|
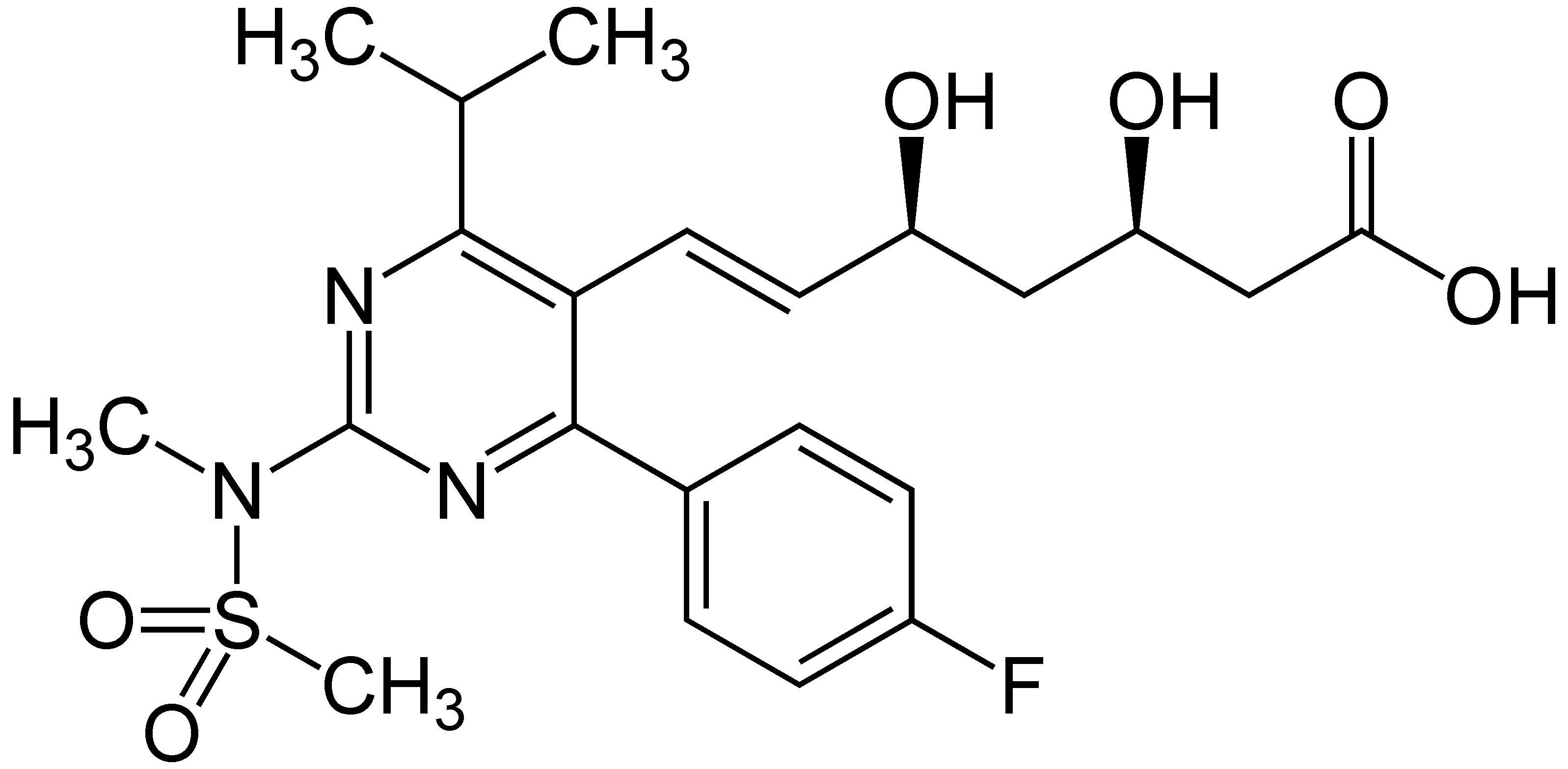
Rimeporide
Rimeporide is an experimental drug for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, being developed by the EspeRare foundation. it has been granted orphan drug status by the European Medicines Agency. Mechanism of action The substance blocks an ion pump called sodium–hydrogen antiporter 1. While the exact mechanism is unknown, it is speculated that inhibition of this pump reduces pH, sodium and calcium overload in cells of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. History Rimeporide was designed as a treatment for chronic heart failure. It was tested in seven Phase I studies clinical trials in patients with congestive heart failure and some degree of renal insufficiency. Subsequently, the drug was licensed to EspeRare, a Swiss nonprofit organisation that aims at repositioning drugs for rare diseases. , the substance has demonstrated efficacy in several animal models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. It has also been recently tested in young boys with Duchenne muscular Dystroph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium–hydrogen Antiporter 1
The sodium-hydrogen antiporter 1 (NHE-1) also known as sodium/hydrogen exchanger 1 or SLC9A1 (SoLute Carrier family 9A1) is an isoform of sodium–hydrogen antiporter that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC9A1'' gene. Function The Na+/H+ antiporter (SLC9A1) is a ubiquitous membrane-bound enzyme involved in volume- and pH-regulation of vertebrate cells. It is inhibited by the non-specific diuretic drug amiloride and activated by a variety of signals including growth factors, mitogens, neurotransmitters, tumor promoters, and others. Interactions Sodium–hydrogen antiporter 1 has been shown to interact with carbonic anhydrase II and CHP. It is also the target of the experimental drug rimeporide, which is being developed for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. Muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four, and worsens quickly. Muscle loss typically occurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biostrophin
Biostrophin is a drug which may serve as a vehicle for gene therapy, in the treatment of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. As mutations in the gene which codes for the protein dystrophin is the underlying defect responsible for both disorders, biostrophin will deliver a genetically-engineered, functional copy of the gene at the molecular level to affected muscle cells. Dosage, as well as a viable means for systemic release of the drug in patients, is currently being investigated with the use of both canine and primate animal models. Biostrophin is being manufactured by Asklepios BioPharmaceuticals, Inc., with funding provided by the Muscular Dystrophy Association. See also Other drugs for Duchenne muscular dystrophy * Ataluren Ataluren, sold under the brand name Translarna, is a medication for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. It was designed by PTC Therapeutics. Medical use Ataluren is used in the European Union to treat people with Duchenne muscular d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmaceutical Drug
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are classified in multiple ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the order of a physician, physician assistant, or qualified nurse) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Another key distinction is between traditional small molecule drugs, usually derived from chemical synthesis, and biopharmaceuticals, which include recombinant proteins, vaccines, blood products used therapeutically (such as IVIG), gene therapy, monoclonal antibodies and cell therapy (for instance, stem cell therapies) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drugs
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Some types are also associated with problems in other organs. Over 30 different disorders are classified as muscular dystrophies. Of those, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) accounts for approximately 50% of cases and affects males beginning around the age of four. Other relatively common muscular dystrophies include Becker muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, and myotonic dystrophy, whereas limb–girdle muscular dystrophy and congenital muscular dystrophy are themselves groups of several – usually ultrarare – genetic disorders. Muscular dystrophies are caused by mutations in genes, usually those involved in making muscle proteins. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idebenone
Idebenone (pronounced eye-deb-eh-known, trade names Catena, Raxone, Sovrima, among others) is a drug that was initially developed by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive defects. This has been met with limited success. The Swiss company Santhera Pharmaceuticals has started to investigate it for the treatment of neuromuscular diseases. In 2010, early clinical trials for the treatment of Friedreich's ataxia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy have been completed. the drug is not approved for these indications in North America or Europe. It is approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for use in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) and was designated an orphan drug in 2007. Chemically, idebenone is an organic compound of the quinone family. It is also promoted commercially as a synthetic analog of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Uses Indications that are or were approved in some territories Nootropic effects and Alzheimer's dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataluren
Ataluren, sold under the brand name Translarna, is a medication for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. It was designed by PTC Therapeutics. Medical use Ataluren is used in the European Union to treat people with Duchenne muscular dystrophy who have a nonsense mutation in the dystrophin gene, can walk, and are more than five years old. Contraindications People who are pregnant or breast feeding should not take ataluren. Adverse effects More than 10% of people taking ataluren in clinical trials experienced vomiting; more than 5% experienced diarrhea, nausea, headache, upper abdominal pain, and flatulence; between 1% and 5% of people experienced decreased appetite and weight loss, high levels of triglycerides, high blood pressure, cough, nosebleeds, abdominal discomfort, constipation, rashes, pain in their arms, legs, and chest muscles, blood in their urine, urinary incontinence, and fever. Interactions Aminoglycosides should not be given to someone taking ataluren, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. Muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four, and worsens quickly. Muscle loss typically occurs first in the thighs and pelvis followed by the arms. This can result in trouble standing up. Most are unable to walk by the age of 12. Affected muscles may look larger due to increased fat content. Scoliosis is also common. Some may have intellectual disability. Females with a single copy of the defective gene may show mild symptoms. The disorder is X-linked recessive. About two thirds of cases are inherited from a person's mother, while one third of cases are due to a new mutation. It is caused by a mutation in the gene for the protein dystrophin. Dystrophin is important to maintain the muscle fiber's cell membrane. Genetic testing can often make the diagnosis at birth. Those affected also have a high level of creatine kinase in their blood. Although there is no know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)