|
Risk-based Audit
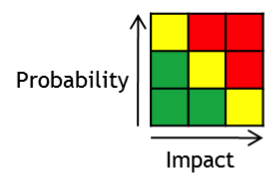
Risk-based auditing is a style of auditing which focuses upon the analysis and management of risk. In the UK, the 1999 Turnbull Report on corporate governance required directors to provide a statement to shareholders of the significant risks to the business. This then encouraged the audit activity of studying these risks rather than just checking compliance with existing controls. Standards for risk management have included the COSO guidelines and the first international standard, AS/NZS 4360. The latter is now the basis for a family of international standards for risk management — ISO 31000. A traditional audit would focus upon the transactions which would make up financial statements such as the balance sheet In financial accounting, a balance sheet (also known as statement of financial position or statement of financial condition) is a summary of the financial balances of an individual or organization, whether it be a sole proprietorship, a business .... A risk-bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Analyzer
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. The international standard definition of risk for common understanding in different applications is “effect of uncertainty on objectives”. The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas ( business, economics, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and generic guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditing
An audit is an "independent examination of financial information of any entity, whether profit oriented or not, irrespective of its size or legal form when such an examination is conducted with a view to express an opinion thereon.” Auditing also attempts to ensure that the books of accounts are properly maintained by the concern as required by law. Auditors consider the propositions before them, obtain evidence, and evaluate the propositions in their auditing report. Audits provide third-party assurance to various stakeholders that the subject matter is free from material misstatement. The term is most frequently applied to audits of the financial information relating to a legal person. Other commonly audited areas include: secretarial and compliance, internal controls, quality management, project management, water management, and energy conservation. As a result of an audit, stakeholders may evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. The international standard definition of risk for common understanding in different applications is “effect of uncertainty on objectives”. The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas ( business, economics, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and generic guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turnbull Report
''Internal Control: Guidance for Directors on the Combined Code'' (1999) also known as the "Turnbull Report" was a report drawn up with the London Stock Exchange for listed companies. The committee which wrote the report was chaired by Nigel Turnbull of The Rank Group plc. The report informed directors of their obligations under the Combined Code with regard to keeping good "internal controls" in their companies, or having good audits and checks to ensure the quality of financial reporting and catch any fraud before it becomes a problem. Revised guidance was issued in 2005. The report was superseded by a further FRC guidance issued in September 2014.https://www.frc.org.uk/Our-Work/Codes-Standards/Corporate-governance/UK-Corporate-Governance-Code/Guidance-for-boards-and-board-committees.aspx See also * UK company law * Corporate Governance * Cadbury Report (1992), ''Financial Aspects of Corporate Governance'', on corporate governance generally. Pdf filhere* Greenbury Report (1995) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate Governance
Corporate governance is defined, described or delineated in diverse ways, depending on the writer's purpose. Writers focused on a disciplinary interest or context (such as accounting, finance, law, or management) often adopt narrow definitions that appear purpose-specific. Writers concerned with regulatory policy in relation to corporate governance practices often use broader structural descriptions. A broad (meta) definition that encompasses many adopted definitions is "Corporate governance” describes the processes, structures, and mechanisms that influence the control and direction of corporations." This meta definition accommodates both the narrow definitions used in specific contexts and the broader descriptions that are often presented as authoritative. The latter include: the structural definition from the Cadbury Report, which identifies corporate governance as "the system by which companies are directed and controlled" (Cadbury 1992, p. 15); and the relational-structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee Of Sponsoring Organizations Of The Treadway Commission
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) is an organization that develops guidelines for businesses to evaluate internal controls, risk management, and fraud deterrence. In 1992 (and subsequently re-released in 2013), COSO published the ''Internal Control - Integrated Framework,'' commonly used by businesses in the United States to design, implement, and conduct systems of internal control over financial reporting and assessing their effectiveness. History In 1985, COSO began as a private sector initiative to investigate the causal factors that lead to fraudulent financial reporting as a result of a number of accounting scandals in the 1970s and mid-1980s. This initiative was termed the National Commission on Fraudulent Financial Reporting; the first president of the Commission was James C. Treadway, Jr., a former Commissioner of the US Securities and Exchange Commission, and therefore the initiative was commonly called the "Treadway Commission". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Accreditation System Of Australia And New Zealand
Joint Accreditation System of Australia and New Zealand (JAS-ANZ) is an independent, third party accreditation body that provides internationally recognised accreditation services. JAS-ANZ was established by International treaty titled ''Agreement between Australia and New Zealand concerning the Establishment of the Council of the Joint Accreditation System of Australia and New Zealand (JAS-ANZ)'' signed in Canberra on 30 October 1991, to strengthen the trading relationship between the two countries and with other countries. Accreditation adds value to the ever growing and increasingly complicated market chain in many ways, including by providing a symbol of assurance that certifiers and inspectors are independent and competent to perform their duties. JAS-ANZ accredits the bodies that certify or inspect organisations, products or people. They do so by developing the assessment criteria certifiers and inspectors must meet to become accredited under these themes: * Business and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 31000
ISO 31000 is a family of standards relating to risk management codified by the International Organization for Standardization. ISO 31000:2018 provides principles and generic guidelines on managing risks that could be negative faced by organizations as these could have consequence in terms of economic performance and professional reputation. ISO 31000 seeks to provide a universally recognized paradigm for practitioners and companies employing risk management processes to replace the myriad of existing standards, methodologies and paradigms that differed between industries, subject matters and regions. For this purpose, the recommendations provided in ISO 31000 can be customized to any organization and its contex As of 2020, ISO/TC 262, the committee responsible for this family of standards, has published five standards, while four additional standards are in the proposal/development stages.Published standards * ISO 31000:2018 - Risk management - Guidelines * ISO/TR 31004:2013 - Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Sheet
In financial accounting, a balance sheet (also known as statement of financial position or statement of financial condition) is a summary of the financial balances of an individual or organization, whether it be a sole proprietorship, a Partnership, business partnership, a corporation, private limited company or other organization such as Government financial statements, government or Nonprofit organization, not-for-profit entity. Assets, liability (financial accounting), liabilities and Equity (finance), ownership equity are listed as of a specific date, such as the end of its financial year. A balance sheet is often described as a "snapshot of a company's financial condition". Of the four basic financial statements, the balance sheet is the only statement which applies to a single point in time of a business's calendar year. A standard company balance sheet has two sides: assets on the left, and financing on the right–which itself has two parts; liabilities and ownership equi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |