|
Rebel Yell
The rebel yell was a battle cry used by Confederate soldiers during the American Civil War. Confederate soldiers used the yell when charging to intimidate the enemy and boost their own morale, although the yell had many other uses. No audio recordings of the yell exist from the Civil War era, but there are audio clips and film footage of veterans performing the yell many years later at Civil War veterans' reunions.What Did the Rebel Yell Sound Like? From the articl Civil War Veterans Come Alive in Audio and Video Recordings ''Smithsonian Magazine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gone With The Wind (film)
''Gone with the Wind'' is a 1939 American epic historical romance film adapted from the 1936 novel by Margaret Mitchell. The film was produced by David O. Selznick of Selznick International Pictures and directed by Victor Fleming. Set in the American South against the backdrop of the American Civil War and the Reconstruction era, the film tells the story of Scarlett O'Hara ( Vivien Leigh), the strong-willed daughter of a Georgia plantation owner, following her romantic pursuit of Ashley Wilkes (Leslie Howard), who is married to his cousin, Melanie Hamilton (Olivia de Havilland), and her subsequent marriage to Rhett Butler (Clark Gable). The film had a troubled production. The start of filming was delayed for two years until January 1939 because of Selznick's determination to secure Gable for the role of Rhett. The role of Scarlett was difficult to cast, and 1,400 unknown women were interviewed for the part. The original screenplay by Sidney Howard underwent many revisions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac. Origin The name ''Army of Northern Virginia'' referred to its primary area of operation, as did most Confederate States Army names. The Army originated as the Army of the Potomac, which was organized on June 20, 1861, from all operational forces in northern Virginia. On July 20 and July 21, the Army of the Shenandoah and forces from the District of Harpers Ferry were added. Units from the Army of the Northwest were merged into the Army of the Potomac between March 14 and May 17, 1862. The Army of the Potomac was renamed ''Army of Northern Virginia'' on March 14. The Army of the Peninsula was merged into it on April 12, 1862.Eicher, pp. 889–90. Robert E. Lee's biographer, Douglas S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
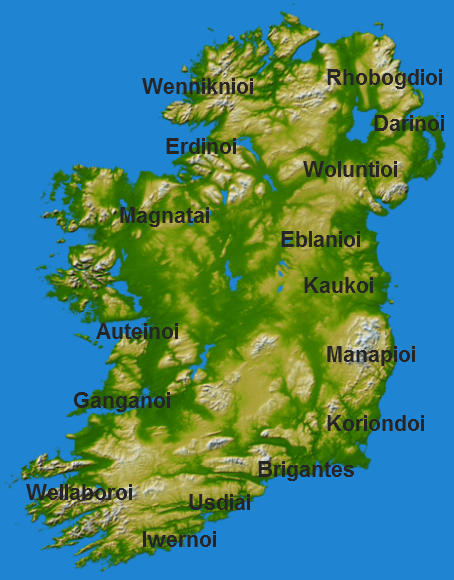
Gael
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising Irish, Manx and Scottish Gaelic. Gaelic language and culture originated in Ireland, extending to Dál Riata in western Scotland. In antiquity, the Gaels traded with the Roman Empire and also raided Roman Britain. In the Middle Ages, Gaelic culture became dominant throughout the rest of Scotland and the Isle of Man. There was also some Gaelic settlement in Wales, as well as cultural influence through Celtic Christianity. In the Viking Age, small numbers of Vikings raided and settled in Gaelic lands, becoming the Norse-Gaels. In the 9th century, Dál Riata and Pictland merged to form the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba. Meanwhile, Gaelic Ireland was made up of several kingdoms, with a High King often claiming lordship over them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Killiecrankie
The Battle of Killiecrankie ( gd, Blàr Choille Chnagaidh), also referred to as the Battle of Rinrory, took place on 27 July 1689 during the 1689 Scottish Jacobite rising. An outnumbered Jacobite force under John Graham, Viscount Dundee and Sir Ewen Cameron of Lochiel defeated a government army commanded by General Hugh Mackay. James VII went into exile in December 1688 after being deposed by the Glorious Revolution in Scotland. In March 1689, he began the Williamite War in Ireland, with a simultaneous revolt led by Dundee, previously military commander in Scotland. Hampered by lack of men and resources, Dundee gambled on a decisive battle which he hoped would attract wider support. Although Killiecrankie was an unexpected and stunning victory, his army suffered heavy casualties and he was killed in the final minutes. It did little to change the overall strategic position, and the Jacobites were unable to take advantage of their success. Background In February 1685, the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Charge
The Highland charge was a battlefield shock tactic used by the clans of the Scottish Highlands which incorporated the use of firearms. Historical development Prior to the 17th century, Highlanders fought in tight formations, led by a heavily armed warrior elite who carried heavy battle axes or claymores (two-handed swords whose name comes from the Scottish Gaelic ''claidheamh mòr'' "great sword"). However, with the introduction of muskets and cannon, such formations became vulnerable. As a result, in the 17th century, Highlander warriors developed a lighter, one-handed basket-hilted broadsword that protected the hand. This was generally used with a shield or targe strapped to the weak arm and a dirk or ''biotag'' "long knife" held in the other hand. The Scottish and Irish warrior Alasdair Mac Colla is sometimes credited with inventing the Highland charge during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms to meet a particular set of battlefield challenges. It was initially known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in Lawton, Oklahoma. The Comanche language is a Numic language of the Uto-Aztecan family. Originally, it was a Shoshoni dialect, but diverged and became a separate language. The Comanche were once part of the Shoshone people of the Great Basin. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Comanche lived in most of present-day northwestern Texas and adjacent areas in eastern New Mexico, southeastern Colorado, southwestern Kansas, and western Oklahoma. Spanish colonists and later Mexicans called their historical territory ''Comanchería''. During the 18th and 19th centuries, Comanche practiced a nomadic horse culture and hunted, particularly bison. They traded with neighboring Native American peoples, and Spanish, French, and American colonists and set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grady McWhiney
Grady McWhiney (July 15, 1928 – April 18, 2006) was a historian of the American south and the U.S. Civil War. Early life and education McWhiney was born in Shreveport, Louisiana, and served in the Marine Corps in 1945. He married in 1947. He attended Centenary College on the G.I. Bill and earned an M.A. in history from Louisiana State University, working with Francis Butler Simkins. He received his Ph.D. in history from Columbia University in New York, working with David Herbert Donald. Career McWhiney's dissertation dealt with Confederate General Braxton Bragg. McWhiney became a noted specialist on the American Civil War era, as well as southern social and economic history. He coauthored ''Attack and Die'' with his doctoral student Perry Jamieson. He published ''Braxton Bragg and Confederate Defeat'', in two volumes, as well as many scholarly and popular articles and reviews. He lectured frequently to both academic and popular audiences. McWhiney and Forrest McDonald w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jubal Early
Jubal Anderson Early (November 3, 1816 – March 2, 1894) was a Virginia lawyer and politician who became a Confederate general during the American Civil War. Trained at the United States Military Academy, Early resigned his U.S. Army commission after the Second Seminole War and his Virginia military commission after the Mexican–American War, in both cases to practice law and participate in politics. Accepting a Virginia and later Confederate military commission as the American Civil War began, Early fought in the Eastern Theater throughout the conflict. He commanded a division under Generals Stonewall Jackson and Richard Ewell, and later commanded a corps. A key Confederate defender of the Shenandoah Valley, during the Valley Campaigns of 1864, Early made daring raids to the outskirts of Washington, D.C., and as far as York, Pennsylvania, but was crushed by Union forces under General Philip Sheridan, losing over half his forces and leading to the destruction of much of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dixie (song)
"Dixie", also known as "Dixie's Land", "I Wish I Was in Dixie", and other titles, is a song about the Southern United States first made in 1859. It is one of the most distinctively Southern musical products of the 19th century. It was not a folk song at its creation, but it has since entered the American folk vernacular. The song likely cemented the word "Dixie" in the American vocabulary as a nickname for the Southern U.S. Most sources credit Ohio-born Daniel Decatur Emmett with the song's composition, although other people have claimed credit, even during Emmett's lifetime. Compounding the problem are Emmett's own confused accounts of its writing and his tardiness in registering its copyright. "Dixie" originated in the minstrel shows of the 1850s and quickly became popular throughout the United States. During the American Civil War, it was adopted as a de facto national anthem of the Confederacy, along with "The Bonnie Blue Flag" and "God Save the South". New versions app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Baruch
Bernard Mannes Baruch (August 19, 1870 – June 20, 1965) was an American financier and statesman. After amassing a fortune on the New York Stock Exchange, he impressed President Woodrow Wilson by managing the nation's economic mobilization in World War I as chairman of the War Industries Board. He advised Wilson during the Paris Peace Conference. He made another fortune in the postwar bull market, but foresaw the Wall Street crash and sold out well in advance. In World War II, he became a close advisor to President Roosevelt on the role of industry in war supply, and he was credited with greatly shortening the production time for tanks and aircraft. Later he helped to develop rehabilitation programs for injured servicemen. In 1946, he was the United States representative to the United Nations Atomic Energy Commission (UNAEC), though his Baruch Plan for international control of atomic energy was rejected by the Soviet Union. Early life and education Bernard Baruch was born t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newsreel
A newsreel is a form of short documentary film, containing news stories and items of topical interest, that was prevalent between the 1910s and the mid 1970s. Typically presented in a cinema, newsreels were a source of current affairs, information, and entertainment for millions of moviegoers. Newsreels were typically exhibited preceding a feature film, but there were also dedicated newsreel theaters in many major cities in the 1930s and ’40s, and some large city cinemas also included a smaller theaterette where newsreels were screened continuously throughout the day. By the end of the 1960s television news broadcasts had supplanted the format. Newsreels are considered significant historical documents, since they are often the only audiovisual record of certain cultural events. History Silent news films were shown in cinemas from the late 19th century. In 1909 Pathé started producing weekly newsreels in Europe. Pathé began producing newsreels for the UK in 1910 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




