|
Rhingia Campestris
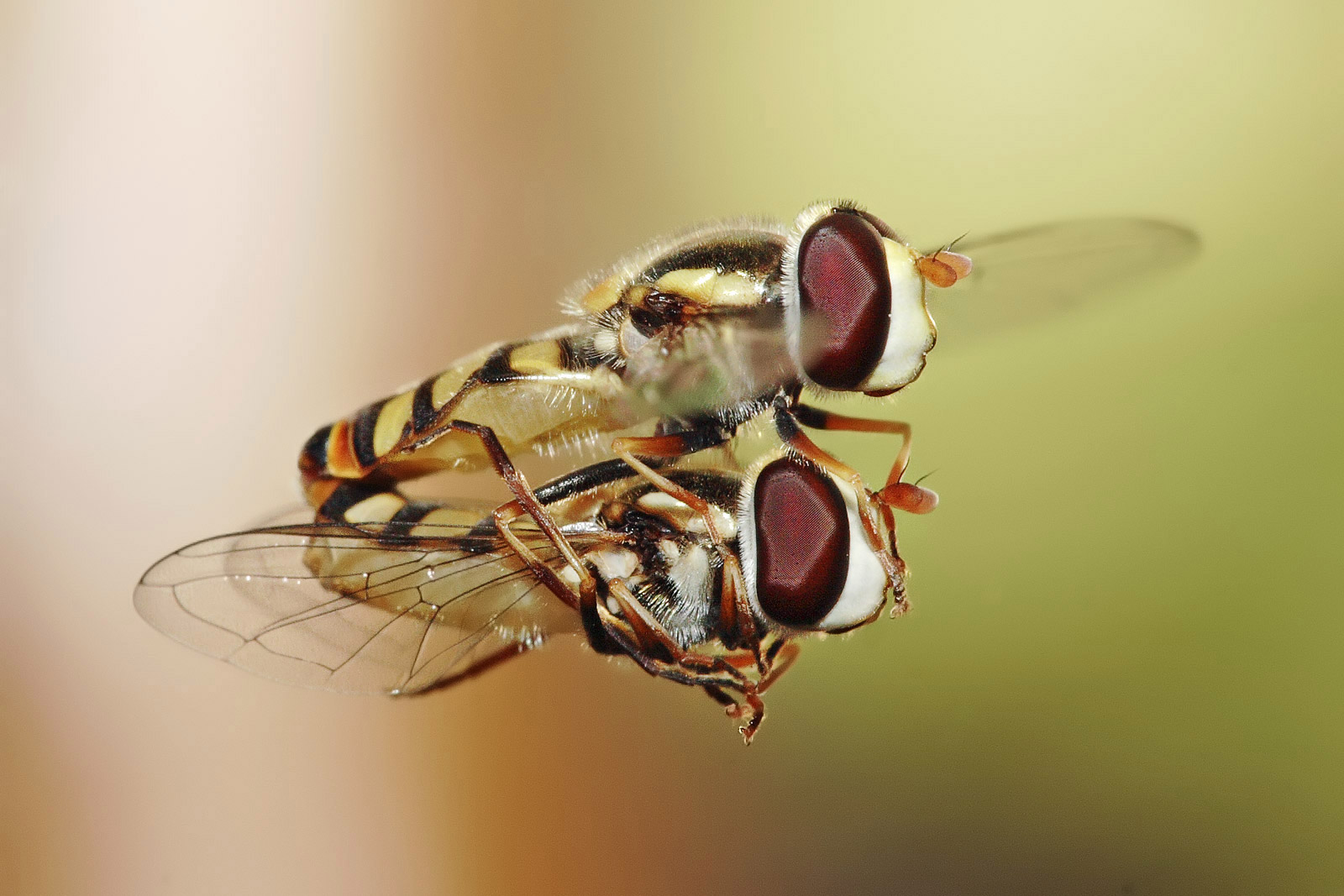
''Rhingia campestris'' is a species of hoverfly, long, with a wingspan of . It is common across the Palearctic from March until November. It has a broad orange abdomen with a black line along the sides (the black line is absent along the sides of ''Rhingia rostrata''), and has the distinctive long snout of all ''Rhingia'' species. ''Rhingia campestris'' is the main pollinator for many plant species and due to its long snout it can forage on tubulous flowers. Larvae are associated with cow dung. Adults males feed on nectar, while adult females feed on protein rich pollen, reflecting the cost of developing eggs. Technical description DescriptionExternal images For terms see |
Johann Wilhelm Meigen
Johann Wilhelm Meigen (3 May 1764 – 11 July 1845) was a German entomologist famous for his pioneering work on Diptera. Life Early years Meigen was born in Solingen, the fifth of eight children of Johann Clemens Meigen and Sibylla Margaretha Bick. His parents, though not poor, were not wealthy either. They ran a small shop in Solingen. His paternal grandparents, however, owned an estate and hamlet with twenty houses. Adding to the rental income, Meigen's grandfather was a farmer and a guild mastercutler in Solingen. Two years after Meigen was born, his grandparents died and his parents moved to the family estate. This was already heavily indebted by the Seven Years' War, then bad crops and rash speculations forced the sale of the farm and the family moved back to Solingen. Meigen attended the town school but only for a short time. He had learned to read and write on his grandfather's estate and he read widely at home as well as taking an interest in natural history. A lodge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
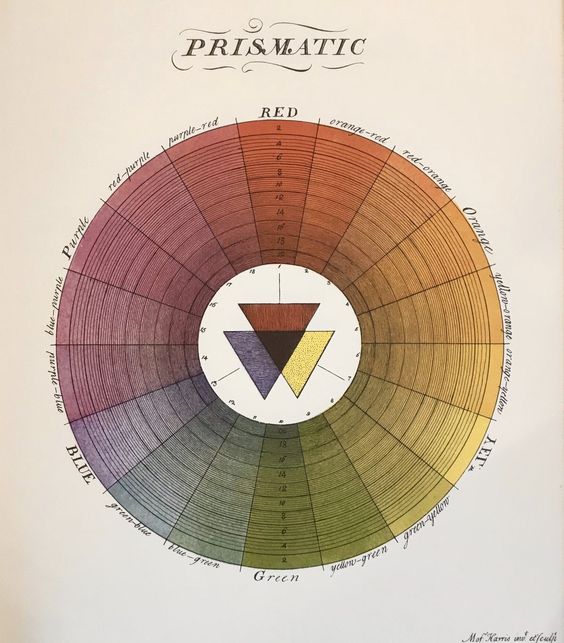
Moses Harris
Moses Harris (15 April 1730 – 1787) was an English entomologist and engraver. Life and work Harris was encouraged in entomology from a young age by his uncle, a member of the Society of the Aurelians. In 1762 he became secretary of a second Society of Aurelians. He was a skilled artist, displaying some of his insect drawings at the Royal Academy in 1785. He drew and engraved illustrations for books including Dru Drury's ''Illustrations of Natural History'' (3 volumes, 1770–1782) and John Coakley Lettsom's ''The Naturalist's and Traveller's Companion'' (1772). Colour theory In "The Natural System of Colours" published in 1766, Harris discussed the multitude of colours that can be created using three "grand or principle" colours: red, yellow and blue. As a naturalist and an engraver, Harris focussed on the relationships between colours and how they are coded and created. He explained how three colours can be íntermixed, tinted and shaded to create 660 colours "materially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoverfly
Hover flies, also called flower flies or syrphid flies, make up the insect family Syrphidae. As their common name suggests, they are often seen hovering or nectaring at flowers; the adults of many species feed mainly on nectar and pollen, while the larvae (maggots) eat a wide range of foods. In some species, the larvae are saprotrophs, eating decaying plant and animal matter in the soil or in ponds and streams. In other species, the larvae are insectivores and prey on aphids, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects. Insects such as aphids are considered a crop pest, and therefore the aphid-eating larvae of some hover flies serve as an economically (as well as ecologically) important predator and even potential agents for use in biological control, while the adults may be pollinators. About 6,000 species in 200 genera have been described. Hover flies are common throughout the world and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. Hover flies are harmless to most mammals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa. The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Siberian region; the Mediterranean Basin; the Sahara and Arabian Deserts; and Western, Central and East Asia. The Palaearctic realm also has numerous rivers and lakes, forming several freshwater ecoregions. The term 'Palearctic' was first used in the 19th century, and is still in use as the basis for zoogeographic classification. History In an 1858 paper for the ''Proceedings of the Linnean Society'', British zoologist Philip Sclater first identified six terrestrial zoogeographic realms of the world: Palaearctic, Aethiopian/Afrotropic, Indian/Indomalayan, Australasian, Nearctic, and Neotropical. The six indicated general groupings of fauna, based on shared biogeography and large-scale geographic barriers to migration. Alfred Wallace a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhingia Rostrata
''Rhingia rostrata'' is a small species of hoverfly, some in length, with a wing span of . It is common in many parts of Europe from March until November, though is slightly less common than ''Rhingia campestris'' in many parts of it range. In Great Britain, Britain it is only found in southern England. It has a broad orange abdomen, but lacking the black line along the side of the abdomen as in ''Rhingia campestris''. Also living ''Rhingia rostrata'' has an orange Scutellum (insect), scutellum, though this fades to brown in dead specimens. But it still has the distinctive long snout of all ''Rhingia'' species. Larvae are associated with cow dung. Adults feed on nectar and pollen. References Eristalinae Diptera of Europe Insects described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus {{Syrphidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhingia
''Rhingia '' is a genus of hoverflies. They all have a very distinctive long snout. The larvae are associated with animal dung. Adults feed on nectar and pollen. Species *'' R. austriaca'' Meigen, 1830 *'' R. borealis'' Ringdahl 1928 *'' R. caerulescens'' Loew, 1858 *'' R. campestris'' Meigen, 1822 *'' R. cnephaeoptera'' Speiser, 1915 *'' R. coerulea'' Bezzi, 1912 *'' R. congensis'' Curran, 1939 *'' R. cuthbertsoni'' Curran, 1939 *'' R. cyanoprora'' Speiser, 1910 *'' R. formosana'' Shiraki, 1930 *'' R. fuscipes'' Bezzi, 1915 *'' R. laevigata'' Loew, 1858 *'' R. lutea'' Bezzi, 1915 *'' R. mecyana'' Speiser, 1910 *'' R. nasica'' Say, 1823 *'' R. nigra'' Macquart, 1845 *'' R. orthoneurina'' Speiser, 1910 *'' R. pellucens'' Bezzi, 1915 *'' R. pulcherrima'' Bezzi, 1908 *'' R. pycnosoma'' Bezzi, 1915 *'' R. rostrata'' (Linnaeus, 1758 Events January–March * January 1 – Swedish biologist Carl Linnaeus (Carl von Linné) publishes in Stockholm the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cow Dung
Cow dung, also known as cow pats, cow pies or cow manure, is the waste product (faeces) of bovine animal species. These species include domestic cattle ("cows"), bison ("buffalo"), yak, and water buffalo. Cow dung is the undigested residue of plant matter which has passed through the animal's gut. The resultant faecal matter is rich in minerals. Color ranges from greenish to blackish, often darkening soon after exposure to air. Uses Cow dung, which is usually a dark brown color, is often used as manure (agricultural fertilizer). If not recycled into the soil by species such as earthworms and dung beetles, cow dung can dry out and remain on the pasture, creating an area of grazing land which is unpalatable to livestock. In many parts of the developing world, and in the past in mountain regions of Europe, caked and dried cow dung is used as fuel. Dung may also be collected and used to produce biogas to generate electricity and heat. The gas is rich in methane and is use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualists, which in turn provide herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and bats. Nectar plays a crucial role in the foraging economics and evolution of nectar-eating species; for example, nectar foraging behavior is largely responsible for the divergent evolution of the African honey bee, ''A. m. scutellata'' and the western honey bee. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of parasitoid wasps (e.g. the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology Of Diptera
Dipteran morphology differs in some significant ways from the broader morphology of insects. The Diptera is a very large and diverse order of mostly small to medium-sized insects. They have prominent compound eyes on a mobile head, and (at most) one pair of functional, membraneous wings, which are attached to a complex mesothorax. The second pair of wings, on the metathorax, are reduced to halteres. The order's fundamental peculiarity is its remarkable specialization in terms of wing shape and the morpho-anatomical adaptation of the thorax – features which lend particular agility to its flying forms. The filiform, stylate or aristate antennae correlate with the Nematocera, Brachycera and Cyclorrhapha taxa respectively. It displays substantial morphological uniformity in lower taxa, especially at the level of genus or species. The configuration of integumental bristles is of fundamental importance in their taxonomy, as is wing venation. It displays a complete metamorphosis (egg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identification Key
In biology, an identification key, taxonomic key, or biological key is a printed or computer-aided device that aids the identification of biological entities, such as plants, animals, fossils, microorganisms, and pollen grains. Identification keys are also used in many other scientific and technical fields to identify various kinds of entities, such as diseases, soil types, minerals, or archaeological and anthropological artifacts. Traditionally identification keys have most commonly taken the form of single-access keys. These work by offering a fixed sequence of ''identification steps'', each with multiple alternatives, the choice of which determines the next step. If each step has only two alternatives, the key is said to be dichotomous, else it is polytomous. Modern multi-access or ''interactive keys'' allow the user to freely choose the identification steps and their order. At each step, the user must answer a question about one or more features (''characters'') of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(Bolemin%2C_cows).jpg)