fully artificial (A). For a list of artificial lakes only, see List of dams and reservoirs in Switzerland. For a list of lakes above that includes smaller water bodies, see List of mountain lakes of Switzerland. Along with the mountains, lakes constitute a major natural feature of Switzerland, with over of shores within the country.Approximately (see coastline paradox) counting only the 17 lakes over (length retrieved from the Google Earth geographical information program). Lakes, large and small, can be found in almost all cantons and provide an important sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lago Di Tom
__NOTOC__ Lago di Tom is a lake in the Piora Valley, in the canton of Ticino, Switzerland. Its surface area is . See also *List of mountain lakes of Switzerland This is a list of high-altitude lakes in Switzerland. It includes all significant lakes, natural or artificial, with an area over 4 hectares and a height over 800 metres above sea level. This height approximately corresponds to the transiti ... Tom {{ticino-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
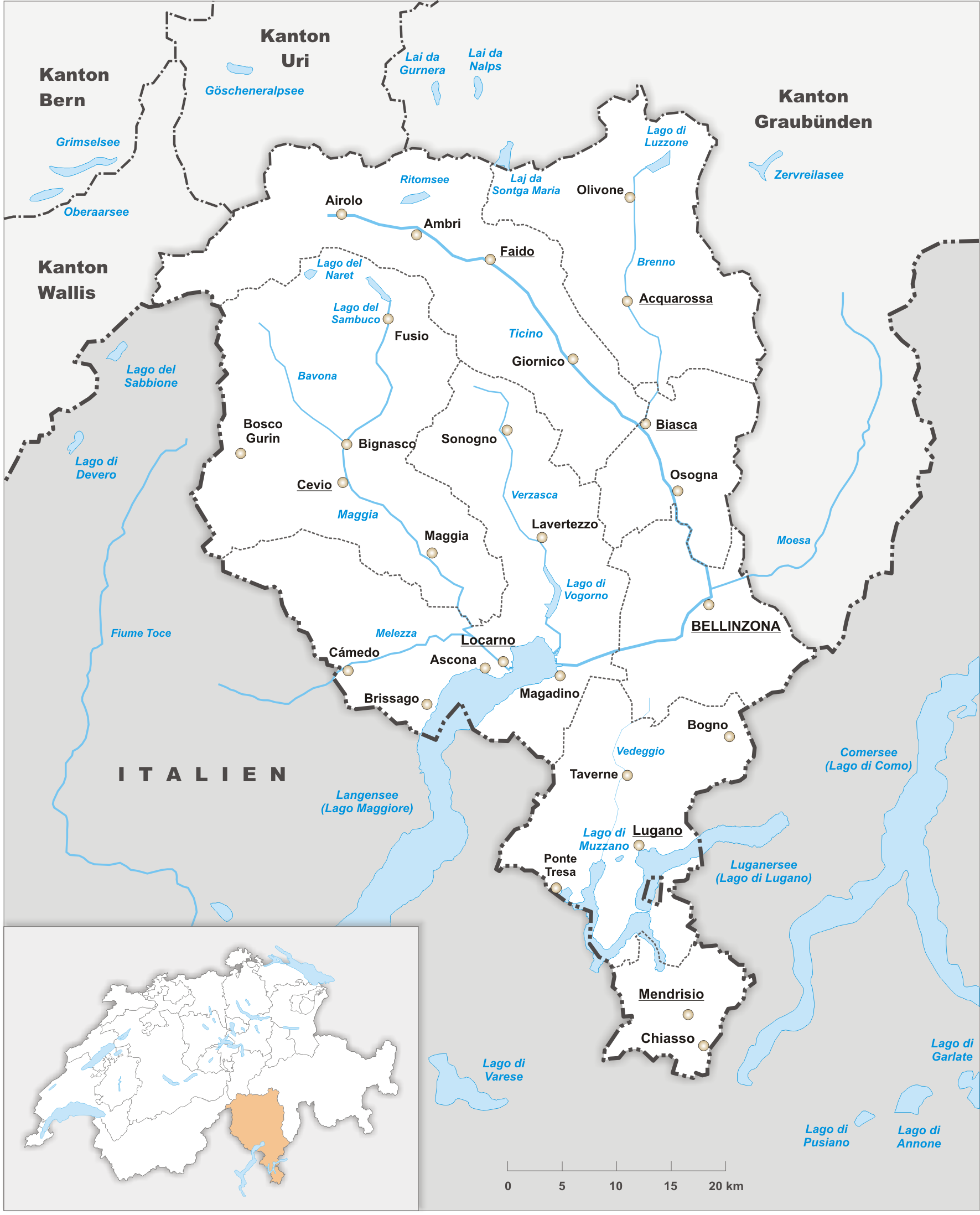
Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts and its capital city is Bellinzona. It is also traditionally divided into the Sopraceneri and the Sottoceneri, respectively north and south of Monte Ceneri. Red and blue are the colours of its flag. Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. It is one of the three large southern Alpine cantons, along with Valais and the Grisons. However, unlike all other cantons, it lies almost entirely south of the Alps, and has no natural access to the Swiss Plateau. Through the main crest of the Gotthard and adjacent mountain ranges, it borders the canton of Valais to the northwest, the canton of Uri to the north and the canton of Grisons to the northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotthardbahn
The Gotthard railway (german: Gotthardbahn; it, Ferrovia del Gottardo) is the Swiss trans-alpine railway line from northern Switzerland to the canton of Ticino. The line forms a major part of an important international railway link between northern and southern Europe, especially on the Rotterdam-Basel-Genoa corridor. The Gotthard Railway Company (german: Gotthardbahn-Gesellschaft) was the former private railway company which financed the construction of, and originally operated, that line. The railway comprises an international main line through Switzerland from Basel (French Bâle) or Zürich to Immensee to Chiasso, together with branches, from Immensee to Lucerne and Rotkreuz, from Arth-Goldau to Zug, and from Bellinzona to Chiasso, via Locarno and Luino. The main line, second highest standard railway in Switzerland, penetrates the Alps by means of the Gotthard Tunnel at above sea level. The line then descends as far as Bellinzona, at above sea level, before climbing aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mountain Lakes Of Switzerland
This is a list of high-altitude lakes in Switzerland. It includes all significant lakes, natural or artificial, with an area over 4 hectares and a height over 800 metres above sea level. This height approximately corresponds to the transition between the foothill zone and the montane zone, in the Alps and in the Jura Mountains. Lakes can be found up to elevations of almost 3000 metres, where is the climatic snow line in the Alps. For each lake, the culminating point of the drainage basin is indicated, along with the river basin of which it is part. For a list of artificial lakes only, see List of dams and reservoirs in Switzerland. For a general list of lakes, see List of lakes of Switzerland. Distribution of mountain lakes by canton Main list See also * List of glaciers in Switzerland * List of mountains of Switzerland * List of lakes of Switzerland Notes and references External linksMountain lakes (MySwitzerland.com) {{Portal bar, Geography, Mountains, Switzerlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelmerbahn Funicular
The Gelmer Funicular is a cable railway in the canton of Bern, Switzerland. It links a lower terminus at Handegg, in the Haslital (the valley of the upper Aar River), with an upper terminus at the Gelmersee lake. The Gelmerbahn was the steepest funicular in Switzerland and Europe, until the opening of the new Stoos Funicular in 2017. The Handegg terminus of the line is close to the road over the Grimsel Pass. It is accessible by car and by an infrequent PostBus service. It is technically not a funicular, which has two cars that counterbalance each other, but is propelled by a winch. History The funicular was originally built to facilitate the construction of the Gelmersee, a reservoir, constructed in 1926 in order to exploit the hydroelectric resources of the area and was not opened for public use until 2001. The line is owned and operated by Kraftwerke Oberhasli AG (KWO) which owns the power station. Operation The line operates from the beginning of June through to mid-Octo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade (slope)
The grade (also called slope, incline, gradient, mainfall, pitch or rise) of a physical feature, landform or constructed line refers to the tangent of the angle of that surface to the horizontal. It is a special case of the slope, where zero indicates horizontality. A larger number indicates higher or steeper degree of "tilt". Often slope is calculated as a ratio of "rise" to "run", or as a fraction ("rise over run") in which ''run'' is the horizontal distance (not the distance along the slope) and ''rise'' is the vertical distance. Slopes of existing physical features such as canyons and hillsides, stream and river banks and beds are often described as grades, but typically grades are used for human-made surfaces such as roads, landscape grading, roof pitches, railroads, aqueducts, and pedestrian or bicycle routes. The grade may refer to the longitudinal slope or the perpendicular cross slope. Nomenclature There are several ways to express slope: # as an ''angle'' of inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funicular
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite ends of a haulage cable, which is looped over a pulley at the upper end of the track. The result of such a configuration is that the two carriages move synchronously: as one ascends, the other descends at an equal speed. This feature distinguishes funiculars from inclined elevators, which have a single car that is hauled uphill. The term ''funicular'' derives from the Latin word , the diminutive of , meaning 'rope'. Operation In a funicular, both cars are permanently connected to the opposite ends of the same cable, known as a ''haul rope''; this haul rope runs through a system of pulleys at the upper end of the line. If the railway track is not perfectly straight, the cable is guided along the track using sheaves – unpowered pulleys tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piora Valley
''Piora'' is a genus of Papuasian plants in the tribe Astereae within the family Asteraceae. ;Species The only known species is ''Piora ericoides'', native to the island of New Guinea New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr .... References Monotypic Asteraceae genera Astereae[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meromictic Lake
A meromictic lake is a lake which has layers of water that do not intermix. In ordinary, holomictic lakes, at least once each year, there is a physical mixing of the surface and the deep waters. The term ''meromictic'' was coined by the Austrian Ingo Findenegg in 1935, apparently based on the older word ''holomictic''. The concepts and terminology used in describing meromictic lakes were essentially complete following some additions by G. Evelyn Hutchinson in 1937. Characteristics Most lakes are ''holomictic''; that is, at least once per year, physical mixing occurs between the surface and the deep waters. In so-called monomictic lakes, the mixing occurs once per year; in dimictic lakes, the mixing occurs twice a year (typically spring and autumn), and in polymictic lakes, the mixing occurs several times a year. In meromictic lakes, however, the layers of the lake water can remain unmixed for years, decades, or centuries. Meromictic lakes can usually be divided into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Cadagno
__NOTOC__ Lake Cadagno (Italian: ''Lago di Cadagno'') is a meromictic lake in the Piora valley (canton of Ticino), Switzerland. As one of a few meromictic lakes in Europe, it is the object of numerous scientific studies. The Piora valley - located in the Saint-Gotthard Massif (central Swiss Alps) in the Southern part of Switzerland near Airolo at an altitude of 1921 m above sea level - is a landlocked alpine valley whose scientific value has been recognized for more than two centuries. In the past, the lake was used as a reservoir. Lake Cadagno is a rare example of crenogenic meromixis. Its waters show a permanent stratification due to a natural geological phenomenon. The lower abounds with dissolved mineral salts (sulphate, magnesium, calcium, carbonate) originating from sublacustrine springs, whereas the separate upper layer is permanently oxygenated. Anaerobic phototrophic bacteria – among them ''Chromatium okenii''—thrive between the two layers where they find the ideal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)

