|
Religious Stratification
Religious stratification is the division of a society into hierarchical layers on the basis of religious beliefs, affiliation, or faith practices. According to Kingsley Davis and Wilbert E. Moore, " e reason why religion is necessary is apparently to be found in the fact that human society achieves its unity primarily through the possession by its members of certain ultimate values and ends in common". Furthermore, Davis and Moore contend that it is "the role of religious belief and ritual to supply and reinforce this appearance of reality" that these "certain ultimate values" have. This is one possible explanation for why religion is one of the underlying factors which links various forms of inequality into a chain of stratification. Critical overview Broadly defined, social stratification is constituted by the division of a society into hierarchical layers of wealth, power, and prestige. These layers, or strata, have been related to a variety of social categories, such as: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Belief
Faith, derived from Latin ''fides'' and Old French ''feid'', is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or In the context of religion, one can define faith as "belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion". Religious people often think of faith as confidence based on a perceived degree of warrant, or evidence while others who are more skeptical of religion tend to think of faith as simply belief without evidence.Russell, Bertrand"Will Religious Faith Cure Our Troubles?" ''Human Society in Ethics and Politics''. Ch 7. Pt 2. Retrieved 16 August 2009. Etymology The English word ''faith'' is thought to date from 1200 to 1250, from the Middle English ''feith'', via Anglo-French ''fed'', Old French ''feid'', ''feit'' from Latin ''fidem'', accusative of ''fidēs'' (trust), akin to ''fīdere'' (to trust). Stages of faith development James W. Fowler (1940–2015) proposes a series of stages of faith-development (or spiritual development) across the human lifespan. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Amendment To The United States Constitution
The First Amendment (Amendment I) to the United States Constitution prevents the government from making laws that regulate an establishment of religion, or that prohibit the free exercise of religion, or abridge the freedom of speech, the freedom of the press, the freedom of assembly, or the right to petition the government for redress of grievances. It was adopted on December 15, 1791, as one of the ten amendments that constitute the Bill of Rights. The Bill of Rights was proposed to assuage Anti-Federalist opposition to Constitutional ratification. Initially, the First Amendment applied only to laws enacted by the Congress, and many of its provisions were interpreted more narrowly than they are today. Beginning with ''Gitlow v. New York'' (1925), the Supreme Court applied the First Amendment to states—a process known as incorporation—through the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. In '' Everson v. Board of Education'' (1947), the Court drew on Thomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majority–minority Relations
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number of individuals is therefore the 'minority'. However, in terms of sociology, economics, and politics; a demographic which takes up the smallest fraction of the population is not necessarily the 'minority'. In the academic context, 'minority' and 'majority' groups are more appropriately understood in terms of hierarchical power structures. For example, in South Africa during Apartheid, white Europeans held virtually all social, economic, and political power over black Africans. For this reason, black Africans are the 'minority group', despite the fact that they outnumber white Europeans in South Africa. This is why academics more frequently use the term 'minority group' to refer to a category of people who experience relative disadvantage as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inequality
Inequality may refer to: Economics * Attention inequality, unequal distribution of attention across users, groups of people, issues in etc. in attention economy * Economic inequality, difference in economic well-being between population groups * Spatial inequality, the unequal distribution of income and resources across geographical regions * Income inequality metrics, used to measure income and economic inequality among participants in a particular economy * International inequality, economic differences between countries Healthcare * Health equity, the study of differences in the quality of health and healthcare across different populations Mathematics * Inequality (mathematics), a relation between two values when they are different Social sciences * Educational inequality, the unequal distribution of academic resources to socially excluded communities * Gender inequality, unequal treatment or perceptions of individuals due to their gender * Participation inequality, the pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Systems
In sociology, a social system is the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. It is the formal Social structure, structure of role and status that can form in a small, stable group. An individual may belong to multiple social systems at once; examples of social systems include nuclear family units, community, communities, City, cities, nations, college campuses, corporations, and Industry (economics), industries. The organization and definition of groups within a social system depend on various shared properties such as location, socioeconomic status, race, religion, societal function, or other distinguishable features. Notable theorists The study of social systems is integral to the fields of sociology and public policy. Social systems have been studied for as long as sociology has existed. Talcott Parsons Talcott Parsons was the first to formulate a systematic theory of social systems, which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropological Categories Of Peoples
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behavior, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. A portmanteau term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological or physical anthropology studies the biological development of humans. Archaeological anthropology, often termed as 'anthropology of the past', studies human activity through investigation of physical evidence. It is considered a branch of anthropology in North America and Asia, while in Europe archaeology is viewed as a discipline in its own right or grouped under other related disciplines, such as history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''anthropology'' is first attested in reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Cornwall
Marie Cornwall (born 1949) is the editor of the ''Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion'', a professor of sociology and women's studies at Brigham Young University (BYU) and a former director of BYU's Women's Research Institute. Biography Cornwall holds a bachelor's degree in English from the University of Utah, a master's degree in sociology from BYU and a Ph.D. in sociology from the University of Minnesota. Career Besides being a member of the BYU faculty Cornwall was also a visiting professor at the University of Utah for one year. She was a researcher for the Priesthood Correlation Program, LDS Church's Correlation Department prior to joining the BYU faculty, where she studied causes/patterns of Mormons leaving church activity for other ways of living. Cornwall was one of the moving figures behind the growth of the Mormon Social Science Association. Publications Among other subjects Cornwall has written articles on women's suffrage, unemployment, gender roles in housek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
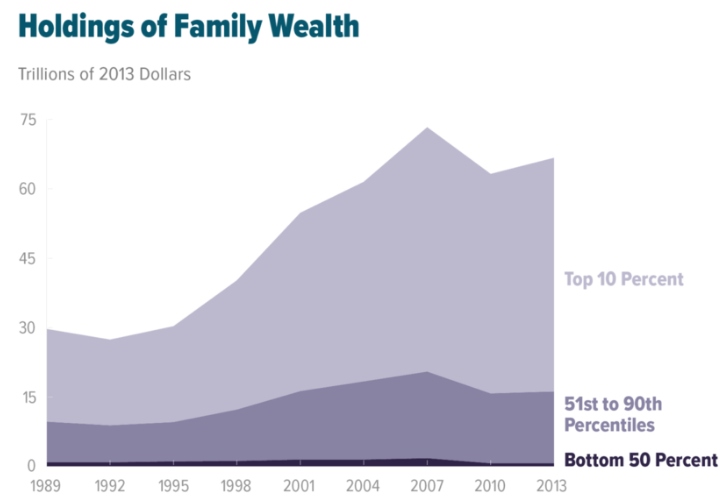
Wealth Inequality In The United States
Wealth inequality in the United States is the unequal distribution of assets among residents of the United States. Wealth commonly includes the values of any homes, automobiles, personal valuables, businesses, savings, and investments, as well as any associated debts. Although different from income inequality, the two are related. Wealth is usually not used for daily expenditures or factored into household budgets, but combined with income, it represents a family's total opportunity to secure stature and a meaningful standard of living, or to pass their class status down to their children. Moreover, wealth provides for both short- and long-term financial security, bestows social prestige, contributes to political power, and can be leveraged to obtain more wealth. Hence, wealth provides mobility and agency—the ability to act. The accumulation of wealth enables a variety of freedoms, and removes limits on life that one might otherwise face. Federal Reserve data indicates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Segregation
Religious segregation is the separation of people according to their religion. The term has been applied to cases of religious-based segregation which occurs as a social phenomenon, as well as segregation which arises from laws, whether they are explicit or implicit. The similar term religious apartheid has also been used for situations where people are separated based on their religion, including sociological phenomena. Bahrain India The debate over the ban on non-Hindus entering Hindu temples began around 30 years ago when singer Yesudas, who planned to take part in a music program, was stopped at the Guruvayur Temple gate. He finally had to sing ''bhajans'' outside the temple wall. Though several temples in Kerala have signs saying non-Hindus are barred entry, few of them enforce it as strictly as Guruvayur Temple, which insists on following its distinct traditions. 'Only Orthodox Hindus are allowed’, reads a signboard hanging from the Lion's Gate of the Sri Jagannath Temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Persecution
Religious persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or a group of individuals as a response to their religion, religious beliefs or affiliations or their irreligion, lack thereof. The tendency of societies or groups within societies to alienate or repress different subcultures is a recurrent theme in human history. Moreover, because a person's religion often determines their sense of morality, worldview, self-image, attitudes towards others, and overall personal identity to a significant extent, religious differences can be significant cultural, personal, and social factors. Religious persecution may be triggered by religious prejudice, bigotry (i.e. when members of a dominant group denigrate religions other than their own) or it may be triggered by the state when it views a particular religious group as a threat to its interests or security. At a societal level, the dehumanization of a particular religious group may readily lead to violence or other forms of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Discrimination
Religious discrimination is treating a person or group differently because of the particular beliefs which they hold about a religion. This includes instances when adherents of different religions, denominations or non-religions are treated unequally due to their particular beliefs, either by the law or in institutional settings, such as employment or housing. Religious discrimination is related to religious persecution, the most extreme forms of which would include instances in which people have been executed for beliefs which have been perceived to be heretical. Laws that only carry light punishments are described as ''mild forms of religious persecution'' or ''religious discrimination''. In recent years, the term religionism has also been used, but "religious discrimination" remains the more widely used term. Even in societies where freedom of religion is a constitutional right, adherents of minority religions sometimes voice their concerns about religious discrimination a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legacy Preferences
Legacy preference or legacy admission is a preference given by an institution or organization to certain applicants on the basis of their familial relationship to alumni of that institution. It is most controversial in college admissions, where students so admitted are referred to as ''legacies'' or ''legacy students''. The practice is particularly widespread in the college admissions in the United States; almost three-quarters of research universities and nearly all liberal arts colleges grant legacy preferences in admissions. Schools vary in how broadly they extend legacy preferences, with some schools granting this favor only to children of undergraduate alumni, while other schools extend the favor to children, grandchildren, siblings, nephews, and nieces of alumni of undergraduate and graduate programs. A 2005 analysis of 180,000 student records obtained from nineteen selective colleges and universities found that, within a set range of SAT scores, being a legacy raised an appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)