|
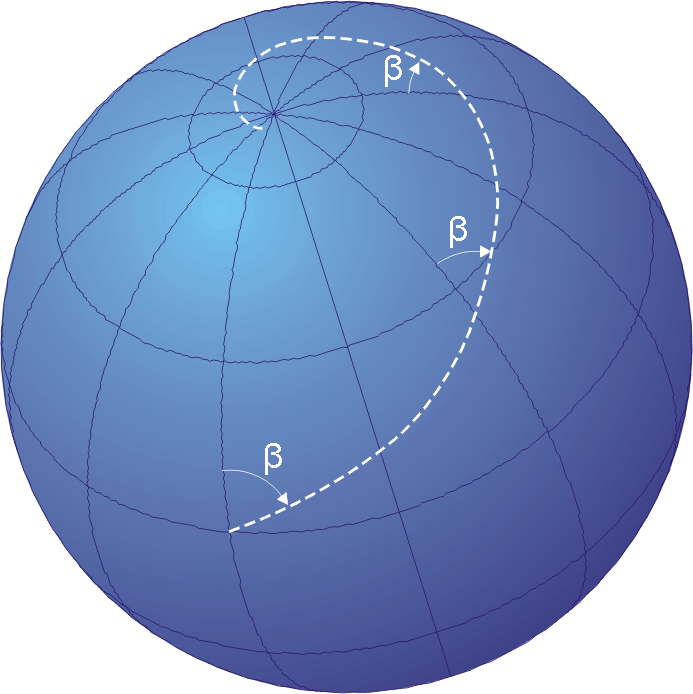
Rhumb Line
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant bearing as measured relative to true north. Introduction The effect of following a rhumb line course on the surface of a globe was first discussed by the Portuguese mathematician Pedro Nunes in 1537, in his ''Treatise in Defense of the Marine Chart'', with further mathematical development by Thomas Harriot in the 1590s. A rhumb line can be contrasted with a great circle, which is the path of shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere. On a great circle, the bearing to the destination point does not remain constant. If one were to drive a car along a great circle one would hold the steering wheel fixed, but to follow a rhumb line one would have to turn the wheel, turning it more sharply as the poles are approached. In other words, a great circle is locally "straight" with zero geodesic curvature, whereas a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loxodrome
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc (geometry), arc crossing all meridian (geography), meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant bearing (navigation), bearing as measured relative to true north. Introduction The effect of following a rhumb line course on the surface of a globe was first discussed by the Portuguese people, Portuguese mathematician Pedro Nunes in 1537, in his ''Treatise in Defense of the Marine Chart'', with further mathematical development by Thomas Harriot in the 1590s. A rhumb line can be contrasted with a great circle, which is the path of shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere. On a great circle, the bearing to the destination point does not remain constant. If one were to drive a car along a great circle one would hold the steering wheel fixed, but to follow a rhumb line one would have to turn the wheel, turning it more sharply as the poles are approached. In other words, a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
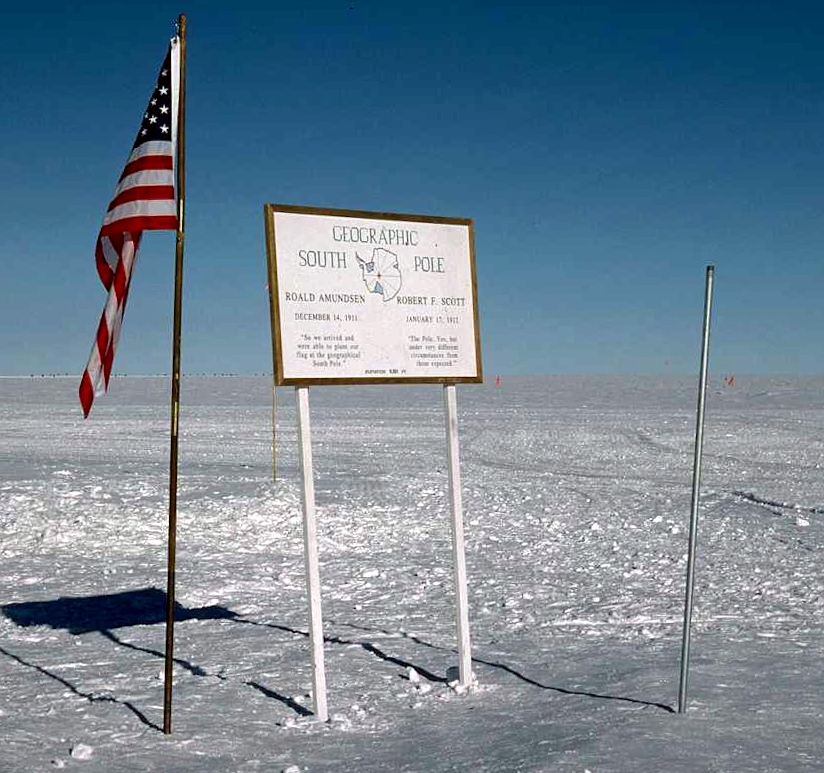
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipodally on the opposite side of Earth from the North Pole, at a distance of 12,430 miles (20,004 km) in all directions. Situated on the continent of Antarctica, it is the site of the United States Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station, which was established in 1956 and has been permanently staffed since that year. The Geographic South Pole is distinct from the South Magnetic Pole, the position of which is defined based on Earth's magnetic field. The South Pole is at the centre of the Southern Hemisphere. Geography For most purposes, the Geographic South Pole is defined as the southern point of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface (the other being the Geographic North Pole). However, Earth's axis of rotat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portolan
Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions. The word ''portolan'' comes from the Italian ''portulano'', meaning "related to ports or harbors", and which since at least the 17th century designates "a collection of sailing directions". Definition The term “portolan chart” was coined in the 1890s because at the time it was assumed that these maps were related to portolani, medieval or early modern books of sailing directions. Other names that have been proposed include rhumb line charts, compass charts or loxodromic charts whereas modern French scholars prefer to call them nautical charts to avoid any relationship with portolani. Several definitions of portolan chart coexist in the literature. A narrow definition includes only medieval or, at the latest, early modern sea charts (i.e. maps that primarily cover maritime rather than inland regions) that include a network of rhumb li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windrose Line
A rhumbline network, more properly called, a windrose network, or sometimes also called harbour-finding chart, compass chart, or rhumb chart, is a navigational aid drawn on early portolan charts dating from the medieval to early modern period. This network is like a web (see picture) forming a grid on the map. Before accurate surveying there was no method for measuring longitude at sea so maps possessed many distortions especially in the east west direction. There was also distortion due to the curvature of the Earth's surface. The multitude of compass roses with straight lines extending outwards across the map derived from how the maps were then made by compiling empirical observations from navigators who attempted to follow a constant bearing at sea. To calculate a course to follow from a ship's position to a point of desired destination, one would identify the windrose thought to be closest to the ship's position. Then, using a parallel rule, the "line of course" taken f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical character recognition (OCR), and stored in its digital database.The basic Google book link is found at: https://books.google.com/ . The "advanced" interface allowing more specific searches is found at: https://books.google.com/advanced_book_search Books are provided either by publishers and authors through the Google Books Partner Program, or by Google's library partners through the Library Project. Additionally, Google has partnered with a number of magazine publishers to digitize their archives. The Publisher Program was first known as Google Print when it was introduced at the Frankfurt Book Fair in October 2004. The Google Books Library Project, which scans works in the collections of library partners and adds them to the digital invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombus
In plane Euclidean geometry, a rhombus (plural rhombi or rhombuses) is a quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. Another name is equilateral quadrilateral, since equilateral means that all of its sides are equal in length. The rhombus is often called a "diamond", after the diamonds suit in playing cards which resembles the projection of an octahedral diamond, or a lozenge, though the former sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 60° angle (which some authors call a calisson after the French sweet – also see Polyiamond), and the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle. Every rhombus is simple (non-self-intersecting), and is a special case of a parallelogram and a kite. A rhombus with right angles is a square. Etymology The word "rhombus" comes from grc, ῥόμβος, rhombos, meaning something that spins, which derives from the verb , romanized: , meaning "to turn round and round." The word was used both by Eucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Language
Portuguese ( or, in full, ) is a western Romance language of the Indo-European language family, originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is an official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as " Lusophone" (). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology in its lexicon. With approximately 250 million native speakers and 24 million L2 (second language) speakers, Portuguese has approximately 274 million total speakers. It is usually listed as the sixth-most spoken language, the third-most sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a world language, global language with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries. It is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance languages, Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico. Spanish is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Language
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a Geometry, geometrical object that is a solid geometry, three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre (geometry), centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. spherical Earth, The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in any direction, so mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithmic Spiral
A logarithmic spiral, equiangular spiral, or growth spiral is a self-similar spiral curve that often appears in nature. The first to describe a logarithmic spiral was Albrecht Dürer (1525) who called it an "eternal line" ("ewige Linie"). More than a century later, the curve was discussed by Descartes (1638), and later extensively investigated by Jacob Bernoulli, who called it ''Spira mirabilis'', "the marvelous spiral". The logarithmic spiral can be distinguished from the Archimedean spiral by the fact that the distances between the turnings of a logarithmic spiral increase in geometric progression, while in an Archimedean spiral these distances are constant. Definition In polar coordinates (r, \varphi) the logarithmic spiral can be written as r = ae^,\quad \varphi \in \R, or \varphi = \frac \ln \frac, with e being the base of natural logarithms, and a > 0, k\ne 0 being real constants. In Cartesian coordinates The logarithmic spiral with the polar equation r = a e^ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |