|
Rhizodont
Rhizodontida is an extinct group of predatory tetrapodomorphs known from many areas of the world from the Givetian through to the Pennsylvanian - the earliest known species is about 377 million years ago (Mya), the latest around 310 Mya. Rhizodonts lived in tropical rivers and freshwater lakes and were the dominant predators of their age. They reached huge sizes - the largest known species, '' Rhizodus hibberti'' from Europe and North America, was an estimated 7 m in length, making it the largest freshwater fish known. Description The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the maxilla and premaxilla, medium-sized fangs on the ectopterygoid and dermopalatine bones, and large tusks on the vomers and premaxillae. On the lower jaw were marginal teeth on the dentary, with fangs on the three coronoids and a huge tusk at the symphysial tip of the dentary. Apparently, the left and right mandibles rotated inwards towards each other on biting. This may have been a kinetic mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barameda
''Barameda'' (Indigenous Australian language: "fish trap") is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish which lived during the Tournaisian stage near the start of the Carboniferous period in Australia; fossils of the genus have been reported from the Snowy Plains Formation. The largest member of this genus, ''Barameda decipiens'', reached an estimated length of around , while smallest species, ''B. mitchelli'' is estimated to have length about . Description The ''Barameda'' has an extremely elongated and thick body typical of Carboniferous rhizodonts. It is covered with moderately thin, cycloidal scales, with thick bony plates covering its head and operculum (gill flaps), a tightly fused Skull roof, and extremely prominent, sharp fangs, devoid of serrations or cutting edges. Its scales preserved lateral line. Originally it is estimated to have a typical narrow pectoral fin, however later study shows that had wider pectoral fin like other Carboniferous rhizodonts. Alongside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letognathus
''Letognathus'' is a genus of rhizodont tetrapodomorph that lived during the Carboniferous period. Its remains come from the Blue Beach Member of the Horton Bluff Formation, near Hantsport, Nova Scotia. Like most rhizodonts, it was of relatively large size, had a large recurved fang at the symphysis of the lower jaw, and a row of three coronoid fangs along the length of the jaw in addition to its marginal dentition. ''Letognathus'' is important for rhizodont systematics because it retains a number of primitive features, such as ossified Meckel's cartilage, are not found in the genera ''Rhizodus'' and ''Strepsodus''. Taxonomic History The members of the Rhizodontida have nearly all had complex taxonomic historiesJeffery, J.E. 2006. The Carboniferous fish genera ''Strepsodus'' and ''Archichthys'' (Rhizodontida: Sarcopterygii): clarifying 150 years of confusion. ''Palaeontology'' 49: 113-132 due to earlier use of the genus ''Strepsodus'' as a wastebasket taxon. The taxon was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archichthys
''Archichthys'' is a genus of rhizodontJ. E. Jeffery. 2006. The Carboniferous fish genera Strepsodus and Archichthys (Sarcopterygii: Rhizodontida): clarifying 150 years of confusion. Palaeontology 49(1):113-132 lobe-finned fish that lived during the Carboniferous period. Holotype of this fish was found in Northumberland Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey. It is bordered by land ..., UK. References External links Fossil specimen: NEWHM NEWHM: G59.64 d – Holotype Carboniferous bony fish Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Rhizodonts {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorph
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodamorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the Stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizodus
''Rhizodus'' (root tooth) is an extinct genus of basal, finned tetrapodomorphs (the group of sarcopterygians that contains modern tetrapods and their extinct relatives). It belonged to Rhizodontida, one of the earliest-diverging tetrapodomorph clades. Two valid species have been described, both of which lived during the Early Carboniferous epoch. The type species ''R. hibberti'' is known from the Viséan stage of the United Kingdom, whereas the species ''R. serpukhovensis'' is from the Serpukhovian of Russia. Some fossils referred to the genus ''Rhizodus'' have also been found in North America. Description The most notable characteristics of ''Rhizodus'', compared to other giant rhizodonts such as '' Barameda'', were the two fangs located near the front of its jaws, followed by other teeth scaling downwards in size. ''Rhizodus'' was a giant apex predator that resided in freshwater lakes, river systems and large swamps, with ''R. hibberti'' reaching in length. It fed on small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strepsodus
''Strepsodus'' is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass includ ... that lived during the Carboniferous period. Fossils have been found in North America and Australia. References Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Carboniferous fish of North America Prehistoric fish of Australia Rhizodonts {{Carboniferous-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauripterus Taylori
''Sauripterus'' ("lizard wing") is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass includ ... that lived during the Devonian period (416-360.7 Ma). This genus was described by J. Hall after its discovery at Powy's Curve in Pennsylvania. References Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Devonian fish of North America Rhizodonts {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauripterus
''Sauripterus'' ("lizard wing") is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass includ ... that lived during the Devonian period (416-360.7 Ma). This genus was described by J. Hall after its discovery at Powy's Curve in Pennsylvania. References Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Devonian fish of North America Rhizodonts {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screbinodus
''Screbinodus'' is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass includ ... that lived during the Carboniferous period. References Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Carboniferous bony fish Rhizodonts {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
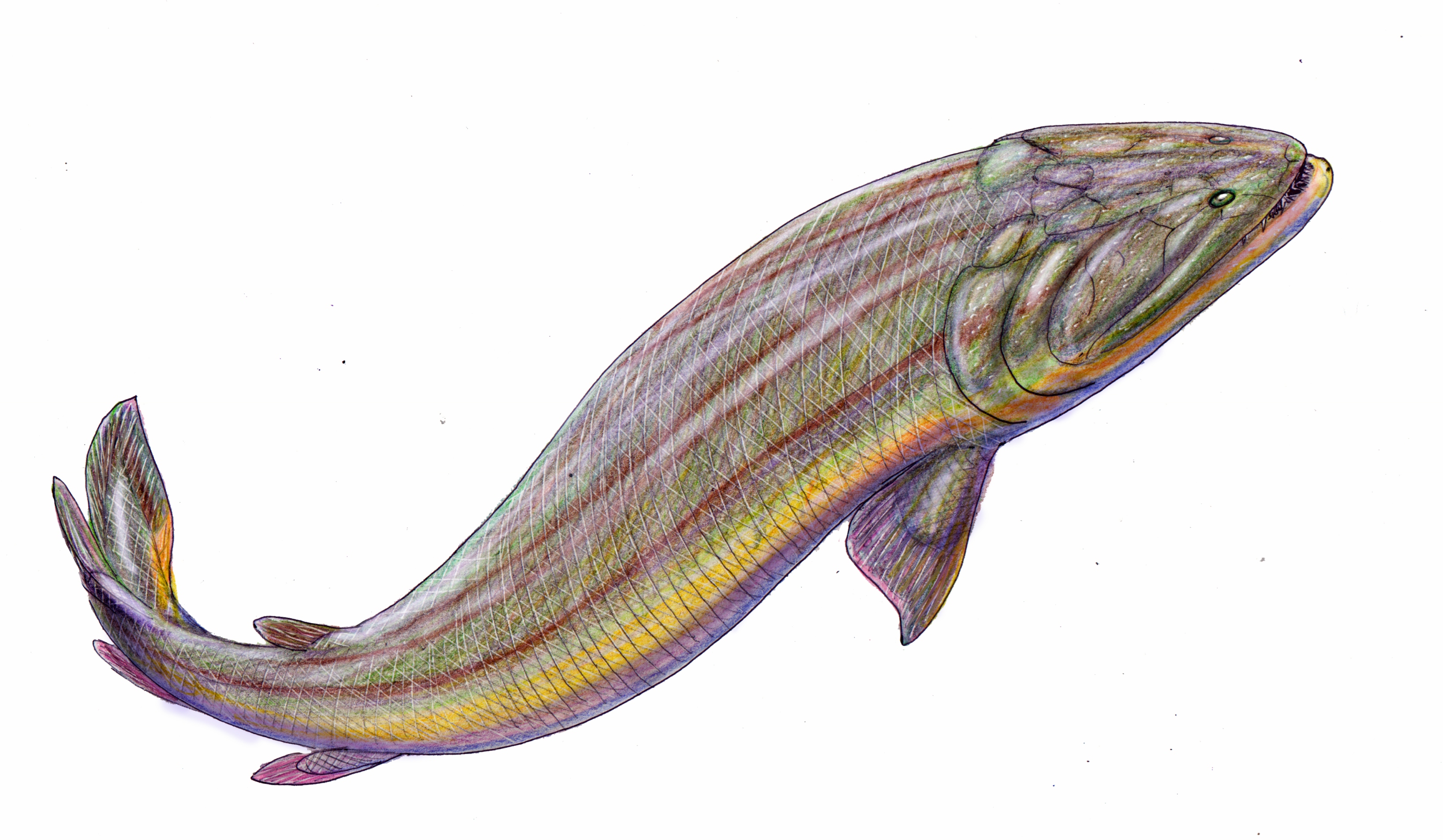
Gooloogongia Loomesi Reconstruction
''Gooloogongia'' ( ) is a genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish which belonged to the group of rhizodont fishes. ''Gooloogongia'' lived during the Late Devonian period (Famennian stage, about 360 million years ago). Fossils have been found in the Canowindra site, (Australia). It was named by Zerina Johanson and Per Ahlberg in 1998. In general size and shape ''Gooloogongia'' is similar to the modern saratoga which lives in the tropical rivers of northern Australia. ''Gooloogongia loomesi'' ("Loomes' Gooloogong") named after Bruce Loomes, the foreman of the 1993 excavation of the Canowindra site, and the town of Gooloogong, NSW. Description ''Gooloogongia'' was large in size (about 90 cm). Like other lobe-finned fishes, ''Gooloogongia'' had two rows of teeth in the jaw, the outer row being small teeth, and the inner row being larger fangs. The fangs of ''Gooloogongia'' are sharp and needle-like, but they were probably not strong enough to penetrate the armor plating of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gooloogongia
''Gooloogongia'' ( ) is a genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish which belonged to the group of rhizodont fishes. ''Gooloogongia'' lived during the Late Devonian period (Famennian stage, about 360 million years ago). Fossils have been found in the Canowindra site, ( Australia). It was named by Zerina Johanson and Per Ahlberg in 1998. In general size and shape ''Gooloogongia'' is similar to the modern saratoga which lives in the tropical rivers of northern Australia. ''Gooloogongia loomesi'' ("Loomes' Gooloogong") named after Bruce Loomes, the foreman of the 1993 excavation of the Canowindra site, and the town of Gooloogong, NSW. Description ''Gooloogongia'' was large in size (about 90 cm). Like other lobe-finned fishes, ''Gooloogongia'' had two rows of teeth in the jaw, the outer row being small teeth, and the inner row being larger fangs. The fangs of ''Gooloogongia'' are sharp and needle-like, but they were probably not strong enough to penetrate the armor plating of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hongyu
''Hongyu'', represented by its type species ''Hongyu chowi'', is an extinct Devonian lobe-finned fish. About 1.5 m in length, it resembles both Elpistostegalia and Rhizodontida, making its phylogenetic placement uncertain. The type specimen was discovered in the Zhongning Formation near Ningxia in China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...’s North China Block. References Tetrapodomorphs Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Devonian bony fish Prehistoric animals of China {{Paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |