|
Retroflex Ejective Affricate
The retroflex ejective affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , though it is frequently simplified to . Features Features of the retroflex ejective affricate: Occurrence See also * List of phonetic topics A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () * Alveolar click () * Alveolar consonant * Alveolar ejectiv ... External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Retroflex Ejective Affricate Affricates Ejectives Retroflex consonants Oral consonants Central consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; , and , pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel (fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose ( nasals). Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, linguists have devised systems such as the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to assign a unique and unambiguous symbol to each attested consonant. The English alphabet has fewer consonant letters than the English language has consonant sounds, so digraphs like , , , and are used to extend the alphabet, though some letters and digraphs represent more than one consonant. For example, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Communication
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are the same word, e.g., "role" or "hotel"), and using those words in their semantic character as words in the lexicon of a language according to the syntactic constraints that govern lexical words' function in a sentence. In speaking, speakers perform many different intentional speech acts, e.g., informing, declaring, asking, persuading, directing, and can use enunciation, intonation, degrees of loudness, tempo, and other non-representational or paralinguistic aspects of vocalization to convey meaning. In their speech, speakers also unintentionally communicate many aspects of their social position such as sex, age, place of origin (through accent), physical states (alertness and sleepiness, vigor or weakness, health or illness), psychologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic transcription, phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form.International Phonetic Association (IPA), ''Handbook''. The IPA is used by lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguistics, linguists, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of wiktionary:lexical, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, phonemes, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, and the separation of words and syllables. To represent additional qualities of speech—such as tooth wiktionary:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
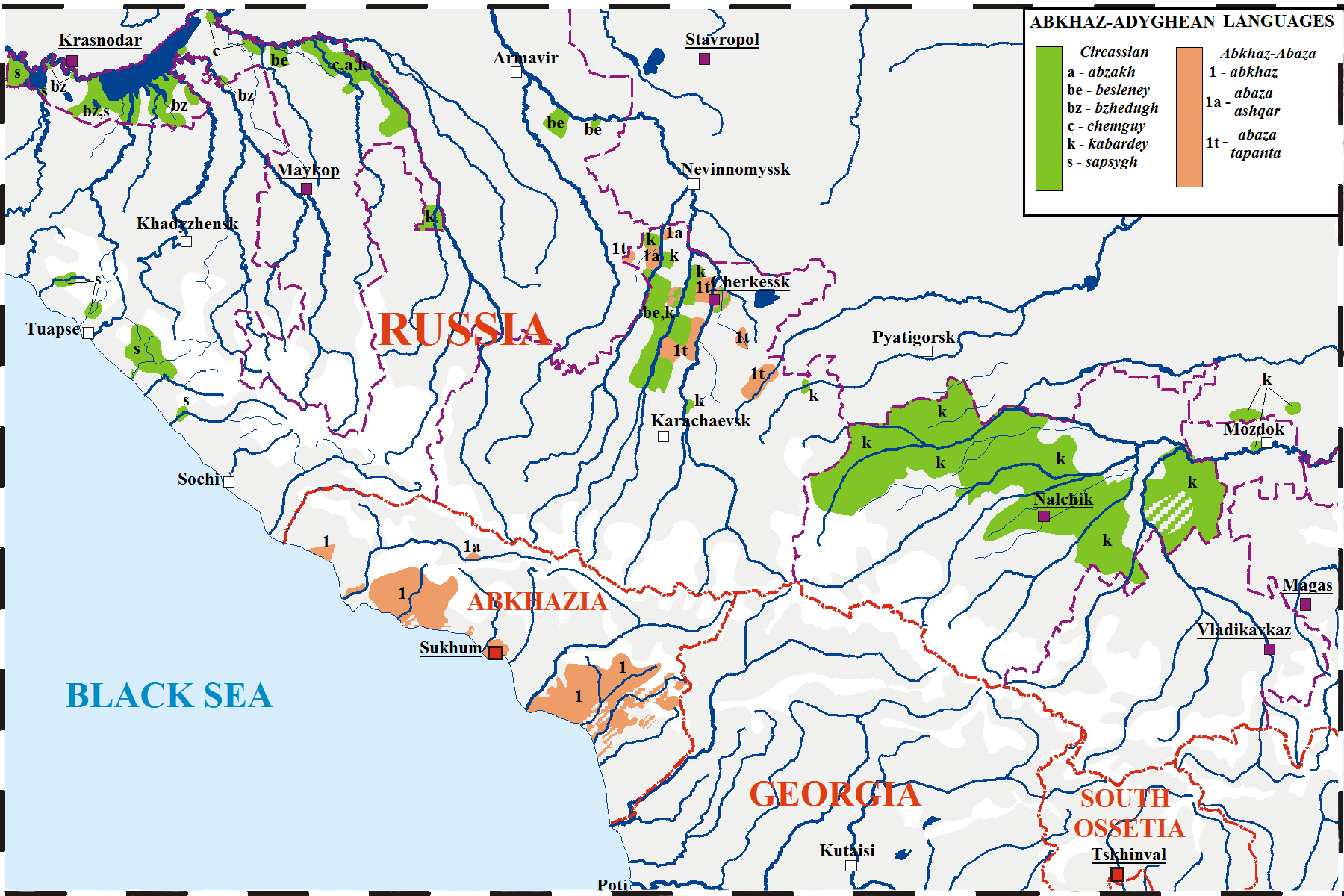
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz ( ; ), sometimes spelled Abxaz and also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 100,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two are very similar; however, the differences in phonology are substantial, it also contains elements characteristic of Kabar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adyghe Language
Adyghe ( or ; ady, Адыгабзэ, Adygabzə, ), also known as West Circassian ( ady, link=no, кӏахыбзэ, khaxybzə), is a Northwest Caucasian language spoken by the western subgroups of Circassians. It is spoken mainly in Russia, as well as in Turkey, Jordan, Syria and Israel, where they settled after the Circassian genocide. It is closely related to the Kabardian (East Circassian) language, though some reject the distinction between the two languages in favor of both being dialects of a unitary Circassian language. The literary language is based on the Temirgoy dialect. Adyghe and Russian are the two official languages of the Republic of Adygea in the Russian Federation. There are around 128,000 speakers of Adyghe in Russia, almost all of them native speakers. In total, some 300,000 speak it worldwide. The largest Adyghe-speaking community is in Turkey, spoken by the diaspora from the Russian–Circassian War (–1864). In addition, the Adyghe language is spoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, Caucasian languages, Caucasian and Iranian languages, Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin script, Latin and Greek alphabet, Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I of Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avar Language
Avar (, , "language of the mountains" or , , "Avar language"), also known as Avaric, is a Northeast Caucasian language of the Avar–Andic subgroup that is spoken by Avars, primarily in Dagestan. In 2010, there were approximately 1 million speakers in Dagestan and elsewhere in Russia. Geographic distribution It is spoken mainly in the western and southern parts of the Russian Caucasus republic of Dagestan, and the Balaken, Zaqatala regions of north-western Azerbaijan. Some Avars live in other regions of Russia. There are also small communities of speakers living in the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia; in Georgia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Jordan, and the Marmara Sea region of Turkey. It is spoken by about 762,000 people worldwide. UNESCO classifies Avar as vulnerable to extinction. Status It is one of six literary languages of Dagestan, where it is spoken not only by the Avar, but also serves as the language of communication between different ethnic groups. Dialec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwichʼin Language
The Gwichʼin language () belongs to the Athabaskan language family and is spoken by the Gwich'in First Nation (Canada) / Alaska Native People (United States). It is also known in older or dialect-specific publications as Kutchin, Takudh, Tukudh, or Loucheux. Gwich'in is spoken primarily in the towns of Inuvik, Aklavik, Fort McPherson, and Tsiigehtchic (formerly Arctic Red River), all in the Northwest Territories and Old Crow in Yukon of Canada. In Alaska of the United States, Gwichʼin is spoken in Beaver, Circle, Fort Yukon, Chalkyitsik, Birch Creek, Arctic Village, Eagle, and Venetie. The ejective affricate in the name ''Gwichʼin'' is usually written with symbol , though the correct character for this use (with expected glyph and typographic properties) is . Written Gwichʼin The missionary Robert McDonald first started working on the written representation of Van Tat and Dagoo dialects Gwichʼin. He also produced a Bible and a hymn book which was written in Gwic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubykh Language
Ubykh or Päkhy was a Northwest Caucasian language once spoken by the Ubykh tribe of Circassians who originally lived along the eastern coast of the Black Sea before being deported ''en masse'' to Turkey in the Circassian genocide. The Ubykh language was ergative and polysynthetic, with a high degree of agglutination, with polypersonal verbal agreement and a very large number of distinct consonants but only two phonemically distinct vowels. With around eighty consonants, it had one of the largest inventories of consonants in the world, and the largest number for any language without clicks. The name Ubykh is derived from (), its name in the Adyghe language. It is known in linguistic literature by many names: variants of Ubykh, such as ''Ubikh'', ( French); and its Germanised variant (from Ubykh ). Major features Ubykh is distinguished by the following features, some of which are shared with other Northwest Caucasian languages: * It is ergative, making no syntactic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokuts Language
Yokuts, formerly known as Mariposa, is an endangered language spoken in the interior of Northern and Central California in and around the San Joaquin Valley by the Yokuts people. The speakers of Yokuts were severely affected by disease, missionaries, and the Gold Rush. While descendants of Yokuts speakers currently number in the thousands, most of the constituent dialects are now extinct. The Yawelmani dialect of Valley Yokuts has been a focus of much linguistic research. Dialects The Yokuts language consists of half a dozen primary dialects. An estimated forty linguistically distinct groups existed before Euro-American contact. The following classification appears in Whistler & Golla (1986). Poso Creek * Palewyami Yokuts (also known as Poso Creek, Altinin) General Yokuts (all others) * Buena Vista :: :: * Nim :* :: :: :: :* ::* ::* ::: ::: ::: ::: ::* (see) Speakers and language revitalization Most Yokuts dialects are extinct, as noted above. Those that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Phonetic Topics
A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () * Alveolar click () * Alveolar consonant * Alveolar ejective affricate () * Alveolar ejective () * Alveolar ejective fricative () * Alveolar flap () * Alveolar lateral approximant (, ) * Alveolar lateral ejective affricate () * Alveolar lateral ejective fricative () * Alveolar lateral flap () * Alveolar nasal () * Alveolar ridge * Alveolar trill (, ) * Alveolo-palatal consonant * Alveolo-palatal ejective fricative () * Apical consonant * Approximant consonant * Articulatory phonetics * Aspirated consonant (◌ʰ) * Auditory phonetics B * Back vowel * Basis of articulation * Bernd J. Kröger * Bilabial click () * Bilabial consonant * Bilabial ejective () * Bilabial flap () * Bilabial nasal () * Bilabial trill () * Breathy voice C * Cardinal vowel * Central consonant * Central vowel * Checke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |