|
Religious Scepticism
Religious skepticism is a type of skepticism relating to religion. Religious skeptics question religious authority and are not necessarily anti-religious but skeptical of specific or all religious beliefs and/or practices. Socrates was one of the most prominent and first religious skeptics of whom there are records; he questioned the legitimacy of the beliefs of his time in the existence of the Greek gods. Religious skepticism is not the same as atheism or agnosticism, and some religious skeptics are deists (or theists who reject the prevailing organized religion they encounter, or even all organized religion). Overview The word skeptic (sometimes ''sceptic'') is derived from the middle French ''sceptique'' or the Latin ''scepticus'', literally "sect of the sceptics". Its origin is in the Greek word ''skeptikos'', meaning inquiring, which was used to refer to members of the Hellenistic philosophical school of Pyrrhonism, which doubted the possibility of knowledge. As suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skepticism
Skepticism, also spelled scepticism, is a questioning attitude or doubt toward knowledge claims that are seen as mere belief or dogma. For example, if a person is skeptical about claims made by their government about an ongoing war then the person doubts that these claims are accurate. In such cases, skeptics normally recommend not disbelief but suspension of belief, i.e. maintaining a neutral attitude that neither affirms nor denies the claim. This attitude is often motivated by the impression that the available evidence is insufficient to support the claim. Formally, skepticism is a topic of interest in philosophy, particularly epistemology. More informally, skepticism as an expression of questioning or doubt can be applied to any topic, such as politics, religion, or pseudoscience. It is often applied within restricted domains, such as morality ( moral skepticism), atheism (skepticism about the existence of God), or the supernatural. Some theorists distinguish "good" or moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Shermer
Michael Brant Shermer (born September 8, 1954) is an American science writer, historian of science, executive director of The Skeptics Society, and founding publisher of ''Skeptic'' magazine, a publication focused on investigating pseudoscientific and supernatural claims. The author of over a dozen books, Shermer is known for engaging in debates on pseudoscience and religion in which he emphasizes scientific skepticism. Shermer was the co-producer and co-host of ''Exploring the Unknown'', a 13-hour Fox Family television series broadcast in 1999. From April 2001 to January 2019, he contributed a monthly ''Skeptic'' column to ''Scientific American'' magazine. Shermer was raised in a non-religious household, before converting to christian fundamentalism as a teenager. He stopped believing in God during graduate school, influenced by a traumatic accident that left his then-girlfriend paralyzed. He identifies as an agnostic and an atheist,Shermer, Michael (June 2005)"Why I Am An Ath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogma
Dogma is a belief or set of beliefs that is accepted by the members of a group without being questioned or doubted. It may be in the form of an official system of principles or doctrines of a religion, such as Roman Catholicism, Judaism, Islam or Protestantism, as well as the Philosophical theory, positions of a philosopher or of a Philosophical movement, philosophical school such as positivism, postmodernism, egalitarianism, and dark enlightenment. It may also be found in political belief-systems, such as Marxism, communism, capitalism, progressivism, liberalism, conservatism, and fascism. In the pejorative sense, dogma refers to enforced decisions, such as those of aggressive political interests or authorities. More generally, it is applied to some strong belief which its adherents are not willing to discuss rationally. This attitude is named as a dogmatic one, or as dogmatism; and is often used to refer to matters related to religion, but is not limited to theistic attitudes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning on the European continent. Along with his teacher, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Ancient Greek philosophy and the Western and Middle Eastern philosophies descended from it. He has also shaped religion and spirituality. The so-called neoplatonism of his interpreter Plotinus greatly influenced both Christianity (through Church Fathers such as Augustine) and Islamic philosophy (through e.g. Al-Farabi). In modern times, Friedrich Nietzsche diagnosed Western culture as growing in the shadow of Plato (famously calling Christianity "Platonism for the masses"), while Alfred North Whitehead famously said: "the safest general characterization of the European philosophical tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Will Durant
William James Durant (; November 5, 1885 – November 7, 1981) was an American writer, historian, and philosopher. He became best known for his work '' The Story of Civilization'', which contains 11 volumes and details the history of eastern and western civilizations. It was written in collaboration with his wife, Ariel Durant, and published between 1935 and 1975. He was earlier noted for '' The Story of Philosophy'' (1926), described as "a groundbreaking work that helped to popularize philosophy". ''The details of this book appear to be wrong – see talk page'' Durant conceived of philosophy as total perspective or seeing things ''sub specie totius'' (i.e., "from the perspective of the whole")—a phrase inspired by Spinoza's '' sub specie aeternitatis'', roughly meaning "from the perspective of the eternal". He sought to unify and humanize the great body of historical knowledge, which had grown voluminous and become fragmented into esoteric specialties, and to vitalize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apology (Plato)
The ''Apology of Socrates'' ( grc-gre, Ἀπολογία Σωκράτους, ''Apología Sokrátous''; la, Apologia Socratis), written by Plato, is a Socratic dialogue of the speech of legal self-defence which Socrates (469–399 BC) spoke at his trial for impiety and corruption in 399 BC. Specifically, the ''Apology of Socrates'' is a defence against the charges of "corrupting the youth" and "not believing in the gods in whom the city believes, but in other '' daimonia'' that are novel" to Athens (24b). Among the primary sources about the trial and death of the philosopher Socrates, the ''Apology of Socrates'' is the dialogue that depicts the trial, and is one of four Socratic dialogues, along with ''Euthyphro'', ''Phaedo'', and ''Crito'', through which Plato details the final days of the philosopher Socrates. The text of apology The ''Apology of Socrates'', by the philosopher Plato (429–347 BC), was one of many explanatory ''apologia'' about Socrates's legal defense ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
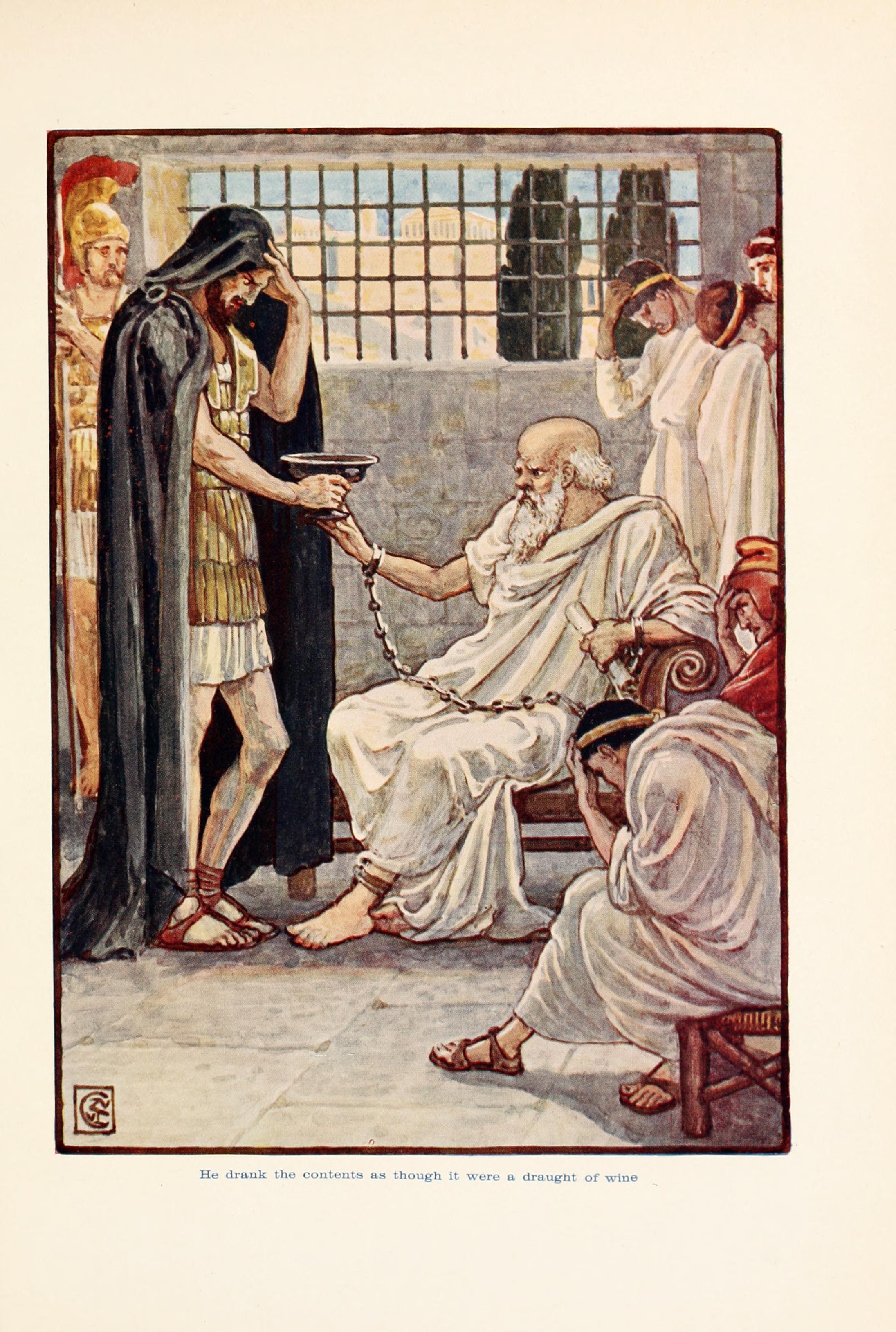
Trial Of Socrates
The trial of Socrates (399 BC) was held to determine the philosopher's guilt of two charges: ''asebeia'' (impiety) against the pantheon of Athens, and corruption of the youth of the city-state; the accusers cited two impious acts by Socrates: "failing to acknowledge the gods that the city acknowledges" and "introducing new deities". The death sentence of Socrates was the legal consequence of asking politico-philosophic questions of his students, which resulted in the two accusations of moral corruption and impiety. At trial, the majority of the ''dikasts'' (male-citizen jurors chosen by lot) voted to convict him of the two charges; then, consistent with common legal practice voted to determine his punishment and agreed to a sentence of death to be executed by Socrates's drinking a poisonous beverage of hemlock. Primary-source accounts of the trial and execution of Socrates are the '' Apology of Socrates'' by Plato and the '' Apology of Socrates to the Jury'' by Xenophon of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropomorphize
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology. Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics to abstract concepts such as nations, emotions, and natural forces, such as seasons and weather. Both have ancient roots as storytelling and artistic devices, and most cultures have traditional fables with anthropomorphized animals as characters. People have also routinely attributed human emotions and behavioral traits to wild as well as domesticated animals. Etymology Anthropomorphism and anthropomorphization derive from the verb form ''anthropomorphize'', itself derived from the Greek ''ánthrōpos'' (, "human") and ''morphē'' (, "form"). It is first attested in 1753, originally in reference to the heresy of applying a human form to the Christian God.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "anthropomorphism, ''n.''" Oxford University P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophanes
Xenophanes of Colophon (; grc, Ξενοφάνης ὁ Κολοφώνιος ; c. 570 – c. 478 BC) was a Greek philosopher A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ..., theologian, poet, and critic of Homer from Ionia who travelled throughout the Greek-speaking world in early Classical Antiquity. As a poet, Xenophanes was known for his critical style, writing poems that are considered among the first satires. He also composed elegiac couplets that criticised his society's traditional values of wealth, excesses, and athletic victories. He also criticised Homer and the other poets in his works for representing the gods as foolish or morally weak. His poems have not survived intact; only fragments of some of his work survives in quotations by later philosophers and literary c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings since the ancient world, the term "supernatural" emerged in the Middle Ages and did not exist in the ancient world. The supernatural is featured in folklore and religious contexts, but can also feature as an explanation in more secular contexts, as in the cases of superstitions or belief in the paranormal. The term is attributed to non-physical entities, such as angels, demons, gods, and spirits. It also includes claimed abilities embodied in or provided by such beings, including magic, telekinesis, levitation, precognition, and extrasensory perception. The philosophy of naturalism contends that nothing exists beyond the natural world, and as such approaches supernatural claims with skepticism. Etymology and history of the concept Occurr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as sacred scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of Christian texts originally written in the Koine Greek language, at different times by various authors. While the Old Testament canon varies somewhat between different Christian denominations, the 27-book canon of the New Testament has been almost universally recognized within Christianity since at least Late Antiquity. Thus, in almost all Christian traditions today, the New Testament consists of 27 books: * 4 canonical gospels (Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John) * The Acts of the Apostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Life And Morals Of Jesus Of Nazareth
''The Life and Morals of Jesus of Nazareth'', commonly referred to as the ''Jefferson Bible'', is one of two religious works constructed by Thomas Jefferson. Jefferson compiled the manuscripts but never published them. The first, ''The Philosophy of Jesus of Nazareth'', was completed in 1804, but no copies exist today. The second, ''The Life and Morals of Jesus of Nazareth'', was completed in 1820 by cutting and pasting with a razor and glue numerous sections from the New Testament as extractions of the doctrine of Jesus. Jefferson's condensed composition excludes all miracles by Jesus and most mentions of the supernatural, including sections of the four gospels that contain the Resurrection and most other miracles, and passages that portray Jesus as divine. Early draft In an 1803 letter to Joseph Priestley, Jefferson stated that he conceived the idea of writing his view of the "Christian System" in a conversation with Benjamin Rush during 1798–99. He proposes beginning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |