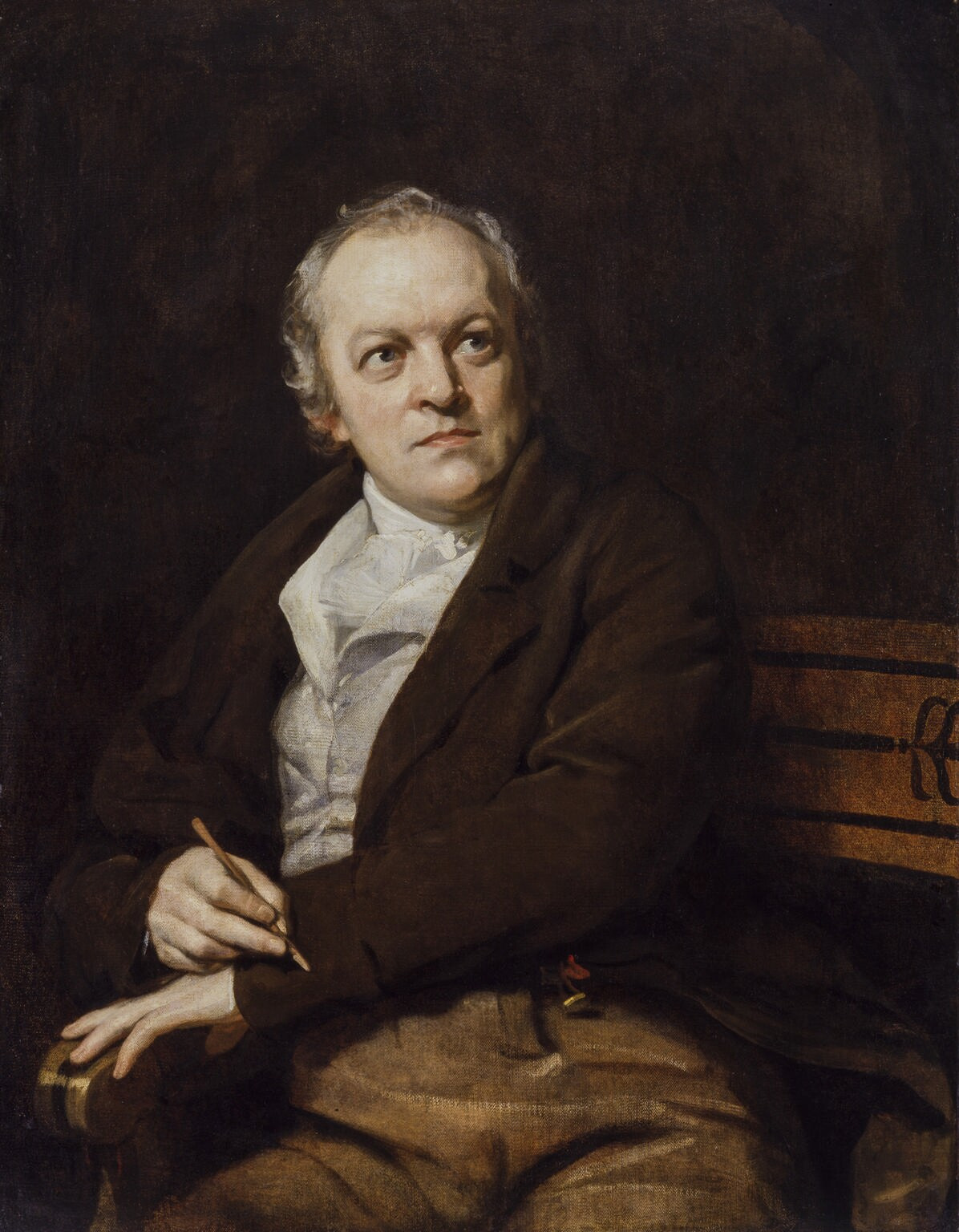|
Richard Morrison (music Critic)
Richard Duncan Morrison (born 24 July 1954) is an English music critic who specializes in classical music. As chief music critic of ''The Times'' since 1992, he "has long been admired for his penetrating cultural column". He also writes for the monthly publication ''BBC Music Magazine'' and has previously written for ''Classical Music'', '' The Listener'' and (as deputy editor) the ''Early Music'' journal. In 2004, he published a history of the London Symphony Orchestra entitled ''Orchestra: The LSO: A Century of Triumph and Turbulence''; Charlotte Higgins of ''The Guardian'' described it as "a pungent, immensely readable first book." Life and career Richard Duncan Morrison was born in London, England, on 24 July 1954. His first classical music experience was attending a 1960 London Symphony Orchestra (LSO) concert at the age of five. He was educated at University College School in Hampstead, and after studying music at Magdalene College, Cambridge worked variously as a pianist, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organist
An organist is a musician who plays any type of organ (music), organ. An organist may play organ repertoire, solo organ works, play with an musical ensemble, ensemble or orchestra, or accompany one or more singers or instrumentalist, instrumental soloists. In addition, an organist may accompany congregational hymn-singing and play liturgy, liturgical music. Classical and church organists The majority of organists, amateur and professional, are principally involved in church music, playing in churches and cathedrals. The pipe organ still plays a large part in the leading of traditional western Christian worship, with roles including the accompaniment of hymns, choral anthems and other parts of the worship. The degree to which the organ is involved varies depending on the church and denomination. It also may depend on the standard of the organist. In more provincial settings, organists may be more accurately described as pianists obliged to play the organ for worship services; nev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Of Hope And Glory
"Land of Hope and Glory" is a British patriotic song, with music by Edward Elgar written in 1901 and lyrics by A. C. Benson later added in 1902. Composition The music to which the words of the refrain 'Land of Hope and Glory, &c' below are set is the 'trio' theme from Edward Elgar's ''Pomp and Circumstance March No. 1''. The words were fitted to the melody on the suggestion of King Edward VII who told Elgar he thought the melody would make a great song. When Elgar was requested to write a work for the King's coronation, he worked the suggestion into his '' Coronation Ode'', for which he used words provided by the poet and essayist A. C. Benson. The last section of the ''Ode'' uses the march's melody. Owing to the King's illness, the coronation was postponed. Elgar created a separate song, which was first performed by Madame Clara Butt in June 1902. In fact, only the first of the seven stanzas of the Ode's final section was re-used, as the first four lines of the second st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
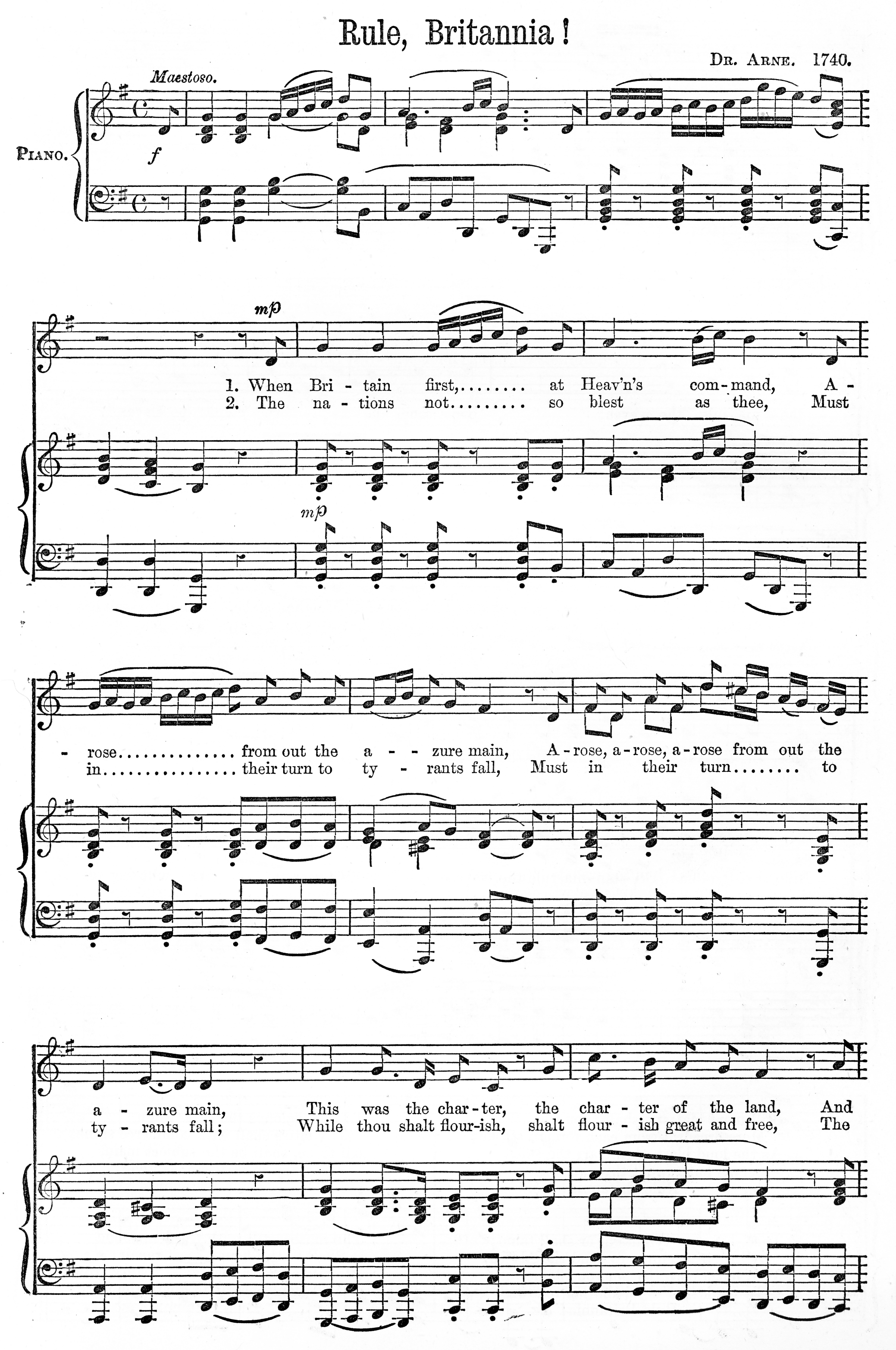
Rule, Britannia!
"Rule, Britannia!" is a British patriotic song, originating from the 1740 poem "Rule, Britannia" by James Thomson and set to music by Thomas Arne in the same year. It is most strongly associated with the Royal Navy, but is also used by the British Army. ''Alfred'' The song was originally the final musical number in Thomas Arne's ''Alfred'', a masque about Alfred the Great, co-written by James Thomson and David Mallet and first performed at Cliveden, the country home of Frederick, Prince of Wales, on 1 August 1740. Lyrics This version is taken from ''The Works of James Thomson'' by James Thomson, Published 1763, Vol II, p. 191, which includes the entire text of ''Alfred''. "Married to a Mermaid" In 1751 Mallet re-used the text of "Rule, Britannia!", omitting three of the original six stanzas and adding three new ones by Lord Bolingbroke, to form the repeated chorus of a comic song "Married to a Mermaid". This became extremely popular when Mallet produced his m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem (hymn)
"And did those feet in ancient time" is a poem by William Blake from the preface to his epic ''Milton: A Poem in Two Books'', one of a collection of writings known as the Blake's prophetic books, Prophetic Books. The date of 1804 on the title page is probably when the plates were begun, but the poem was printed .Cox, Michael, editor, ''The Concise Oxford Chronology of English Literature'', "1808", p 289, Oxford University Press, 2004, Today it is best known as the hymn "Jerusalem", with music written by Hubert Parry, Sir Hubert Parry in 1916. The famous orchestration was written by Sir Edward Elgar. It is not to be confused with another poem, much longer and larger in scope and also by Blake, called ''Jerusalem The Emanation of the Giant Albion''. It is often assumed that the poem was inspired by the apocryphal story that a young Jesus, accompanied by Joseph of Arimathea, a tin merchant, travelled to what is now England and visited Glastonbury during his unknown years of Jesus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online news coverage. The service maintains 50 foreign news bureaus with more than 250 correspondents around the world. Deborah Turness has been the CEO of news and current affairs since September 2022. In 2019, it was reported in an Ofcom report that the BBC spent £136m on news during the period April 2018 to March 2019. BBC News' domestic, global and online news divisions are housed within the largest live newsroom in Europe, in Broadcasting House in central London. Parliamentary coverage is produced and broadcast from studios in London. Through BBC English Regions, the BBC also has regional centres across England and national news c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Der Rosenkavalier
(''The Knight of the Rose'' or ''The Rose-Bearer''), Op. 59, is a comic opera in three acts by Richard Strauss to an original German libretto by Hugo von Hofmannsthal. It is loosely adapted from the novel ''Les amours du chevalier de Faublas'' by Louvet de Couvrai and Molière's comedy ''Monsieur de Pourceaugnac''. It was first performed at the Königliches Opernhaus in Dresden on 26 January 1911 under the direction of Max Reinhardt, Ernst von Schuch conducting. Until the premiere, the working title was ''Ochs auf Lerchenau''. (The choice of the name Ochs is not accidental, for in German "Ochs" means "ox", which describes the character of the Baron throughout the opera.) The opera has four main characters: the aristocratic Marschallin; her very young lover, Count Octavian Rofrano; her brutish cousin Baron Ochs; and Ochs' prospective fiancée, Sophie von Faninal, the daughter of a rich bourgeois. At the Marschallin's suggestion, Octavian acts as Ochs' ''Rosenkavalier'' by pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tara Erraught
Tara Erraught (born 1986, Dublin, Ireland) is an Irish mezzo-soprano, a graduate of the Royal Irish Academy of Music (RIAM). Erraught is known for her work with Bavarian State Opera, for which she has been given a ' award. She stepped in on five-days' notice, learning the role of Romeo in Bellini's ''I Capuleti e i Montecchi'' at the Bayerische Staatsoper in 2011. In the seasons since, Erraught has sung a world premiere, made her US opera debut, numerous role debuts, and toured North America twice. Career Erraught has performed a wide variety of operatic roles including an acclaimed American opera debut with the Washington National Opera as Angelina in ''La Cenerentola''; role debuts as Carlotta in Strauss's ''Die schweigsame Frau'', Christa in Janáček's ''The Makropulos Affair'', Despina (having previously sung the role of Dorabella) in Mozart's '' Così fan tutte'', Prince Orlovsky in ''Die Fledermaus,'' Cherubino in ''Le nozze di Figaro,'' as well as singing Hänsel in ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezzo-soprano
A mezzo-soprano or mezzo (; ; meaning "half soprano") is a type of classical female singing voice whose vocal range lies between the soprano and the contralto voice types. The mezzo-soprano's vocal range usually extends from the A below middle C to the A two octaves above (i.e. A3–A5 in scientific pitch notation, where middle C = C4; 220–880 Hz). In the lower and upper extremes, some mezzo-sopranos may extend down to the F below middle C (F3, 175 Hz) and as high as "high C" (C6, 1047 Hz). The mezzo-soprano voice type is generally divided into the coloratura, lyric, and dramatic mezzo-soprano. History While mezzo-sopranos typically sing secondary roles in operas, notable exceptions include the title role in Bizet's '' Carmen'', Angelina (Cinderella) in Rossini's ''La Cenerentola'', and Rosina in Rossini's ''Barber of Seville'' (all of which are also sung by sopranos and contraltos). Many 19th-century French-language operas give the leading female role to mezzos, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleological
Teleology (from and )Partridge, Eric. 1977''Origins: A Short Etymological Dictionary of Modern English'' London: Routledge, p. 4187. or finalityDubray, Charles. 2020 912Teleology" In ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'' 14. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved 3 May 2020. – via ''New Advent'', transcribed by D. J. Potter is a reason or an explanation for something which serves as a function of its end, its purpose, or its goal, as opposed to something which serves as a function of its cause. A purpose that is imposed by human use, such as the purpose of a fork to hold food, is called ''extrinsic''. ''Natural teleology,'' common in classical philosophy, though controversial today, contends that natural entities also have ''intrinsic'' purposes, regardless of human use or opinion. For instance, Aristotle claimed that an acorn's intrinsic ''telos'' is to become a fully grown oak tree. Though ancient atomists rejected the notion of natural teleology, teleological accounts of non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Professional Publishers Association
The Professional Publishers Association (PPA), formerly known as the Periodical Publishers Association until 2011, is the main publishing industry body which promotes companies involved in the production of media, supporting the creative economy at governmental level in the United Kingdom. History The organisation was first founded in 1913 as the Society of Weekly Newspapers and Periodical Proprieters to discuss matters around unionisation, distribution and material supplies in the early 20th Century. It celebrated its centenary on November 19, 2013. Operations Much of the PPA's work is carried out through events, committees and public relations work as documented in their extensive archive of organisational documents dating back to 1942. The association now also covers digital media and a specific committee for smaller, independent publishers, the PPA Independent Publishers Network (IPN). The current CEO of the PPA is Owen Meredith, appointed in 2020 after Barry McIlheney stepped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Griffiths (writer)
Paul Anthony Griffiths (born 1947) is a British music critic, novelist and librettist. He is particularly noted for his writings on modern classical music and for having written the libretti for two 20th century operas, Tan Dun's ''Marco Polo'' and Elliott Carter's ''What Next?''. Career Paul Griffiths was born on 24 November 1947 in the Welsh town of Bridgend to Fred and Jeanne Griffiths. He received his BA and MSc in biochemistry from University of Oxford, and from 1971 worked as a freelance music critic. He joined the editorial staff of ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' in 1973 and in 1982 became the chief music critic for ''The Times'', a post which he held for ten years. From 1992 to 1996, he was a music critic for ''The New Yorker'', and from 1997 to 2005, for ''The New York Times''. A collection of his musical criticism for these and other periodicals was published in 2005 as ''The substance of things heard: writings about music'', Volume 31 of ''Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)