|
Rhinocladiella Mackenziei
''Rhinocladiella mackenziei'' is a deeply pigmented fungus that is a common cause of human cerebral phaeohyphomycosis. ''Rhinocladiella mackenziei'' was believed to be endemic solely to the Middle East, due to the first cases of infection being limited to the region. However, cases of ''R. mackenziei'' infection are increasingly reported from regions outside the Middle East. This pathogen is unique in that the majority of cases have been reported from immunologically normal people. History ''Rhinocladiella mackenziei'' was first identified in 1993 as ''Ramichloridium mackenziei'' by C.K. Campbell & Al-Hedaithy when it was identified as the cause of eight cases of human cerebral phaeohyphomycosis. All eight patients had abscess formation and six of the patients had aspirated pus with branching hyphae. Campbell and Al-Hedaithy considered different genera for the un-named fungus, including ''Zasmidium'', ''Leptodontidium'', ''Ramichloridium'', and ''Rhinocladiella''. They elected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeohyphomycosis
Phaeohyphomycosis is a diverse group of fungal infections, caused by dematiaceous fungi whose morphologic characteristics in tissue include hyphae, yeast-like cells, or a combination of these. It can be associated an array of melanistic filamentous fungi including ''Alternaria'' species'','' ''Exophiala jeanselmei,'' and ''Rhinocladiella mackenziei''. The term "phaeohyphomycosis" was introduced to determine infections caused by dematiaceous (pigmented) filamentous fungi which contain melanin in their cell walls. Phaeohyphomycosis is an uncommon infection, but the number of cases reported has been increasing in recent years. Fungal melanin is thought to be a virulence factor. The outcome of antifungal treatment is poor, and mortality is almost 80%.Sanjay G.R., J.E. Patterson, D.DA. Sutton, R.Pullen, and M.G. Rinaldi. 2002. Disseminated phaeohyphomycosis:review of an emerging Mycosis. Clinical Infectious Disease 34:467-476. Phaeohyphomycosis has been attributed to more than 100 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), also termed primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system (DLBCL-CNS), is a primary intracranial tumor appearing mostly in patients with severe immunodeficiency (typically patients with AIDS). It is a subtype and one of the most aggressive of the diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. PCNSLs represent around 20% of all cases of lymphomas in HIV infections. (Other types are Burkitt's lymphomas and immunoblastic lymphomas). Primary CNS lymphoma is highly associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection (> 90%) in immunodeficient patients (such as those with AIDS and those immunosuppressed), and does not have a predilection for any particular age group. Mean CD4+ count at time of diagnosis is ~50/µL. In immunocompromised patients, prognosis is usually poor. In immunocompetent patients (that is, patients who do not have AIDS or some other acquired or secondary immunodeficiency), there is rarely an association w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-flucytosine
Flucytosine, also known as 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC), is an antifungal medication. It is specifically used, together with amphotericin B, for serious ''Candida'' infections and cryptococcosis. It may be used by itself or with other antifungals for chromomycosis. Flucytosine is used by mouth and by injection into a vein. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, loss of appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, and psychosis. Anaphylaxis and other allergic reactions occasionally occur. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Flucytosine is in the fluorinated pyrimidine analogue family of medications. It works by being converted into fluorouracil inside the fungus, which impairs its ability to make protein. Flucytosine was first made in 1957. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. As of 2016, in the United States the medication cost about US$2,000 per day while in the United Kingdom it is about US$22 per day. It is not available in mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isavuconazole
Isavuconazonium sulfate, sold under the brand name Cresemba, is a systemic antifungal medication of the triazole class which is used to treat invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis. The most common side effects include abnormal liver tests, nausea, vomiting, difficulty breathing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, injection site reactions, headache, low blood potassium and skin rash. Isavuconazonium is a prodrug of isavuconazole. Medical uses Isavuconazonium is used to treat invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis in adults aged eighteen years old and older. It is available in a capsule for administration by mouth and as a powder for administration via infusion. Contraindications Isavuconazonium is contraindicated in people taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, strong CYP3A4 inducers, or moderate CYP3A4 or CYP3A5 inducers. It is contraindicated in people with familial short QT syndrome. Side effects Common adverse effects (occurring in between 1 and 10% of people) include low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posaconazole
Posaconazole, sold under the brand name Noxafil among others, is a triazole antifungal medication. It was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2006, and is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Posaconazole is used to treat invasive ''Aspergillus'' and '' Candida'' infections. It is also used for the treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC), including OPC refractory to itraconazole and/or fluconazole therapy. It is also used to treat invasive infections by ''Candida'', ''Mucor'', and ''Aspergillus'' species in severely immunocompromised patients. Clinical evidence for its utility in treatment of invasive disease caused by ''Fusarium'' species (fusariosis) is limited. It appears to be helpful in a mouse model of naegleriasis. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Posaconazole works by disrupting the close packing of acyl chains of phospholipids, impairing the functions of certain membrane-bound enzyme systems such as ATPase and enzymes of the el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itraconazole
Itraconazole, sometimes abbreviated ITZ, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It may be given by mouth or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash, and headache. Severe side effects may include liver problems, heart failure, Stevens–Johnson syndrome and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. It is unclear if use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe. It is in the triazole family of medications. It stops fungal growth by affecting the cell membrane or affecting their metabolism. Itraconazole was patented in 1978 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1992. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Recent research works suggest itraconazole (ITZ) could also be used in the treatment of cancer by inhibiting the hedgehog pathway in a similar way to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
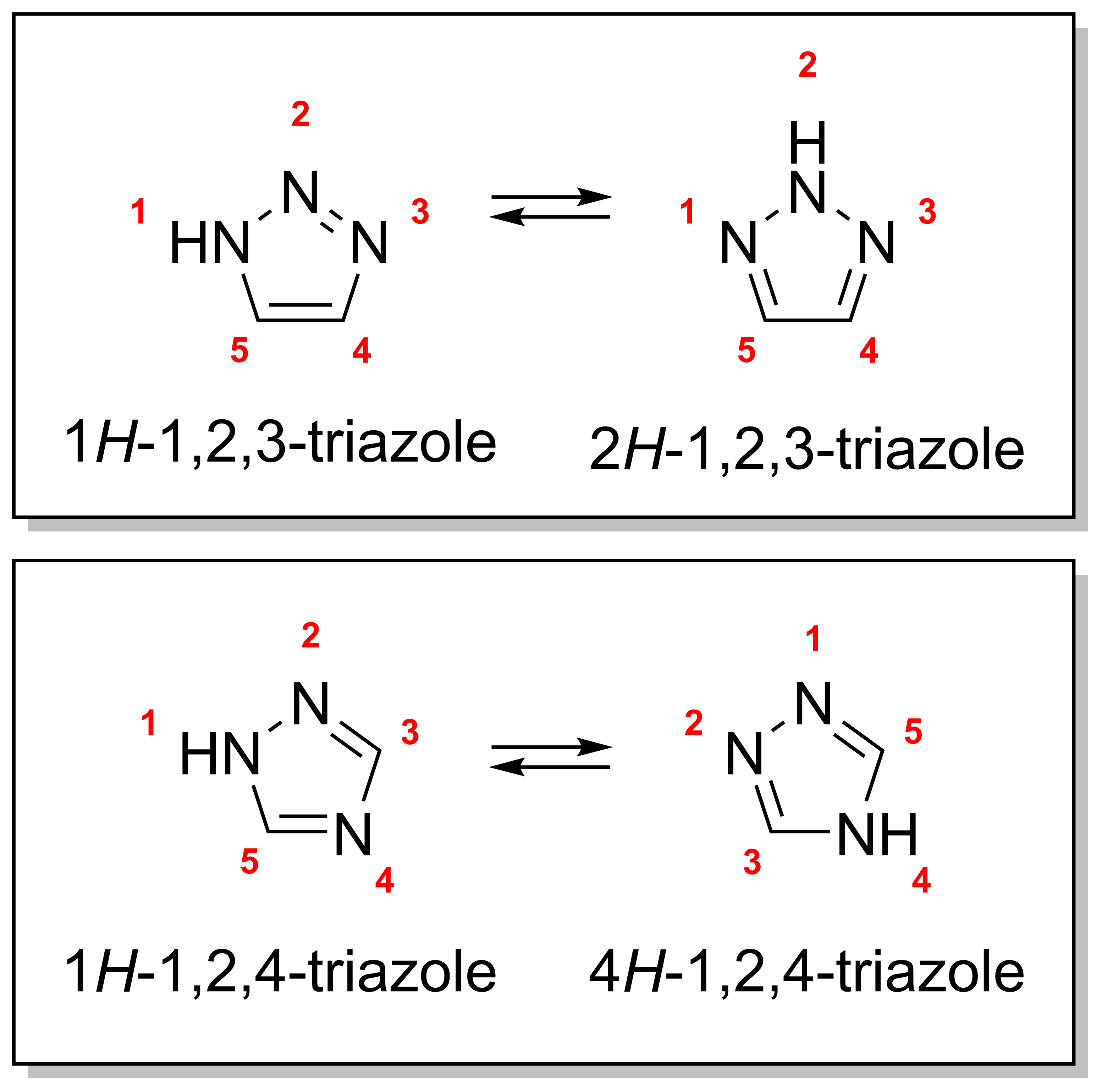
Triazoles
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of tautomers. In the 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category has two tautomers that differ by which nitrogen has a hydrogen bonded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. For certain infections it is given with flucytosine. It is typically given intravenously (injection into a vein). Common side effects include a reaction with fever, chills, and headaches soon after the medication is given, as well as kidney problems. Allergic symptoms including anaphylaxis may occur. Other serious side effects include low blood potassium and myocarditis (inflammation of the heart). It appears to be relatively safe in pregnancy. There is a lipid formulation that has a lower risk of side effects. It is in the polyene class of medications and works in part by interfering with the cell membrane of the fungus. Amphotericin B was isolated from '' Streptomyces nodosus'' in 1955 at the Squibb For Medical Research Institute from c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Scavenger
A scavenger in chemistry is a chemical substance added to a mixture in order to remove or de-activate impurities and unwanted reaction products, for example oxygen, to make sure that they will not cause any unfavorable reactions. Their use is wide-ranged: * In atmospheric chemistry, the most common scavenger is the hydroxyl radical, a short-lived radical produced photolytically in the atmosphere. It is the most important oxidant for carbon monoxide, methane and other hydrocarbons, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and most of other contaminants, removing them from the atmosphere. * In molecular laser isotope separation, methane is used as a scavenger gas for fluorine atoms. * Hydrazine and ascorbic acid are used as oxygen scavenger corrosion inhibitors. * Tocopherol and naringenin are bioactive free radical scavengers that act as antioxidants; synthetic catalytic scavengers are their synthetic counterparts * Organotin compounds are used in polymer manufacture as hydrochloric acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |