|
Right Fourth File Rook
In shogi, Right Fourth File Rook (右四間飛車 ''migi shikenbisha'') is a Static Rook opening in which the rook is positioned on the fourth file if played by Black or the sixth file if played by White. Typically, Right Fourth File Rook develops the right silver into a Reclining Silver attacking structure. Fortress vs Right Fourth File Rook Right Fourth File Rook vs Fourth File Rook A Right Fourth File Rook strategy may be played against a Ranging Rook position such as Fourth File Rook. In a Right Fourth File Rook vs Fourth File Rook game, each player's rook will be directly opposing each other on the fourth file supported by attacking silvers. Below shows an example of Black's Right Fourth File Rook against White's Fourth File Rook. 1. P-76 P-34, 2. P-26 P-44, 3. S-48 R-42. The first six moves are standard Static Rook vs Fourth File Rook piece development. (See: Left Silver-57 Rapid Attack vs Fourth File Rook for explication.) 4. P-46. The Right Fourth Fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
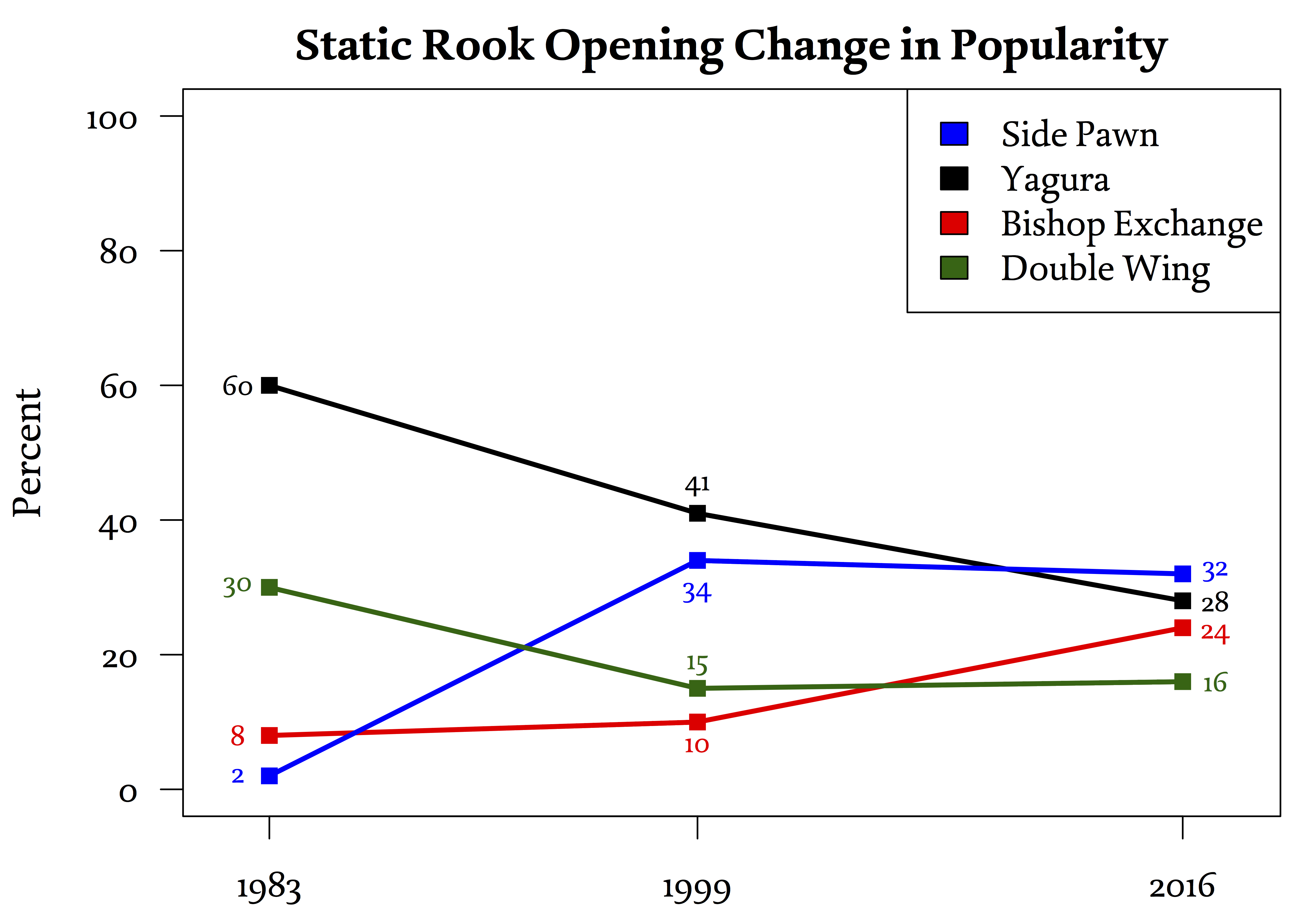
Static Rook
Static Rook (居飛車 ''ibisha'') openings in shogi typically have the player's rook at its start position, which is the second file (on the 28 square) for Black and the eighth file (on the 82 square) for White. Explanation Static Rook is a set of openings in which the rook remains on its starting square, which is the 28 square if played by Black and the 82 square if played by White. It is also possible to include other openings where the rook moves to another file that is still on the players right side of the board, such as the third file or the fourth file. The reason for including these other openings where the rook is not technically ''static'' is because the typical castle fortifications constructed to the protect the Static Rook player's king are usually the same for these openings. Nonetheless, some shogi theory does categorize these openings with right side rook movement into the same group as Ranging Rook openings despite the disparity in castle formation. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Opening
A shogi opening ( ) is the sequence of initial moves of a shogi game before the middle game. The more general Japanese term for the beginning of the game is ()''.'' A '' jōseki'' () is the especially recommended sequence of moves for a given opening that was considered balanced play at one point in time for both sides by professional players. (However, some ''s'' have become outdated when they are reevaluated to no longer give balanced play.) ''s'' also typically include commentary about the possible reasons to deviate from the especially regarding blunders. Note that not all openings have ''s''. For example, trap openings like Demon Slayer, while they may have standard moves, are considered to favor one player and are not balanced play. Thus, the Demon Slayer opening is not a jōseki. Introduction The very first opening moves in most games are pawn pushes. In particular, most games start with two types of pawn pushes. A player can move the rook pawn forward (P-26) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reclining Silver
In shogi, Reclining Silver (腰掛け銀 ''koshikakegin'') is a piece formation used in different Double Static Rook openings. It may also be played in Double Ranging Rook openings as well and in Right Fourth File Rook (Static Rook) positions against Ranging Rook positions. The Reclining Silver has the right silver positioned on central file above the central pawn and to the right of the silver is the pawn that was advancing in order to let the silver move through the line of pawns. The silver is said to recline on the seat of pawns. In the adjacent board diagram, both Black and White have created Reclining Silver positions. Black has their silver on 56 (with pawns on 46 and 57) while White has their silver on 54 (pawns on 53, 64). Reclining Silver can often played as a component of several different Static Rook openings such as Double Wing or Bishop Exchange. Clanging Silvers Clanging Silvers (ガッチャン銀 ''gatchan gin'') is an attacking development from a Dou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranging Rook
Ranging Rook or Swinging Rook (振り飛車 ''furibisha'') openings in shogi position the rook to the center or left of the player's board to support an attack there. Ranging Rook strategies used in Ranging Rook vs Static Rook are among the oldest of shogi strategies attested in the historical documents that first describe the rules of shogi around 1600. Description Types of Ranging Rook Traditionally, Ranging Rook has been used as a defensive strategy for White against Static Rook openings played by Black. White's rook can be moved flexibly to counteract Black's attacks. These types of White openings are named simply Ranging Rook (振り飛車 ''furibisha''). In describing the game positions of both opponents, the term is Static Rook vs Ranging Rook (居飛車対振り飛車 ''ibisha tai furibisha''). In these games, Black has the initiative, and White quickly builds a defense by castling the king and seeks counterattacking opportunities. By default, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth File Rook
In shogi, Fourth File Rook (四間飛車 ''shikenbisha'') is a class of Ranging Rook openings in which the rook is initially positioned on the fourth file if played by White or the sixth file if played by Black. History The earliest recorded shogi game was a Static Rook vs. Fourth File Rook game from 1607. Black was who played a Right Fourth File Rook position (Static Rook) against Sansa Hon'inbō's Fourth File Rook. Ōhashi won the game. Fourth File Rook vs Static Rook Normal Fourth File Rook The opening starts by the usual 4-move sequence that characterizes Static Rook vs Ranging Rook games as shown in the first adjacent board position. (See: Normal Ranging Rook.) Fujii System The Fujii System is a set of Fourth File Rook strategies used against various Static Rook strategies (mainly Left Mino and Bear-in-the-hole Static Rook). vs Rapid Attack Tateishi Fourth File Rook A Fourth File Rook opening created by amateur player Katsuki Tateishi, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Silver-57 Rapid Attack
Left Silver-57 Rapid Attack or Left Silver-5g Rapid Attack or Left Silver-5g Quick Attack (5七銀左急戦 ''go-nana gin hidari kyuusen'') is a fast attacking strategy in shogi used with several different Static Rook openings often played by Black against Ranging Rook positions played by White. It is characterized by moving the left silver from its start position on 79 to the 57 square. The Static Rook position is usually combined with a Boat castle. Against Fourth File Rook When Left Silver-57 Rapid Attack is used against a Fourth File Rook opponent, Left Silver-57 Rapid Attack often transitions to the (4六銀左 ''yon-roku gin hidari'') class of openings. The Left Silver-57 Rapid Attack openings against Fourth File Rook include the Yamada joseki (山田定跡 ''yamada jouseki''), the Saginomiya joseki (鷺宮定跡 ''saginomiya jouseki''), and or Pawn-45 Rapid Engage (4五歩早仕掛け ''yon-go fu haya-shikake'') among others. The opening starts by the usual Stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortress Opening
Fortress (矢倉 or 櫓 ''yagura'') is both a Static Rook opening (矢倉戦法 ''yagura senpō'') and a castle in shogi. It is usually played in a Double Static Rook opening, which is often a Double Fortress opening. However, it may also occur in different Double Static Rook openings such as Fortress vs Right Fourth File Rook. The Fortress castle (矢倉囲い ''yagura gakoi''), which is the defining characteristic of Fortress games, was considered by many to be one of the strongest defensive positions in Double Static Rook games in the 1980s. The term ''yagura'' is the Japanese word for a tower-like structure in traditional Japanese castles. Double Fortress The most commonly encountered Fortress strategies occur in Double Fortress games where both players use a Fortress formation. Historical Fortress Earlier josekis for Fortress in the Edo period (usually spelled 櫓 at that time) were very different from the current josekis. For instance, in one variation, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Openings
, also known as Japanese chess, is a Abstract strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as chess, Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and ''janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century Mercenary#15th to 18th centuries, mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |