|
Recyca
Rechytsa ( be, Рэчыца, ; russian: Речица; pl, Rzeczyca; lt, Rečyca) is a city in the Gomel Region in southeastern Belarus. It is center of the Rechytsa District. The city is located on the Rechytsa River, which flows into the Dnieper. , the population was 66,400. History Rechytsa is one of the oldest towns in Belarus. First settlements in this region are dated back to the epoch of mesolite (9 – 5th centuries B.C.). Later, this area was inhabited by the Dregovichi tribe. The town was first mentioned in the Novgorod chronicle in 1213 as a town of the Principality of Chernigov. Rechytsa was also ruled by Kiev and Turov, Belarus, Turov Grand Dukes. At the time of Gediminas reign (1311–1341) the town was annexed to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, from 1385 forming part of the Polish–Lithuanian union. Rečyca as well as Orsha, Shklow, Mogilev, Stary Bychaw and Rahachow formed a well-developed frontier defense system at the River Dniepr. 1392–1430 – the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rechytsa River
Rechytsa ( be, Рэчыца, ; russian: Речица; pl, Rzeczyca; lt, Rečyca) is a city in the Gomel Region in southeastern Belarus. It is center of the Rechytsa District. The city is located on the Rechytsa River, which flows into the Dnieper. , the population was 66,400. History Rechytsa is one of the oldest towns in Belarus. First settlements in this region are dated back to the epoch of mesolite (9 – 5th centuries B.C.). Later, this area was inhabited by the Dregovichi tribe. The town was first mentioned in the Novgorod chronicle in 1213 as a town of the Principality of Chernigov. Rechytsa was also ruled by Kiev and Turov, Belarus, Turov Grand Dukes. At the time of Gediminas reign (1311–1341) the town was annexed to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, from 1385 forming part of the Polish–Lithuanian union. Rečyca as well as Orsha, Shklow, Mogilev, Stary Bychaw and Rahachow formed a well-developed frontier defense system at the River Dniepr. 1392–1430 – the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gomel Region
Gomel Region or Gomel Oblast or Homiel Voblasts ( be, Го́мельская во́бласць, Homielskaja vobłasć, russian: Гомельская область, Gomelskaya oblast) is one of the regions of Belarus. Its administrative center is Gomel. The total area of the region is , the population in 2011 stood at 1,435,000 with the number of inhabitants per km2 at 36. Important cities within the region include: Homiel, Mazyr, Zhlobin, Svietlahorsk, Rechytsa, Kalinkavichy, Rahachow and Dobrush. Both the Gomel Region and the Mogilev Region suffered severely from the Chernobyl disaster. The Gomel Province borders the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone in places, and parts of it have been designated as mandatory or voluntary resettlement areas as a result of the radioactive contamination. Administrative territorial entities Gomel Region comprises 21 districts and 2 city municipalities. The districts have 278 selsovets, and 17 cities and towns. Districts of Gomel Region * Akciabrski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
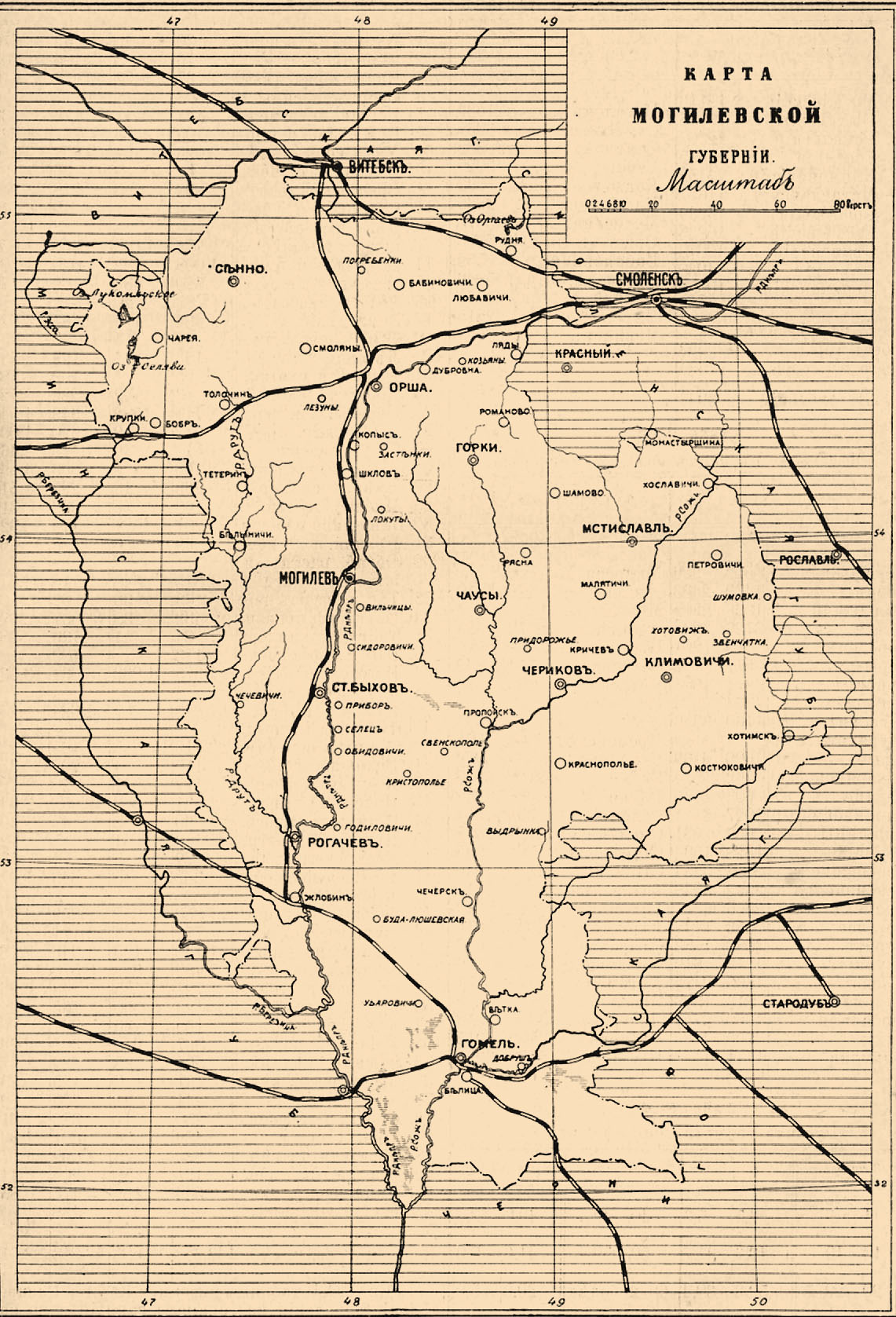
Mogilev
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the border with Russia's Bryansk Oblast. , its population was 360,918, up from an estimated 106,000 in 1956. It is the administrative centre of Mogilev Region and the third-largest city in Belarus. History The city was first mentioned in historical records in 1267. From the 14th century, it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and since the Union of Lublin (1569), part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, where it became known as ''Mohylew''. In the 16th-17th centuries, the city flourished as one of the main nodes of the east–west and north–south trading routes. In 1577, Polish King Stefan Batory granted it city rights under Magdeburg law. In 1654, the townsmen negotiated a treaty of surrender to the Russians peacefully, if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812). Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk Governorate
The Minsk Governorate (russian: Минская губерния, Belarusian: ) or Government of Minsk was a governorate ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire. The seat was in Minsk. It was created in 1793 from the land acquired in the partitions of Poland and lasted until 1921. Administrative structure *Bobruysky Uyezd *Borisovsky Uyezd *Igumensky Uyezd *Minsky Uyezd *Mozyrsky Uyezd *Novogrudsky Uyezd (part of Grodno Governorate before 1843) * Pinsky Uyezd *Rechitsky Uyezd *Slutsky Uyezd Vileysky and Disnensky Uyezds passed to the Vilna Governorate in 1843. In 1919, Baranovichsky Uyezd was created from Novogorodoksky Uyezd and Nesvizhsky Uyezd was created from Slutsky Uyezd. In 1920, Novogrudoksky, Pinsky, Baranovichsky, and Nesvizhsky Uyezds were controlled by Poland Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rechitsky Uyezd
Rechitsky Uyezd (russian: Речицкий уезд) was one of the Uyezds of Minsk Governorate and the Governorate-General of Minsk of the Russian Empire and then of Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic with its center in Rechytsa from 1793 until its formal abolition in 1924 by Soviet authorities. Demographics At the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897, Rechitsky Uyezd had a population of 221,771. Of these, 82.5% spoke Belarusian, 12.8% Yiddish, 1.7% Ukrainian, 1.4% Russian, 1.1% Polish, 0.2% Czech, 0.1% Latvian, 0.1% German and 0.1% Romani Romani may refer to: Ethnicities * Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia ** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule * Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ... as their native language. Демоскоп Weekly - � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Partition Of Poland
The 1793 Second Partition of Poland was the second of three partitions (or partial annexations) that ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The second partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation of 1792, and was approved by its territorial beneficiaries, the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia. The division was ratified by the coerced Polish parliament (Sejm) in 1793 (see the Grodno Sejm) in a short-lived attempt to prevent the inevitable complete annexation of Poland, the Third Partition. Background By 1790, on the political front, the Commonwealth had deteriorated into such a helpless condition that it was forced into an alliance with its enemy, Prussia. The Polish-Prussian Pact of 1790 was signed, giving false hope that the Commonwealth might have at last found an ally that would shield it while it reformed itself. The May Constitution of 1791 enfranchised the bourgeoisie, estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, religious, and economic diversity. From the 10th–17th centuries, the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truce Of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 between the Tsardom of Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which had fought the Russo-Polish War since 1654 over the territories of modern-day Ukraine and Belarus. Afanasy Ordin-Nashchokin (for Russia) and Jerzy Chlebowicz (for the Commonwealth) signed the truce on 30 January/9 February 1667 in the village of Andrusovo not far from Smolensk. Representatives of the Cossack Hetmanate were not allowed. Terms The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia (Muscovy) agreed on the following terms: * A truce was signed for 13.5 years during which both states were obligated to prepare the conditions for eternal peace. * Russia secured the territories of Left-bank Ukraine, Siever lands, and Smolensk. * Poland-Lithuania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or , sk, kozáci , uk, козаки́ are a predominantly East Slavic Orthodox Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of Ukraine and southern Russia. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic-speaking Orthodox Christians. The Cossacks were particularly noted for holding democratic traditions. The rulers of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk Voivodeship
, la, Palatinatus Minscensis) was a unit of administrative division and local government in Grand Duchy of Lithuania since 1566Stanisław Kutrzeba: Historia ustroju Polski w zarysie, Tom drugi: Litwa. Lwów i Warszawa: 1921, s. 88. and later in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, until the partitions of the Commonwealth in 1793. Centred on the city of Minsk and subordinate to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the region continued the traditions – and shared the borders – of several previously existing units of administrative division, notably a separate Duchy of Minsk, annexed by Lithuania in the 13th century. It was replaced with Minsk Governorate in 1793. Geography The voivodeship was stretched along the Berezina and Dneper rivers, with the earlier river having both its source and its estuary within the limits of the voivodeship, as well as most of its basin. To the north east it bordered Polotsk, Vitebsk and Mscislaw voivodeships. To the east it bordered with the lands of Che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania ruled by a common Monarchy, monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and List of Lithuanian monarchs, Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish language, Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages. The Commonwealth was established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569, but the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania had been in a ''de facto'' personal union since 1386 with the marriage of the Polish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)