|
Refraction Microtremor
Refraction microtremor (ReMi) is a surface-performed geophysical survey developed by Dr. John Louie (and others) based on previously existing principles of evaluating surface waves and in particular Rayleigh waves. The refraction microtremor technology was developed at the University of Nevada and is owned by the State of Nevada. Optim of Reno, Nevada has the exclusive license to develop the technology, and SeisOpt® ReMi™ has been available commercially from Optim since 2004. Since Rayleigh waves are dispersive, the propagating waves are measured along a linear seismic array and evaluated relative to wave frequency and slowness (or the inverse of the velocity). Due to the dispersive characteristics of higher frequency waves travelling through the more shallow conditions and lower frequency waves passing through deeper materials, a 1-D subsurface profile can be generated based on the velocity with depth. Equipment and Field Procedures The method utilizes equipment typically empl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical Survey
Geophysical survey is the systematic collection of geophysical data for spatial studies. Detection and analysis of the geophysical signals forms the core of Geophysical signal processing. The magnetic and gravitational fields emanating from the Earth's interior hold essential information concerning seismic activities and the internal structure. Hence, detection and analysis of the electric and Magnetic fields is very crucial. As the Electromagnetic and gravitational waves are multi-dimensional signals, all the 1-D transformation techniques can be extended for the analysis of these signals as well. Hence this article also discusses multi-dimensional signal processing techniques. Geophysical surveys may use a great variety of sensing instruments, and data may be collected from above or below the Earth's surface or from aerial, orbital, or marine platforms. Geophysical surveys have many applications in geology, archaeology, mineral and energy exploration, oceanography, and engineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Waves
In physics, a surface wave is a mechanical wave that propagates along the interface between differing media. A common example is gravity waves along the surface of liquids, such as ocean waves. Gravity waves can also occur within liquids, at the interface between two fluids with different densities. Elastic surface waves can travel along the surface of solids, such as '' Rayleigh'' or ''Love'' waves. Electromagnetic waves can also propagate as "surface waves" in that they can be guided along with a refractive index gradient or along an interface between two media having different dielectric constants. In radio transmission, a ''ground wave'' is a guided wave that propagates close to the surface of the Earth. Mechanical waves In seismology, several types of surface waves are encountered. Surface waves, in this mechanical sense, are commonly known as either ''Love waves'' (L waves) or ''Rayleigh waves''. A seismic wave is a wave that ''travels through the Earth, often as the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
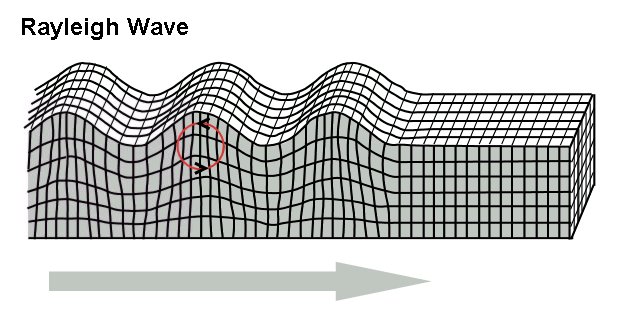
Rayleigh Waves
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by piezo-electric transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructive testing for detecting defects. Rayleigh waves are part of the seismic waves that are produced on the Earth by earthquakes. When guided in layers they are referred to as Lamb waves, Rayleigh–Lamb waves, or generalized Rayleigh waves. Characteristics Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids. Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. There is a phase difference between these component motions. The existence of Rayleigh waves was predicted in 1885 by Lord Rayleigh, after whom they were named. In isotropic solids these waves cause the surface particles to move in ellipses in planes normal to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity Dispersion
In astronomy, the velocity dispersion (''σ'') is the statistical dispersion of velocities about the mean velocity for a group of astronomical objects, such as an open cluster, globular cluster, galaxy, galaxy cluster, or supercluster. By measuring the radial velocities of the group's members through astronomical spectroscopy, the velocity dispersion of that group can be estimated and used to derive the group's mass from the virial theorem.Collins Dictionary of Astronomy, 2nd Ed.; Harper Collins Publishers; 2000; pp. 444, 449 Radial velocity is found by measuring the Doppler width of spectral lines of a collection of objects; the more radial velocities one measures, the more accurately one knows their dispersion. A ''central velocity dispersion'' refers to the σ of the interior regions of an extended object, such as a galaxy or cluster. The relationship between velocity dispersion and matter (or the observed electromagnetic radiation emitted by this matter) takes several forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Refraction
Seismic refraction is a geophysical principle governed by Snell's Law of refraction. The seismic refraction method utilizes the refraction of seismic waves by rock or soil layers to characterize the subsurface geologic conditions and geologic structure. Seismic refraction is exploited in engineering geology, geotechnical engineering and exploration geophysics. Seismic refraction traverses ( seismic lines) are performed using an array of seismographs or geophones and an energy source. The methods depend on the fact that seismic waves have differing velocities in different types of soil or rock. The waves are refracted when they cross the boundary between different types (or conditions) of soil or rock. The methods enable the general soil types and the approximate depth to strata boundaries, or to bedrock, to be determined. P-wave refraction P-wave refraction evaluates the compression wave generated by the seismic source located at a known distance from the array. The wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophone
A geophone is a device that converts ground movement (velocity) into voltage, which may be recorded at a recording station. The deviation of this measured voltage from the base line is called the seismic response and is analyzed for structure of the earth. Etymology The term geophone derives from the Greek word "γῆ (ge) " meaning "earth" and "phone" meaning "sound". Construction Geophones have historically been passive analog devices and typically comprise a spring-mounted wire coil moving within the field of a case-mounted permanent magnet to generate an electrical signal. Recent designs have been based on microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology which generates an electrical response to ground motion through an active feedback circuit to maintain the position of a small piece of silicon. The response of a coil/magnet geophone is proportional to ground velocity, while MEMS devices usually respond proportional to acceleration. MEMS have a much higher noise level (50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |