|
Ridiculously Resilient Ridge
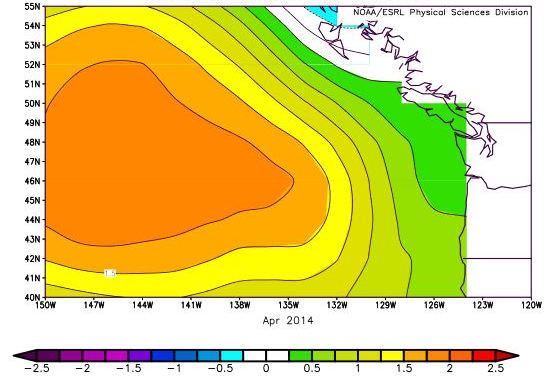
The "Ridiculously Resilient Ridge", sometimes shortened to "Triple R" or "RRR", is the nickname given to a persistent anticyclone that occurred over the far northeastern Pacific Ocean, contributing to the 2011–2017 California drought. The "Ridiculously Resilient Ridge" nickname was originally coined in December 2013 by Daniel Swain on the Weather West Blog, but has since been used widely in popular media as well as in peer-reviewed scientific literature. Features The Ridiculously Resilient Ridge was characterized by a broad region of anomalously positive geopotential height on monthly to annual timescales. This persistent high pressure system acted to "block" the prevailing mid-latitude westerlies, shifting the storm track northward and suppressing extratropical cyclone (winter storm) activity along the West Coast of the United States. Such a pattern is similar to—but of greater magnitude and longevity than—atmospheric configurations noted during previous California drought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple R NDJFMAM 2012 2015 Printable
Triple is used in several contexts to mean "threefold" or a "treble": Sports * Triple (baseball), a three-base hit * A basketball three-point field goal * A figure skating jump with three rotations * In bowling terms, three strikes in a row * In cycling, a crankset with three chainrings Places * Triple Islands, an uninhabited island group in Nunavut, Canada * Triple Island, British Columbia, Canada * Triple Falls (other), four waterfalls in the United States & Canada * Triple Glaciers, in Grand Teton National Park, Wyoming * Triple Crossing, Richmond, Virginia, believed to be the only place in North America where three Class I railroads cross * Triple Bridge, a stone arch bridge in Ljubljana, Slovenia Transportation * Kawasaki triple, a Japanese motorcycle produced between 1969 and 1980 * Triumph Triple, a motorcycle engine from Triumph Motorcycles Ltd * A straight-three engine * A semi-truck with three trailers Science and technology * Triple (mathematics) (3-tup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, most populous U.S. state and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 3rd largest by area. It is also the most populated Administrative division, subnational entity in North America and the 34th most populous in the world. The Greater Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous Statistical area (United States), urban regions respectively, with the former having more than 18.7million residents and the latter having over 9.6million. Sacramento, California, Sacramento is the state's capital, while Los Angeles is the List of largest California cities by population, most populous city in the state and the List of United States cities by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2014–15 North American Winter
The 2014–15 North American winter was frigid and prolifically wintry, especially across the eastern half of North America in the months of January–March. The season began early, with many places in North America experiencing their first wintry weather during mid-November. A period of below-average temperatures affected much of the contiguous United States, and several records were broken. An early trace of snowfall was recorded in Arkansas. There were greater accumulations of snow across parts of Oklahoma as well. A quasi-permanent phenomenon referred to as the polar vortex may have been partly responsible for the cold weather. Temperatures in much of the United States dropped below average by November 19, following a southward "dip" of the polar vortex into the eastern two-thirds of the country. The effects of this dip were widespread, bringing about temperatures as low as in Pensacola, Florida. Following a significant snowstorm there, Buffalo, New York received severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013–14 North American Winter
The 2013–14 North American winter was one of the most significant for the United States, due in part to the breakdown of the polar vortex in November 2013, which allowed very cold air to travel down into the United States, leading to an extended period of very cold temperatures. The pattern continued mostly uninterrupted throughout the winter and numerous significant winter storms affected the Eastern United States, with the most notable one being a powerful winter storm that dumped ice and snow in the Southeastern United States and the Northeastern United States in mid-February. Most of the cold weather abated by the end of March, though a few winter storms did affect the Western United States towards the end of the winter. While there is no well-agreed-upon date used to indicate the start of winter in the Northern Hemisphere, there are two definitions of winter which may be used. Based on the astronomical definition, winter begins at the winter solstice, which in 2013 occurr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclones
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure. Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge. The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Pacific High
The North Pacific High is a semi-permanent, subtropical anticyclone located in the northeastern portion of the Pacific Ocean, located northeast of Hawaii and west of California. It is strongest during the northern hemisphere summer and shifts towards the equator during the winter, when the Aleutian Low becomes more active. It is responsible for California's typically dry summer and fall and typically wet winter and spring, as well as Hawaii's year-round trade winds. During the 2011–2017 California drought, the North Pacific High persisted longer than usual, due to a mass of warm water in the Pacific Ocean, resulting in the Ridiculously Resilient Ridge. This significantly limited the number of powerful winter storms that were able to reach California, resulting in historic drought conditions in that state for several years. See also * South Pacific High * North Pacific Current * California Current * El Niño–Southern Oscillation El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Blob (Pacific Ocean)
The Blob is a large mass of relatively warm water in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of North America that was first detected in late 2013 and continued to spread throughout 2014 and 2015. It is an example of a marine heatwave. Sea surface temperatures indicated that the Blob persisted into 2016, but it was initially thought to have dissipated later that year. By September 2016, the Blob resurfaced and made itself known to meteorologists. The warm water mass was unusual for open ocean conditions and was considered to have played a role in the formation of the unusual weather conditions experienced along the Pacific coast of North America during the same time period. The warm waters of the Blob were nutrient-poor and adversely affected marine life. In 2019 another scare was caused by a weaker form of the effect referred as "The Blob 2.0" and in 2021 the appearance of "The Southern Blob" at south of the equator near New Zealand has caused a major effect in South America, particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storm Track
''Storm Track'' was the first magazine for and about storm chasing. The magazine was in circulation between 1977 and 2002. History and profile ''Storm Track'' was started in 1977 by chasing pioneer David Hoadley following an informal meeting of storm chasers at an American Meteorological Society conference. In the beginning, it was published in newsletter format in Falls Church, Virginia, but in time assumed a magazine format and was published bimonthly throughout its history. In 1986, editorship was handed over to Tim Marshall, a storm damage engineer (and meteorologist). Production of paper issues ceased in 2002 after a 25-year run; however, an accompanying website started in 1996 and continues primarily in the form of a large discussion board. ''Storm Track'', among other topics, published storm chase accounts, discussions of issues affecting storm chasing, history of storm chasing and meteorology, meteorological analysis and case studies, climatology, reviews, biographies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure. Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge. The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term " cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Earth between 30° and 60° latitude. They are term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. The westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere (called also 'Brave West winds' at striking Chile, Tasmania and New Zealand), in areas where land is absent, because land amplifies the flow pattern, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)