|
Replicator (Band)
Replicator may refer to various things related to replication: Science * Replicator (evolution unit), the theoretical basic unit of evolution in the gene-centered view of evolution * Replicator (self-replication), a component that facilitates self-replication ** DNA replication, the process of producing two identical copies from one original DNA molecule * Replicator (nanotechnology), a device to precisely position molecules to guide chemical reactions * Clanking replicator, an artificial self-replicating system that relies on conventional large-scale technology and automation * Replicator equation, a deterministic monotone non-linear and non-innovative game dynamic used in evolutionary game theory * Replicator (cellular automaton) In cellular automata, a replicator is a pattern that produces copies of itself. In the one-dimensional Rule 90 cellular automaton, every pattern is a replicator. The same is true in the life-like cellular automaton rule Replicator (B1357/S1357 . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replication (other)
Replication may refer to: Science * Replication (scientific method), one of the main principles of the scientific method, a.k.a. reproducibility ** Replication (statistics), the repetition of a test or complete experiment ** Replication crisis * Self-replication, the process in which an entity (a cell, virus, program, etc.) makes a copy of itself ** DNA replication or DNA synthesis, the process of copying a double-stranded DNA molecule ** Semiconservative replication, mechanism of DNA replication ** Viral replication, the process by which viruses produce copies of themselves * Replication (metallography), the use of thin plastic films to duplicate the microstructure of a component * Self-replicating machines Computing * Replication (computing), the use of redundant resources to improve reliability, fault-tolerance, or performance * Replication (optical media) In optical disc manufacturing, replication is the process of producing discs via methods that do not involve "burning" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replicator (evolution Unit)
With gene defined as "not just one single physical bit of DNA utall replicas of a particular bit of DNA distributed throughout the world", the gene-centered view of evolution, gene's eye view, gene selection theory, or selfish gene theory holds that adaptive evolution occurs through the differential survival of competing genes, increasing the allele frequency of those alleles whose phenotypic trait effects successfully promote their own propagation. The proponents of this viewpoint argue that, since heritable information is passed from generation to generation almost exclusively by DNA, natural selection and evolution are best considered from the perspective of genes. Proponents of the gene-centered viewpoint argue that it permits understanding of diverse phenomena such as altruism and intragenomic conflict that are otherwise difficult to explain from an organism-centered viewpoint. The gene-centered view of evolution is a synthesis of the theory of evolution by natural sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replicator (self-replication)
Self-replication is any behavior of a dynamical system that yields construction of an identical or similar copy of itself. Biological cells, given suitable environments, reproduce by cell division. During cell division, DNA is replicated and can be transmitted to offspring during reproduction. Biological viruses can replicate, but only by commandeering the reproductive machinery of cells through a process of infection. Harmful prion proteins can replicate by converting normal proteins into rogue forms. Computer viruses reproduce using the hardware and software already present on computers. Self-replication in robotics has been an area of research and a subject of interest in science fiction. Any self-replicating mechanism which does not make a perfect copy (mutation) will experience genetic variation and will create variants of itself. These variants will be subject to natural selection, since some will be better at surviving in their current environment than others and will ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replicator (nanotechnology)
A molecular assembler, as defined by K. Eric Drexler, is a "proposed device able to guide chemical reactions by positioning reactive molecules with atomic precision". A molecular assembler is a kind of molecular machine. Some biological molecules such as ribosomes fit this definition. This is because they receive instructions from messenger RNA and then assemble specific sequences of amino acids to construct protein molecules. However, the term "molecular assembler" usually refers to theoretical human-made devices. Beginning in 2007, the British Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council has funded development of ribosome-like molecular assemblers. Clearly, molecular assemblers are possible in this limited sense. A technology roadmap project, led by the Battelle Memorial Institute and hosted by several U.S. National Laboratories has explored a range of atomically precise fabrication technologies, including both early-generation and longer-term prospects for programmab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
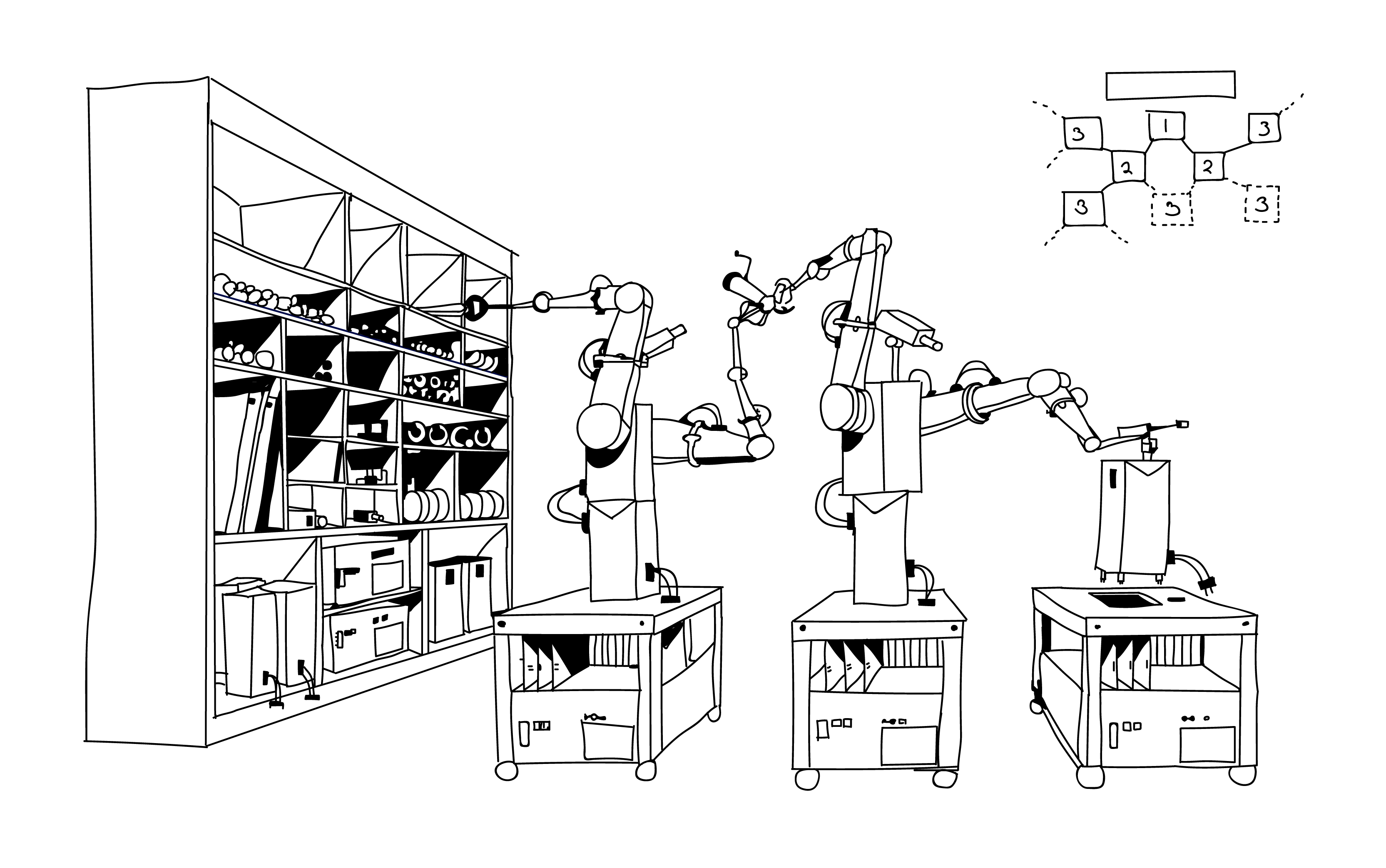
Clanking Replicator
A self-replicating machine is a type of autonomous robot that is capable of reproducing itself autonomously using raw materials found in the environment, thus exhibiting self-replication in a way analogous to that found in nature. The concept of self-replicating machines has been advanced and examined by Homer Jacobson, Edward F. Moore, Freeman Dyson, John von Neumann, Konrad Zuse and in more recent times by K. Eric Drexler in his book on nanotechnology, '' Engines of Creation'' (coining the term clanking replicator for such machines) and by Robert Freitas and Ralph Merkle in their review ''Kinematic Self-Replicating Machines'' which provided the first comprehensive analysis of the entire replicator design space. The future development of such technology is an integral part of several plans involving the mining of moons and asteroid belts for ore and other materials, the creation of lunar factories, and even the construction of solar power satellites in space. The von Neuman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replicator Equation
In mathematics, the replicator equation is a deterministic monotone non-linear and non-innovative game dynamic used in evolutionary game theory. The replicator equation differs from other equations used to model replication, such as the quasispecies equation, in that it allows the fitness function to incorporate the distribution of the population types rather than setting the fitness of a particular type constant. This important property allows the replicator equation to capture the essence of selection. Unlike the quasispecies equation, the replicator equation does not incorporate mutation and so is not able to innovate new types or pure strategies. Equation The most general continuous form of the replicator equation is given by the differential equation: : \dot = x_i f_i(x) - \phi(x) \quad \phi(x) = \sum_^ where x_i is the proportion of type i in the population, x=(x_1, \ldots, x_n) is the vector of the distribution of types in the population, f_i(x) is the fitness of type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replicator (cellular Automaton)
In cellular automata, a replicator is a pattern that produces copies of itself. In the one-dimensional Rule 90 cellular automaton, every pattern is a replicator. The same is true in the life-like cellular automaton Life-Like was a manufacturer of model trains and accessories. In 1960, the company purchased the assets of the defunct Varney Scale Models and began manufacturing model trains and accessories under the name Life-Like in 1970. In 2005 the parent co ... rule Replicator (B1357/S1357)... Highlife (B36/S23) rule has a simple replicator. On November 23, 2013, Dave Greene built the first replicator in Conway's Game of Life (B3/S23). References External linksCellular Automata: Replicators Cellular a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replicator (Stargate)
Over its decade of existence, science fiction TV series ''Stargate SG-1'' developed an extensive and detailed backdrop of diverse characters. Many of the characters are members of alien species discovered while exploring the galaxy through the Stargate, although there are an equal number of characters from offworld human civilizations. While ''Stargate SG-1'', ''Stargate Atlantis'' and ''Stargate Universe'' are separate shows, they take part in the same fictional universe, so no character is internally show-specific. Main characters Except for the commanders of the top-secret Stargate Command military base (SGC), all main characters of ''Stargate SG-1'' are members of the SG-1 team, the primary unit of the SGC in the show. SG-1's duties include first contact, reconnaissance and combat, diplomacy, initial archaeological surveying, and technological assessment. The composition of SG-1 changes several times during the series run and varies in several alternative universes. Jack O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replicator (Star Trek)
In ''Star Trek'' a replicator is a machine that can create (and recycle) things. Replicators were originally seen to simply synthesize meals on demand, but in later series much larger non-food items appear. The technical aspects of replicated versus "real" things is sometimes a plot element. Origins and limitations Although previous sci-fi writers had speculated about the development of "replicating" or "duplicating" technology, the term "replicator" was not itself used until '' Star Trek: The Next Generation''. In simple terms, it was described as a 24th century advancement from the 23rd century "food synthesizer" seen in ''Star Trek: The Original Series''. In Star Trek: The Original Series, food was created in various colored cubes. In the animated series (1974), various types of realistic-looking food could be requested, as in the episode entitled "The Practical Joker." The mechanics of these devices were never clearly explained on that show. The subsequent prequel series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |