|
Reid Vapor Pressure
Reid vapor pressure (RVP) is a common measure of the volatility of gasoline and other petroleum products. It is defined as the absolute vapor pressure exerted by the vapor of the liquid and any dissolved gases/moisture at 37.8 °C (100 °F) as determined by the test method ASTM-D-323, which was first developed in 1930 and has been revised several times (the latest version is ASTM D323-15a). The test method measures the vapor pressure of gasoline, volatile crude oil, jet fuels, naphtha, and other volatile petroleum products but is not applicable for liquefied petroleum gases. ASTM D323-15a requires that the sample be chilled to 0 to 1 degrees Celsius and then poured into the apparatus; for any material that solidifies at this temperature, this step cannot be performed. RVP is commonly reported in kilopascals (kPa) or pounds per square inch (psi) and represents volatization at atmospheric pressure because ASTM-D-323 measures the gauge pressure of the sample in a non-evac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. On average, U.S. refineries produce, from a barrel of crude oil, about 19 to 20 gallons of gasoline; 11 to 13 gallons of distillate fuel (most of which is sold as diesel fuel); and 3 to 4 gallons of jet fuel. The product ratio depends on the processing in an oil refinery and the crude oil assay. A barrel of oil is defined as holding 42 US gallons, which is about 159 liters or 35 imperial gallons. The characteristic of a particular gasoline blend to resist igniting too early (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating, which is produced in several grades. Tetraethyl lead and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
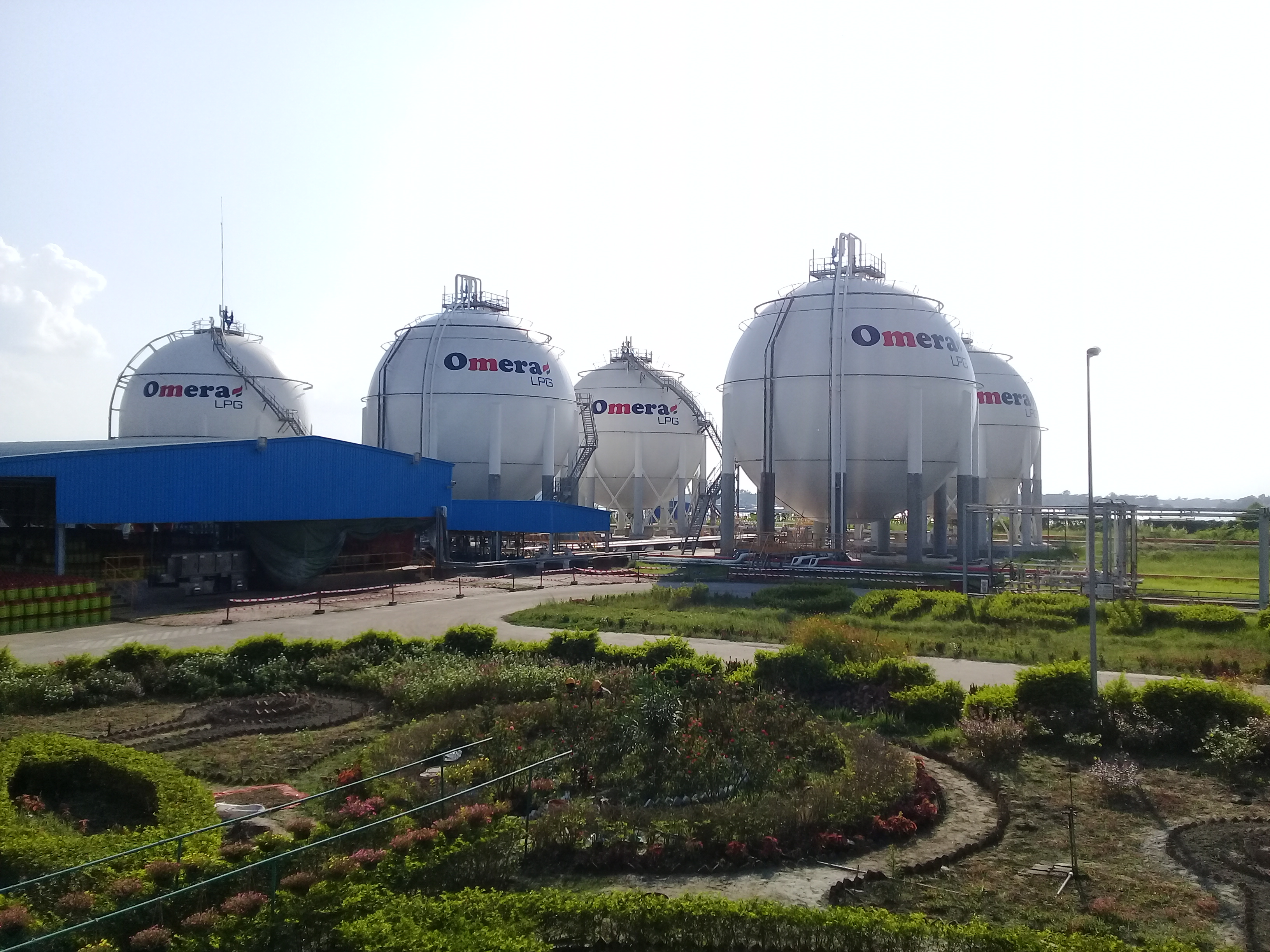
Liquefied Petroleum Gas
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas) is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, propylene, butylene, isobutane and n-butane. LPG is used as a fuel gas in heating appliances, cooking equipment, and vehicles. It is increasingly used as an aerosol propellant and a refrigerant, replacing chlorofluorocarbons in an effort to reduce damage to the ozone layer. When specifically used as a vehicle fuel, it is often referred to as autogas or even just as gas. Varieties of LPG that are bought and sold include mixes that are mostly propane (), mostly butane (), and, most commonly, mixes including both propane and butane. In the northern hemisphere winter, the mixes contain more propane, while in summer, they contain more butane. In the United States, mainly two grades of LPG are sold: commercial propane and HD-5. These specifications are published by the Gas Processors Association (GPA) and the American Society of Testing and Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilopascal
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI), and is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is defined as one newton per square metre and is equivalent to 10 barye (Ba) in the CGS system. The unit of measurement called standard atmosphere (atm) is defined as 101,325 Pa. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Canada these reports are given in kilopascals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pounds Per Square Inch
The pound per square inch or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch (symbol: lbf/in2; abbreviation: psi) is a unit of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units. It is the pressure resulting from a force of one pound-force applied to an area of one square inch. In SI units, 1 psi is approximately equal to 6895 Pa. Pounds per square inch absolute (psia) is used to make it clear that the pressure is relative to a vacuum rather than the ambient atmospheric pressure. Since atmospheric pressure at sea level is around , this will be added to any pressure reading made in air at sea level. The converse is pounds per square inch gauge (psig), indicating that the pressure is relative to atmospheric pressure. For example, a bicycle tire pumped up to 65 psig in a local atmospheric pressure at sea level (14.7 psi) will have a pressure of 79.7 psia (14.7 psi + 65 psi). When gauge pressure is referenced to something other than ambient atmospheric pressure, then the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor Lock
Vapor lock is a problem caused by liquid fuel changing state to gas while still in the fuel delivery system of gasoline-fueled internal combustion engines. This disrupts the operation of the fuel pump, causing loss of feed pressure to the carburetor or fuel injection system, resulting in transient loss of power or complete stalling. Restarting the engine from this state may be difficult. The fuel can vaporize due to being heated by the engine, by the local climate or due to a lower boiling point at high altitude. In regions where fuels with lower viscosity (and lower boiling threshold) are used during the winter to improve engine startup, continued use of the specialized fuels during the summer can cause vapor lock to occur more readily. Causes and incidence Vapor lock was far more common in older gasoline-fuel systems incorporating a low-pressure mechanical fuel pump driven by the engine, located in the engine compartment and feeding a carburetor. Such pumps were typically locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
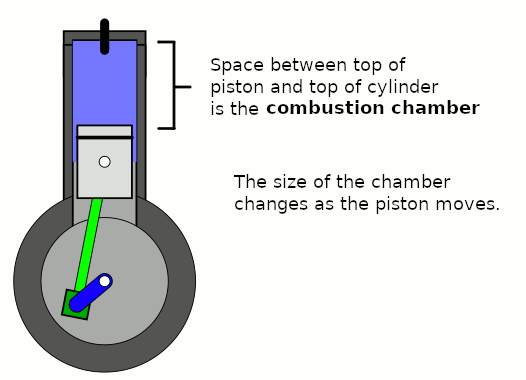
Combustion Chambers
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such that the bottom of combustion chamber is roughly in li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefied petroleum gas and petroleum naphtha. Petrochemicals feedstock like ethylene and propylene can also be produced directly by cracking crude oil without the need of using refined products of crude oil such as naphtha. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products. In 2020, the total capacity of global refineries for crude oil was about 101.2 million barrels per day. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units, such as distillation columns. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Vapor Pressure
True vapor pressure (TVP) is a common measure of the volatility of petroleum distillate fuels. It is defined as the equilibrium partial pressure exerted by a volatile organic liquid as a function of temperature as determined by the test method ASTM D 2879. The true vapor pressure (TVP) at 100 °F differs slightly from the Reid vapor pressure Reid vapor pressure (RVP) is a common measure of the volatility of gasoline and other petroleum products. It is defined as the absolute vapor pressure exerted by the vapor of the liquid and any dissolved gases/moisture at 37.8 °C (100 ... (RVP) (per definition also at 100 °F), as it excludes dissolved fixed gases such as air. Conversions between the two can be found iAP 42, Fifth Edition, Volume I Chapter 7: Liquid Storage Tanks(p 7.1-54 and onwards) References External links * ttp://www.epa.gov/ttn/chief/ap42/ch07/final/c07s01.pdf USA's Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) publication ''AP-42, Compilation of Air Pollutant E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crude Oil Assay
A crude oil assay is the chemical evaluation of crude oil feedstocks by petroleum testing laboratories. Each crude oil type has unique molecular and chemical characteristics. No two crude oil types are identical and there are crucial differences in crude oil quality. The results of crude oil assay testing provide extensive detailed hydrocarbon analysis data for refiners, oil traders and producers. Assay data help refineries determine if a crude oil feedstock is compatible for a particular petroleum refinery or if the crude oil could cause yield, quality, production, environmental and other problems. The assay can be an inspection assay or comprehensive assay. Testing can include crude oil characterization of whole crude oils and the various boiling range fractions produced from physical or simulated distillation by various procedures. Information obtained from the petroleum assay is used for detailed refinery engineering and client marketing purposes. Feedstock assay data are an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in English-speaking countries other than the US; see spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid's evaporation rate. It relates to the tendency of particles to escape from the liquid (or a solid). A substance with a high vapor pressure at normal temperatures is often referred to as '' volatile''. The pressure exhibited by vapor present above a liquid surface is known as vapor pressure. As the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules also increases. As the kinetic energy of the molecules increases, the number of molecules transitioning into a vapor also increases, thereby increasing the vapor pressure. The vapor pressure of any substance increases non-linearly with temperature according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congressional Research Service
The Congressional Research Service (CRS) is a public policy research institute of the United States Congress. Operating within the Library of Congress, it works primarily and directly for members of Congress and their committees and staff on a confidential, nonpartisan basis. CRS is sometimes known as Congress' think tank due to its broad mandate of providing research and analysis on all matters relevant to national policymaking. CRS has roughly 600 employees reflecting a wide variety of expertise and disciplines, including lawyers, economists, reference librarians, and scientists. In the 2016 fiscal year, it was appropriated a budget of roughly $106.9 million by Congress. CRS was founded during the height of the Progressive Era as part of a broader effort to professionalize the government by providing independent research and information to public officials. Its work was initially made available to the public, but between 1952 and 2018 was restricted only to members of Congr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Properties
A chemical property is any of a material's properties that becomes evident during, or after, a chemical reaction; that is, any quality that can be established only by changing a substance's chemical identity.William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley, "Chemistry: Principles and Reactions", 6th edition. Brooks/Cole Cengage Learning, 2009, p.1(Google books)/ref> Simply speaking, chemical properties cannot be determined just by viewing or touching the substance; the substance's internal structure must be affected greatly for its chemical properties to be investigated. When a substance goes under a chemical reaction, the properties will change drastically, resulting in chemical change. However, a catalytic property would also be a chemical property. Chemical properties can be contrasted with physical properties, which can be discerned without changing the substance's structure. However, for many properties within the scope of physical chemistry, and other disciplines at the boundary betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |