|
Rhombozoa
Dicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods. Taxonomy Classification is controversial. Traditionally, dicyemids have been grouped with the Orthonectida in the Mesozoa, and, as of 2017, molecular evidence appears to confirm this. However, other molecular phylogenies have placed the dicyemids more closely related to the roundworms. Additional molecular evidence suggests that this phylum is derived from the ''Lophotrochozoa. The phylum is not divided in classes or orders, but contains three families, Conocyemidae, Dicyemidae, and Kantharellidae. Anatomy Adult dicyemids range in length from , and they can be easily viewed through a light microscope. They display eutely, a condition in which each adult individual of a given species has the same number of cells, making cell number a useful identifying character. Dicyemida lack respiratory, circulatory, excretory, digestive, and nervous systems. The organism' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicyemida
Dicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods. Taxonomy Classification is controversial. Traditionally, dicyemids have been grouped with the Orthonectida in the Mesozoa, and, as of 2017, molecular evidence appears to confirm this. However, other molecular phylogenies have placed the dicyemids more closely related to the roundworms. Additional molecular evidence suggests that this phylum is derived from the ''Lophotrochozoa. The phylum is not divided in classes or orders, but contains three families, Conocyemidae, Dicyemidae, and Kantharellidae. Anatomy Adult dicyemids range in length from , and they can be easily viewed through a light microscope. They display eutely, a condition in which each adult individual of a given species has the same number of cells, making cell number a useful identifying character. Dicyemida lack respiratory, circulatory, excretory, digestive, and nervous systems. The organism' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoa
The Mesozoa are minuscule, worm-like parasites of marine invertebrates. Generally, these tiny, elusive creatures consist of a somatoderm (outer layer) of ciliated cells surrounding one or more reproductive cells. A recent study recovered Mesozoa as a monophyletic group that emerged in the Lophotrochozoa as sister of the Rouphozoa. Some workers previously classified Mesozoa as the sole phylum of the lonely subkingdom Agnotozoa. Cavalier-Smith argued that at least some of the mesozoans are in fact protistans, not animals. In the 19th century, the Mesozoa were a wastebasket taxon for multicellular organisms which lacked the invaginating gastrula which was thought to define the Metazoa. Evolution Mesozoa were once thought to be evolutionary intermediate forms between Protozoans and Metazoans, but now they are thought to be degenerate or simplified metazoa. Their ciliated larvae are similar to the miracidium of trematodes, and their internal multiplication is similar to what h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conocyemidae
Conocyemidae is a family of worms belonging to the class Rhombozoa Dicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods. Taxonomy Classification is controversial. Traditionally, dicyemids have been grouped with the Orthonectida in the Mesozoa, an ..., order unknown. Genera: * '' Conocyema'' Van Beneden, 1882 * '' Microcyema'' Van Beneden, 1882 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q275460 Dicyemida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kantharellidae
Kantharellidae is a family of worms belonging to the class Rhombozoa Dicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods. Taxonomy Classification is controversial. Traditionally, dicyemids have been grouped with the Orthonectida in the Mesozoa, ..., order unassigned. The family consists of only one genus: ''Kantharella'' Czaker, 1994. References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q2184637, from2=Q2783387 Dicyemida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropreda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and eubacteria, bacteria. Many Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms including plants, animals, and Fungus, fungi can also reproduce asexually. In vertebrates, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited. Komodo dragons and some monitor lizards can also reproduce asexually. While all prokaryotes reproduce without the formation and fusion of gametes, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Phyla
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
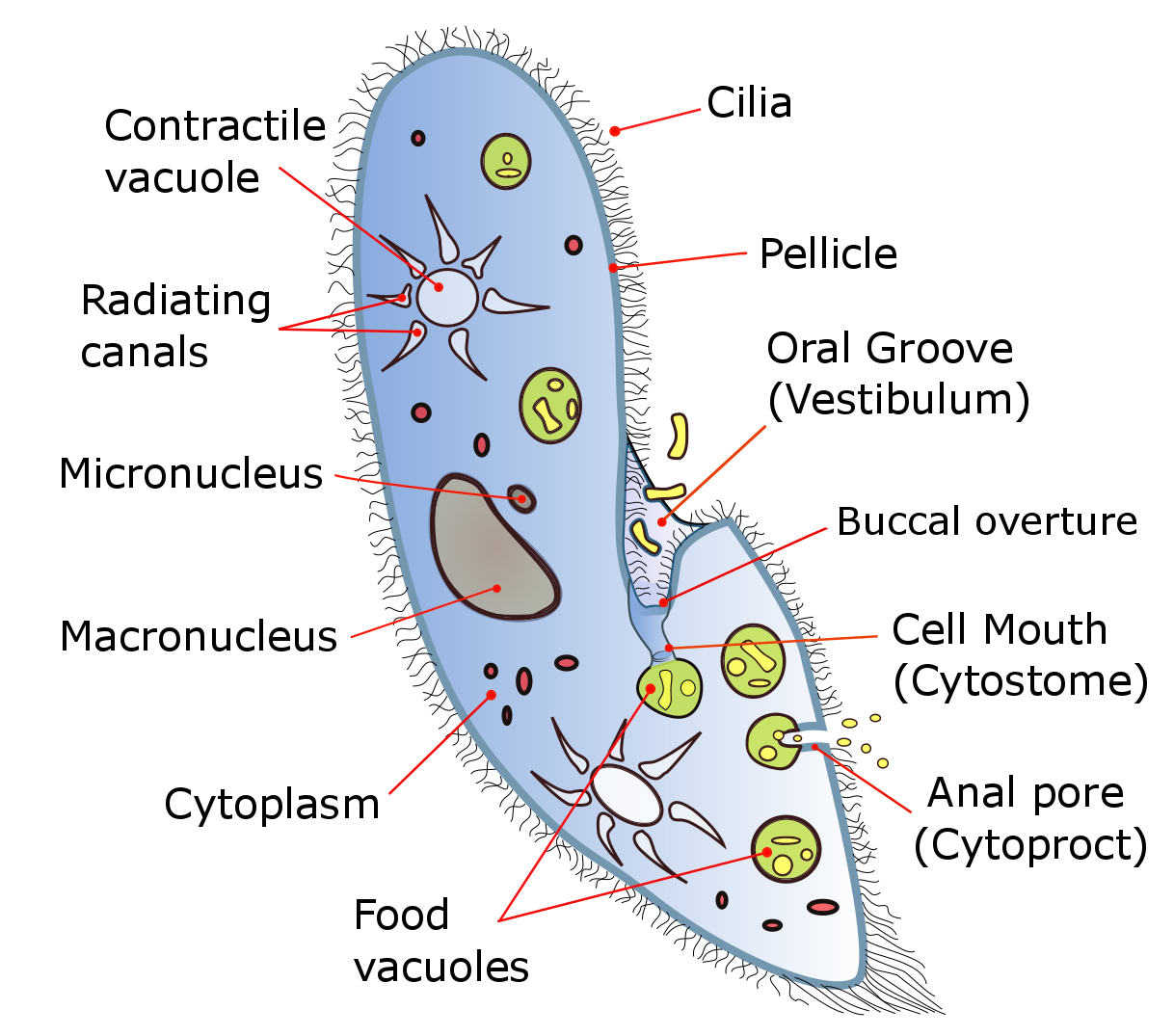
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the shore line (intertidal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small and usually only have precipitation changes. In temperate climates, not only do latitudinal positions influence temperature changes, but sea currents, prevailing wind direction, continentality (how large a landmass is) and altitude also shape temperate climates. The Köppen climate classification defines a climate as "temperate" C, when the mean temperature is above but below in the coldest month to account for the persistency of frost. However, other climate classifications set the minimum at . Zones and climates The north temperate zone extends from the Tropic of Cancer (approximately 23.5° north latitude) to the Arctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sperm in the form of spermatozoa. The female gonad, the ovary, produces egg cells. Both of these gametes are haploid cells. Some hermaphroditic animals have a type of gonad called an ovotestis. Evolution It is hard to find a common origin for gonads, but gonads most likely evolved independently several times. Regulation The gonads are controlled by luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, produced and secreted by gonadotropes or gonadotrophins in the anterior pituitary gland. This secretion is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone produced in the hypothalamus. Development Gonads start developing as a common primordium (an organ in the earliest stage of development), in the form of genital ridges, which are only l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |