|
Reference Frame (video)
''Reference frames'' are frames of a compressed video that are used to define future frames. As such, they are only used in inter-frame compression techniques. In older video encoding standards, such as MPEG-2, only one reference frame – the previous frame – was used for P-frames. Two reference frames (one past and one future) were used for B-frames. Multiple reference frames Some modern video encoding standards, such as H.264/AVC, allow the use of multiple reference frames. This allows the video encoder to choose among more than one previously decoded frame on which to base each macroblock in the next frame. While the best frame for this purpose is usually the previous frame, the extra reference frames can improve compression efficiency and/or video quality. Note that different reference frames can be chosen for different macroblocks in the same frame. The maximum number of concurrent reference frames supported by H.264 is 16. Different reference frames can be chosen for ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Frame
In filmmaking, video production, animation, and related fields, a frame is one of the many ''still images'' which compose the complete ''moving picture''. The term is derived from the historical development of film stock, in which the sequentially recorded single images look like a framed picture when examined individually. The term may also be used more generally as a noun or verb to refer to the edges of the image as seen in a camera viewfinder or projected on a screen. Thus, the camera operator can be said to keep a car in frame by panning with it as it speeds past. Overview When the moving picture is displayed, each frame is flashed on a screen for a short time (nowadays, usually 1/24, 1/25 or 1/30 of a second) and then immediately replaced by the next one. Persistence of vision blends the frames together, producing the illusion of a moving image. The frame is also sometimes used as a unit of time, so that a momentary event might be said to last six frames, the actual dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I-frame
In the field of video compression a video frame is compressed using different algorithms with different advantages and disadvantages, centered mainly around amount of data compression. These different algorithms for video frames are called picture types or frame types. The three major picture types used in the different video algorithms are I, P and B. They are different in the following characteristics: * I‑frames are the least compressible but don't require other video frames to decode. * P‑frames can use data from previous frames to decompress and are more compressible than I‑frames. * B‑frames can use both previous and forward frames for data reference to get the highest amount of data compression. Summary Three types of ''pictures'' (or frames) are used in video compression: I, P, and B frames. An I‑frame ( Intra-coded picture) is a complete image, like a JPG or BMP image file. A P‑frame (Predicted picture) holds only the changes in the image from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding; encoding done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a signal. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter Frame
An inter frame is a frame in a video compression stream which is expressed in terms of one or more neighboring frames. The "inter" part of the term refers to the use of ''Inter frame prediction''. This kind of prediction tries to take advantage from temporal redundancy between neighboring frames enabling higher compression rates. Inter frame prediction An inter coded frame is divided into blocks known as macroblocks. After that, instead of directly encoding the raw pixel values for each block, the encoder will try to find a block similar to the one it is encoding on a previously encoded frame, referred to as a reference frame. This process is done by a block matching algorithm. If the encoder succeeds on its search, the block could be encoded by a vector, known as motion vector, which points to the position of the matching block at the reference frame. The process of motion vector determination is called motion estimation. In most cases the encoder will succeed, but the block fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locality Of Reference
In computer science, locality of reference, also known as the principle of locality, is the tendency of a processor to access the same set of memory locations repetitively over a short period of time. There are two basic types of reference locality temporal and spatial locality. Temporal locality refers to the reuse of specific data and/or resources within a relatively small time duration. Spatial locality (also termed ''data locality''"NIST Big Data Interoperability Framework: Volume 1"urn:doi:10.6028/NIST.SP.1500-1r2) refers to the use of data elements within relatively close storage locations. Sequential locality, a special case of spatial locality, occurs when data elements are arranged and accessed linearly, such as traversing the elements in a one-dimensional Array data structure, array. Locality is a type of predictability, predictable behavior that occurs in computer systems. Systems that exhibit strong ''locality of reference'' are great candidates for performance optimiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animation
Animation is a method by which image, still figures are manipulated to appear as Motion picture, moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent cel, celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Today, most animations are made with computer-generated imagery (CGI). Computer animation can be very detailed Computer animation#Animation methods, 3D animation, while Traditional animation#Computers and traditional animation, 2D computer animation (which may have the look of traditional animation) can be used for stylistic reasons, low bandwidth, or faster real-time renderings. Other common animation methods apply a stop motion technique to two- and three-dimensional objects like cutout animation, paper cutouts, puppets, or Clay animation, clay figures. A cartoon is an animated film, usually a short film, featuring an cartoon, exaggerated visual style. The style takes inspiration from comic strips, often featuring anthropomorphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live-action
Live action (or live-action) is a form of cinematography or videography that uses photography instead of animation. Some works combine live-action with animation to create a live-action animated film. Live-action is used to define film, video games or similar visual media. According to the Cambridge English Dictionary, live action " nvolvesreal people or animals, not models, or images that are drawn, or produced by computer." Overview As the normal process of making visual media involves live-action, the term itself is usually superfluous. However, it makes an important distinction in situations in which one might normally expect animation, such as when the work is adapted from a video game, or from an animated cartoon, such as ''Scooby-Doo'', ''The Flintstones'', '' 101 Dalmatians'' films, or ''The Tick'' television program. The phrase "live-action" also occurs within an animation context to refer to non-animated characters: in a live-action/animated film such as ''Space Jam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heuristics
A heuristic (; ), or heuristic technique, is any approach to problem solving or self-discovery that employs a practical method that is not guaranteed to be optimal, perfect, or rational, but is nevertheless sufficient for reaching an immediate, short-term goal or approximation. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of making a decision. Examples that employ heuristics include using trial and error, a rule of thumb or an ansatz, educated guess. Heuristics are the strategies derived from previous experiences with similar problems. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings, machines and abstract issues. When an individual applies a heuristic in practice, it generally performs as expected. However it can alternati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
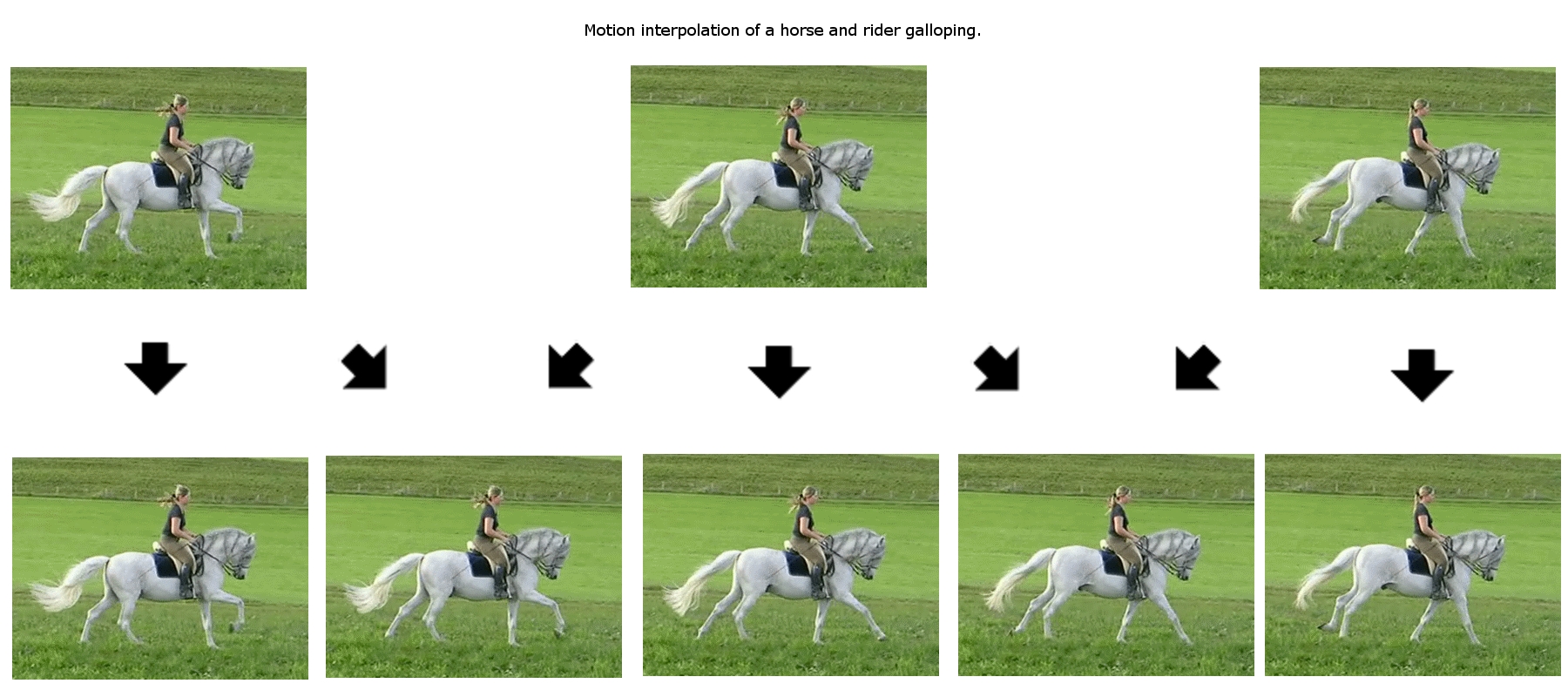
Motion Estimation
Motion estimation is the process of determining ''motion vectors'' that describe the transformation from one 2D image to another; usually from adjacent frames in a video sequence. It is an ill-posed problem as the motion is in three dimensions but the images are a projection of the 3D scene onto a 2D plane. The motion vectors may relate to the whole image (global motion estimation) or specific parts, such as rectangular blocks, arbitrary shaped patches or even per pixel. The motion vectors may be represented by a translational model or many other models that can approximate the motion of a real video camera, such as rotation and translation in all three dimensions and zoom. Related terms More often than not, the term motion estimation and the term ''optical flow'' are used interchangeably. It is also related in concept to ''image registration'' and '' stereo correspondence''. In fact all of these terms refer to the process of finding corresponding points between two images or vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theora
Theora is a free file format, free Lossy compression, lossy video compression format. It is developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation and distributed without licensing fees alongside their other free and open media projects, including the Vorbis audio format and the Ogg container. The libtheora video codec is the reference implementation (computing), reference implementation of the Theora video compression format being developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation. Theora is derived from the formerly Proprietary software, proprietary VP3 codec, released into the public domain by On2 Technologies. It is broadly comparable in design and bitrate efficiency to MPEG-4 Part 2, early versions of Windows Media Video, and RealVideo while lacking some of the features present in some of these other codecs. It is comparable in open standards philosophy to the BBC's Dirac (video compression format), Dirac codec. Theora is named after Theora Jones, Edison Carter's Controller on the ''Max Headroom (TV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding; encoding done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a signal. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow (codec)
FFmpeg is a free and open-source software project consisting of a suite of libraries and programs for handling video, audio, and other multimedia files and streams. At its core is the command-line ffmpeg tool itself, designed for processing of video and audio files. It is widely used for format transcoding, basic editing (trimming and concatenation), video scaling, video post-production effects and standards compliance (SMPTE, ITU). FFmpeg also includes other tools: ffplay, a simple media player and ffprobe, a command-line tool to display media information. Among included libraries are libavcodec, an audio/video codec library used by many commercial and free software products, libavformat (Lavf), an audio/video container mux and demux library, and libavfilter, a library for enhancing and editing filters through a Gstreamer-like filtergraph. FFmpeg is part of the workflow of many other software projects, and its libraries are a core part of software media players such as VLC, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |