|
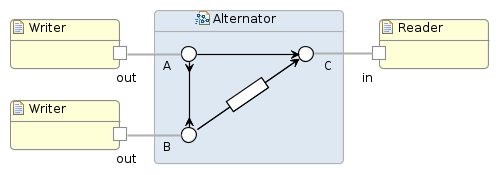
Reo Coordination Language
Reo is a domain-specific language for programming and analyzing coordination protocols that compose individual ''processes'' into full ''systems'', broadly construed. Examples of classes of systems that can be composed with Reo include component-based systems, service-oriented systems, multithreading systems, biological systems, and cryptographic protocols. Reo has a graphical syntax in which every Reo program, called a ''connector'' or ''circuit'', is a labeled directed hypergraph. Such a graph represents the data-flow among the processes in the system. Reo has formal semantics, which stand at the basis of its various formal verification techniques and compilation tools. Definitions In Reo, a concurrent system consists of a set of components which are glued together by a circuit that enables flow of data between components. Components can perform I/O operations on the ''boundary nodes'' of the circuit to which they are connected. There are two kinds of I/O operations: put-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alternator Circuit
An alternator (or synchronous generator) is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy Electrical energy is the energy transferred as electric charges move between points with different electric potential, that is, as they move across a voltage, potential difference. As electric potential is lost or gained, work is done changing the ... in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary Armature (electrical engineering), armature.Gordon R. Selmon, ''Magnetoelectric Devices'', John Wiley and Sons, 1966 no ISBN pp. 391-393 Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any alternating current, AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually, the term refers to small rotating machines driven by Car, automotive and other internal combustion engines. An alternator that uses a magnet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Automata Theory
Automata theory is the study of abstract machines and automata, as well as the computational problems that can be solved using them. It is a theory in theoretical computer science with close connections to cognitive science and mathematical logic. The word ''automata'' comes from the Greek word αὐτόματος, which means "self-acting, self-willed, self-moving". An automaton (automata in plural) is an abstract self-propelled computing device which follows a predetermined sequence of operations automatically. An automaton with a finite number of states is called a finite automaton (FA) or finite-state machine (FSM). The figure on the right illustrates a finite-state machine, which is a well-known type of automaton. This automaton consists of states (represented in the figure by circles) and transitions (represented by arrows). As the automaton sees a symbol of input, it makes a transition (or jump) to another state, according to its transition function, which takes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Models Of Computation
In computer science, and more specifically in computability theory and computational complexity theory, a model of computation is a model which describes how an output of a mathematical function is computed given an input. A model describes how units of computations, memories, and communications are organized. The computational complexity of an algorithm can be measured given a model of computation. Using a model allows studying the performance of algorithms independently of the variations that are specific to particular implementations and specific technology. Categories Models of computation can be classified into three categories: sequential models, functional models, and concurrent models. Sequential models Sequential models include: * Finite-state machines * Post machines ( Post–Turing machines and tag machines). * Pushdown automata * Register machines ** Random-access machines * Turing machines * Decision tree model * External memory model Functional models Functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |