|
Refuge Emílio Goeldi
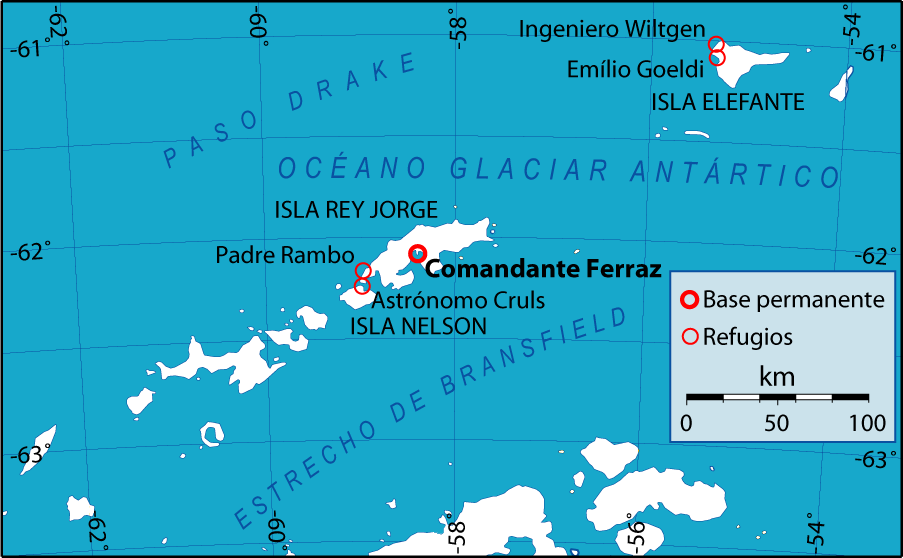
Refuge Emílio Goeldi ( pt, Refúgio Emílio Goeldi) is a Brazilian Antarctic summer facility named after the Swiss-Brazilian naturalist and zoologist Émil Goeldi. Built in 1988, the structure is located on Elephant Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The structure can accommodate up to 6 scientists for up to 40 days, and depends both logistically and administratively on Comandante Ferraz Brazilian Antarctic Base, Comandante Ferraz station. It and Refuge Astronomer Cruls, located on Nelson Island (South Shetland Islands), Nelson Island, constitute the basic infrastructure to support the Brazilian Antarctic Program in Antarctica. See also * Research stations in Antarctica#List of research stations, List of Antarctic research stations * Antarctic field camps, List of Antarctic field camps *Refuge Astronomer Cruls *Brazilian Antarctic Program References Brazilian Antarctica Outposts of the South Shetland Islands Outposts of Antarctica 1988 establishments i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Stations In Antarctica
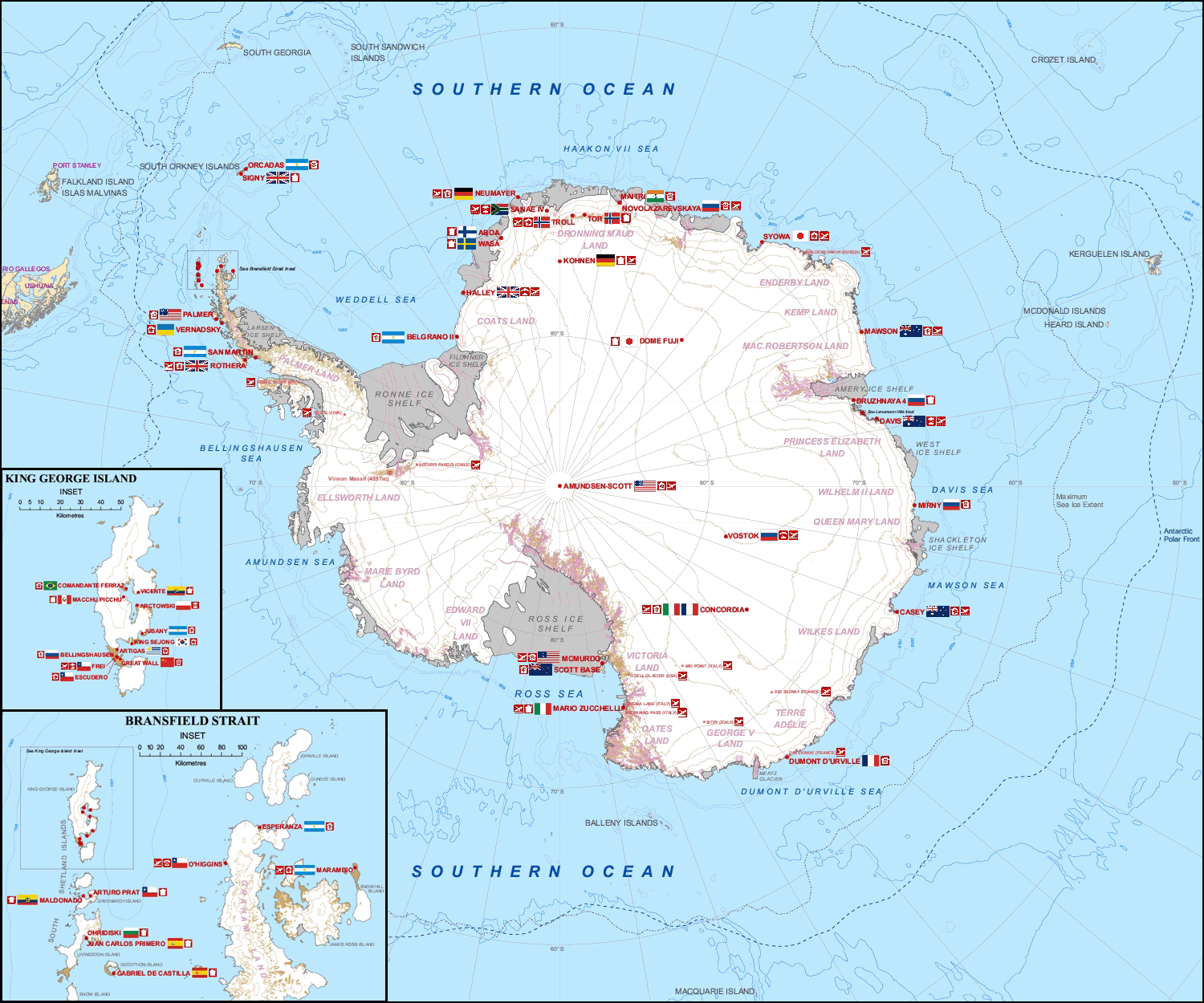
Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rock or on ice that is (for practical purposes) fixed in place. Many of the stations are demographics of Antarctica, staffed throughout the year. A total of 42 countries (as of October 2006), all signatories to the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, operate seasonal (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent. The population of people performing and supporting scientific research on the continent and nearby islands varies from approximately 4,000 during the summer season to 1,000 during winter (June). In addition to these permanent stations, approximately Antarctic field camps, 30 field camps are established each summer to support specific projects. History First bases During the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant Island
Elephant Island is an ice-covered, mountainous island off the coast of Antarctica in the outer reaches of the South Shetland Islands, in the Southern Ocean. The island is situated north-northeast of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, west-southwest of South Georgia, south of the Falkland Islands, and southeast of Cape Horn. It is within the Antarctic claims of Argentina, Chile and the United Kingdom. The Brazilian Antarctic Program maintains a shelter on the island, Goeldi, supporting the work of up to six researchers each during the summer, and formerly had another ( Wiltgen), which was dismantled in the summers of 1997 and 1998. Toponym Elephant Island's name is attributed to both its elephant head-like appearance and the sighting of elephant seals by Captain George Powell in 1821, one of the earliest sightings. However, in Russia it is still known under the name given by its discoverers in 1821 – Mordvinova Island. Geography The island is oriented approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes. The islands have been claimed by the United Kingdom since 1908 and as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962. They are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province) and Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries maintain research stations on the islands. Most of them are situated on King George Island, benefitting from the airfield of the Chilean base Eduardo Frei. There are sixteen research stations in different parts of the islands, with Chilean stations being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazilian Antarctic Program
The Brazilian Antarctic Program ( pt, Programa Antártico Brasileiro; PROANTAR) is a program of the Brazilian Navy which has presence in the continent of Antarctica. It coordinates research and the operational support for research in the region. It currently maintains a year-round research station in Antarctica (Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station), as well as several seasonal field camps. It also maintains two research vessels that sail in the Antarctic waters (the icebreakers '' Almirante Maximiano'' and '' Ary Rongel''). History The program was officially created in January 1982, when the Brazilian Navy acquired the Danish icebreaker ''Thala Dan,'' later renamed '' Barão de Teffé''. That same year, Brazil sent its first expedition ("Operation Antarctica I") to the Antarctic continent and the ''Barão de Teffé'' performed a reconnaissance mission to the northwestern sector of Antarctica in order to select the location where the future Brazilian Antarctic Station would be buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time In Brazil
Time in Brazil is calculated using standard time, and the country (including its offshore islands) is divided into four standard time zones: UTC−02:00, UTC−03:00, UTC−04:00 and UTC−05:00. Time zones Fernando de Noronha time (UTC−02:00) This is the standard time zone only on a few small offshore Atlantic islands. The only such island with a permanent population is Fernando de Noronha, with 3,140 inhabitants (2021 estimate), 0.0015% of Brazil's population.Population estimates Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, 2021. The other islands ( |
Zoologist
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the Animal, animal kingdom, including the anatomy, structure, embryology, evolution, Biological classification, classification, Ethology, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinction, extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study'). Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and made use of this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. The Greek physician Galen studied human anatomy and was one of the greatest surgeons of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émil Goeldi
Émil August Goeldi (var. Göldi, Portuguese language, Portuguese var. Emílio Augusto Goeldi) (28 August 1859 – 5 July 1917 in Bern), was a Swiss-Brazilian natural history, naturalist and zoologist. He was the father of Oswaldo Goeldi, a noted Brazilian engraver and illustrator. Biography Goeldi studied zoology in Jena, Germany with Ernst Haeckel, and in 1884 he was invited by Ladislau de Souza Mello Netto, the influential director of the Brazilian Museu Imperial e Nacional, to work at that institution. Goeldi arrived in Rio de Janeiro in 1885 to work in the National Museum (now the Museu Nacional (Brazil), Museu Nacional do Rio de Janeiro. In May 1890, he was fired, due to political circumstances related to the proclamation of the republic and the exile of his principal benefactor, Emperor Pedro II of Brazil, D. Pedro II. He was then invited by the governor of the state of Pará, Lauro Sodré, to reorganize the Pará Museum of Natural History and Ethnography, in Belém, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comandante Ferraz Brazilian Antarctic Base
The Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station ( pt, Estação Antártica Comandante Ferraz) is a permanent Antarctic research station named after the Brazilian Navy Commander Luís Antônio de Carvalho Ferraz (1940-1982), who visited Antarctica many times with the British exploration team and managed to convince his government to create a self-guided Brazilian Antarctic Program. Located in Admiralty Bay ( pt, Baía do Almirantado), King George Island ( pt, Ilha do Rei George), near the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, 130 km north of the peninsula, the station began operating on 6 February 1984, brought to Antarctica in modules by the oceanographic ship ''Barão de Teffé'' and several other Brazilian naval ships. It now houses about 64 people, including researchers, technicians and staff, military and civilians. History The station was named after Navy Commander Luís Antônio de Carvalho Ferraz, a hydrographer and oceanographer who visited Antarctica twice on British vessel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refuge Astronomer Cruls
Refuge Astronomer Cruls ( pt, Refúgio Astrônomo Cruls) is a Brazilian Antarctic summer facility named after astronomer Luis Cruls who set up an expedition in 1882 to Punta Arenas in order to observe the passage of Venus across the disk of the Sun. The structure, established on 25 January 1985, is situated on Nelson Island (South Shetland Islands), southwest of King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The refuge, which can accommodate up to 6 scientists for up to 40 days, depends both logistically and administratively on Comandante Ferraz station. Together with Refuge Emílio Goeldi Refuge Emílio Goeldi ( pt, Refúgio Emílio Goeldi) is a Brazilian Antarctic summer facility named after the Swiss-Brazilian naturalist and zoologist Émil Goeldi. Built in 1988, the structure is located on Elephant Island, South Shetland I ..., located on Elephant Island, constitute the basic infra-structure to support the Brazilian Antarctic Program in Antarctica. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Island (South Shetland Islands)
Nelson Island (historical names ''Leipzig Island'', ''O'Cain's Island'' and ''Strachans Island'') is an island long and wide, lying southwest of King George Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The name Nelson Island dates back to at least 1821 and is now established in international usage. Eco-Nelson Station The private research station Eco-Nelson is located on Nelson Island, which is one of the South Shetland Islands. The station was founded in 1988 by the Czech polar explorer Jaroslav Pavlíček. Eco-Nelson Station hosts international researchers and therefore it is not considered a Czech station. See also * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * List of Antarctic research stations * List of Antarctic field camps * SCAR * Edgell Bay * Spiro Hill * Territorial claims in Antarctica Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)