|
Revolutionary Communist Party Of Argentina
The Revolutionary Communist Party ( es, Partido Comunista Revolucionario) is a Marxism–Leninism–Maoism, Marxist–Leninist–Maoist in Argentina. The party is part of the Frente de Todos (2019 coalition), Frente de Todos coalition that supported the presidential candidate Alberto Fernández during the 2019 Argentine general election. History Beginnings as PC(CNRR) The party emerged from a split in the Communist Party of Argentina in 1967.Partido Comunista Revolucionario de la Argentina. Fundado el 6 de enero de 1968 – Partido Comunista Revolucionario de la Argentina' On January 6, 1968 (the 50th anniversary of the founding of the Communist Party) the dissidents formed the Communist Party – National Revolutionary Recovery Committee ( es, Partido Comunista-Comité Nacional de Recuperación Revolucionaria, abbreviated PC(CNRR)). The founders of PC(CNRR) came mainly from the Communist Youth Federation (FJC), although the group also included some Communist Party cadres. Leade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Carlos Alderete
Juan Carlos Alderete (born 19 September 1952) is an Argentina, Argentine trade unionist, social activist and politician, and the leader of the Corriente Clasista y Combativa (CCC), the Trade unions in Argentina, labour wing of the Revolutionary Communist Party (Argentina), Revolutionary Communist Party. He rose to prominence in the late 1990s due to his role in the Piquetero movement. Since December 2019, he has been a Argentine Chamber of Deputies, National Deputy representing Buenos Aires Province. He sits in the Frente de Todos Parliamentary group, bloc. Early and personal life Alderete was born on 19 September 1952 in Salta, in Northeastern Argentina. His father was a General Confederation of Labour (Argentina), CGT leader. The eighth of nine children, he dropped out of primary school when he was 9 years old. From an early age, he was a firm believer in the ideal of the Socialist revolution and admired Che Guevara. When he was 14, Alderete ran away from his home intending to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Che Guevara
Ernesto Che Guevara (; 14 June 1928The date of birth recorded on /upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/78/Ernesto_Guevara_Acta_de_Nacimiento.jpg his birth certificatewas 14 June 1928, although one tertiary source, (Julia Constenla, quoted by Jon Lee Anderson), asserts that he was actually born on 14 May of that year. Constenla alleges that she was told by Che's mother, Celia de la Serna, that she was already pregnant when she and Ernesto Guevara Lynch were married and that the date on the birth certificate of their son was forged to make it appear that he was born a month later than the actual date to avoid scandal. ( Anderson 1997, pp. 3, 769.) – 9 October 1967) was an Argentine Marxist revolutionary. A major figure of the Cuban Revolution, his stylized visage has become a ubiquitous countercultural symbol of rebellion and global insignia in popular culture. As a young medical student, Guevara traveled throughout South America and was radicalized by the poverty, hunger, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1989 Argentine General Election
The Argentine general election of 1989 was held on 14 May 1989. Voters chose both the President of Argentina, President and their legislators and with a turnout of 85.3%, Carlos Menem won the presidency, and the peronist Justicialist Party won the control of both houses of Congress. This is the last presidential election the president was elected by the electoral college. Background Inheriting a difficult legacy from his National Reorganization Process, military predecessors, President Raúl Alfonsín's tenure had been practically defined by the foreign debt Argentina's last dictatorship left behind. Signs of unraveling in Alfonsín's 1985 Argentine austral, Austral Plan for economic stabilization cost his centrist Radical Civic Union (UCR) its majorities in the Argentine Chamber of Deputies, Chamber of Deputies (lower house of Congress) and among the nation's 22 governorships in the September 1987 mid-term elections. Facing a restive armed forces opposed to trials against pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1987 Argentine Legislative Election
The Argentine legislative elections of 1987 were held on 6 September. Voters chose their legislators and governors, with a turnout of 83.6%. The ruling Radical Civic Union lost their majority in the Chamber of Deputies. Background The domestic and international esteem President Raúl Alfonsín earned for advancing the Trial of the Juntas suffered in December 1986, when on his initiative, Congress passed the Full Stop Law, which limited the civil trials against roughly 300 officers implicated in the 1976-79 Dirty War against dissidents to those indicted within 60 days of the law's passage, a tall order given the reluctance of many victims and witnesses to testify. These concessions did not placate hard-liners in the Argentine military who, though in a minority, put Argentina's hard-earned Democracy at risk in April 1987, when a group identified as ''Carapintadas'' ("painted faces," from their use of camouflage paint) loyal to Army Major Aldo Rico staged a mutiny of the important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Party Of Labour And Of The People
The Revolutionary Communist Party ( es, Partido Comunista Revolucionario) is a Marxist–Leninist–Maoist in Argentina. The party is part of the Frente de Todos coalition that supported the presidential candidate Alberto Fernández during the 2019 Argentine general election. History Beginnings as PC(CNRR) The party emerged from a split in the Communist Party of Argentina in 1967.Partido Comunista Revolucionario de la Argentina. Fundado el 6 de enero de 1968 – Partido Comunista Revolucionario de la Argentina' On January 6, 1968 (the 50th anniversary of the founding of the Communist Party) the dissidents formed the Communist Party – National Revolutionary Recovery Committee ( es, Partido Comunista-Comité Nacional de Recuperación Revolucionaria, abbreviated PC(CNRR)). The founders of PC(CNRR) came mainly from the Communist Youth Federation (FJC), although the group also included some Communist Party cadres. Leaders of PC(CNRR) included Jorge Rocha, Carlos Echagüe, Lucila I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
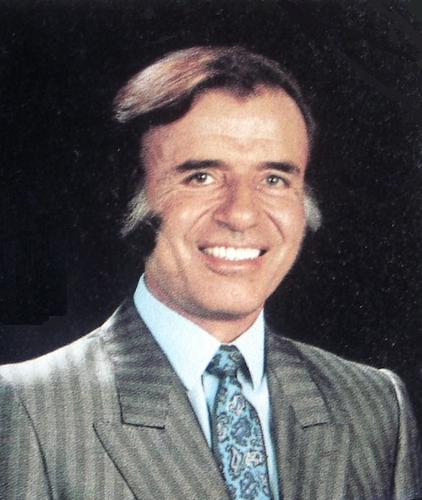
Isabel Perón
Isabel Martínez de Perón (, born María Estela Martínez Cartas, 4 February 1931), also known as Isabelita, is an Argentine politician who served as President of Argentina from 1974 to 1976. She was one of the first female republican heads of state in the world, and the first woman to serve as president of a country. Isabel Perón was the third wife of President Juan Perón. During her husband's third term as president from 1973 to 1974, she served as both Vice President and First Lady of Argentina. Following her husband's death in office in 1974, she served as President for almost two years before the military took over the government with the 1976 coup. Perón was then placed under house arrest for five years before she was exiled to Spain in 1981. In 2007 an Argentine judge ordered Perón's arrest over the forced disappearance of an activist in February 1976, on the grounds that the disappearance was authorized by her signing of decrees allowing Argentina's armed forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March 1973 Argentine General Election
See also ''September 1973 Argentine presidential election'' The first Argentine general election of 1973 was held on 11 March. Voters chose both the President and their legislators. Background The 1966 coup d'état against the moderate President Arturo Illia was carried out largely as a reaction to Illia's decision to honor local and legislative elections in which Peronists, officially banned from political activity following the violent overthrow of President Juan Perón in 1955, did well. Five years later, however, President Alejandro Lanusse found himself heading an unpopular junta, saddled by increasing political violence and an economic wind-down from the prosperous 1960s. Seizing the initiative, he gathered leaders from across the nation's political and intellectual spectrum for a July 1971 '' asado'', a time-honored Argentine custom as much about camaraderie as about steak. The result was Lanusse's "Great National Agreement," a road map to the return to democratic rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Committee
Central committee is the common designation of a standing administrative body of Communist party, communist parties, analogous to a board of directors, of both ruling and nonruling parties of former and existing socialist states. In such party organizations, the committee would typically be made up of delegates elected at a party congress. In Communist state, those states where it constituted the state power, the central committee made decisions for the party between congresses and usually was (at least nominally) responsible for electing the politburo. In non-ruling communist parties, the central committee is usually understood by the party membership to be the ultimate decision-making authority between congresses once the process of democratic centralism has led to an agreed-upon position. Non-communist organizations are also governed by central committees, such as the right-wing Likud party in Israel, the North American Mennonite Central Committee, Mennonite Church and Alcoholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peronism
Peronism, also called justicialism,. The Justicialist Party is the main Peronist party in Argentina, it derives its name from the concept of social justice., name=, group= is an Argentine political movement based on the ideas and legacy of Argentina, Argentine ruler Juan Perón (1895–1974). It has been an influential movement in 20th and 21st century Argentine politics. Since 1946, Peronists have won 10 out of the 13 presidential elections in which they have been allowed to run. The main Peronist party is the Justicialist Party. The policies of Peronist presidents have differed greatly, but the general ideology has been described as "a vague blend of nationalism and labourism" or populism. Perón became Argentina's Ministry of Labour, Employment and Social Security (Argentina), labour secretary after participating in the 1943 Argentine coup d'état, 1943 military coup and was elected president of Argentina in 1946 Argentine general election, 1946. He introduced social progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peronismo De Base
Peronism, also called justicialism,. The Justicialist Party is the main Peronist party in Argentina, it derives its name from the concept of social justice., name=, group= is an Argentine political movement based on the ideas and legacy of Argentine ruler Juan Perón (1895–1974). It has been an influential movement in 20th and 21st century Argentine politics. Since 1946, Peronists have won 10 out of the 13 presidential elections in which they have been allowed to run. The main Peronist party is the Justicialist Party. The policies of Peronist presidents have differed greatly, but the general ideology has been described as "a vague blend of nationalism and labourism" or populism. Perón became Argentina's labour secretary after participating in the 1943 military coup and was elected president of Argentina in 1946. He introduced social programs that benefited the working class, supported labor unions and called for additional involvement of the state in the economy. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Obrero
EL, El or el may refer to: Religion * El (deity), a Semitic word for "God" People * EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer * El DeBarge, music artist * El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American politician * Ephrat Livni (born 1972), American street artist Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * El, short for Eleven, a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in ''Superman'' *E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film ''Road Trip'' Literature * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 2000 Japanese adult visual novel Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él'' (Lucero album), a 1982 album by Lucero * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from ''Caminando'' (album) * "Él" (Luc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palabra Obrera
''Movimiento de Agrupaciones Obreras'' ('Workers Groups Movement', abbreviated MAO) was a political labour organization in Argentina. MAO was founded in mid-1957 by a Nahuel Moreno's Trotskyist tendency (which had been organized in the Revolutionary Workers Party, POR, until that party had merged into the Socialist Party of the National Revolution in 1954). MAO formed part of the trade unionist resistance to the '' Revolución Libertadora''.Biagini, Hugo E., Arturo Andrés Roig, and Carlos Alemián. El pensamiento alternativo en la Argentina del siglo XX'. Buenos Aires: Editorial Biblos, 2004. p. 301 On July 23, 1957, MAO began publishing the weekly newspaper ''Palabra Obrera'' ('Workers Word'). The organization became commonly known by the name of its publication.''Un siglo de luchas: historia del movimiento obrero argentino''. Buenos Aires: Ediciones Antídoto, 1988. pp. 122-123http://www.razonyrevolucion.org/textos/revryr/luchadeclases/ryr3Camarero.pdf Through MAO, Moreno's gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_-_2.jpg)
