|
Real Data Type
A real data type is a data type used in a computer program to represent an approximation of a real number. Because the real numbers are not countable, computers cannot represent them exactly using a finite amount of information. Most often, a computer will use a rational approximation to a real number. Rational numbers The most general data type for a rational number (a number that can be expressed as a fraction) stores the numerator and the denominator as integers. For example 1/3, which can be calculated to any desired precision. Rational number are used, for example, in Interpress from Xerox Corporation. Fixed-point numbers A fixed-point data type uses the same, implied, denominator for all numbers. The denominator is usually a power of two. For example, in a hypothetical fixed-point system that uses the denominator 65,536 (216), the hexadecimal number 0x12345678 (0x1234.5678 with sixteen fractional bits to the right of the assumed radix point) means 0x12345678/65536 or 30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Data Type
In computer science and computer programming, a data type (or simply type) is a collection or grouping of data values, usually specified by a set of possible values, a set of allowed operations on these values, and/or a representation of these values as machine types. A data type specification in a program constrains the possible values that an expression, such as a variable or a function call, might take. On literal data, it tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data. Most programming languages support basic data types of integer numbers (of varying sizes), floating-point numbers (which approximate real numbers), characters and Booleans. Concept A data type may be specified for many reasons: similarity, convenience, or to focus the attention. It is frequently a matter of good organization that aids the understanding of complex definitions. Almost all programming languages explicitly include the notion of data type, though the possible d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radix Point
alt=Four types of separating decimals: a) 1,234.56. b) 1.234,56. c) 1'234,56. d) ١٬٢٣٤٫٥٦., Both a full_stop.html" ;"title="comma and a full stop">comma and a full stop (or period) are generally accepted decimal separators for international use. The apostrophe and Arabic decimal separator are also used in certain contexts. A decimal separator is a symbol that separates the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form. Different countries officially designate different symbols for use as the separator. The choice of symbol can also affect the choice of symbol for the thousands separator used in digit grouping. Any such symbol can be called a decimal mark, decimal marker, or decimal sign. Symbol-specific names are also used; decimal point and decimal comma refer to a dot (either baseline or middle) and comma respectively, when it is used as a decimal separator; these are the usual terms used in English, with the aforementioned generic te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IEEE 754
The IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic (IEEE 754) is a technical standard for floating-point arithmetic originally established in 1985 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The standard #Design rationale, addressed many problems found in the diverse floating-point implementations that made them difficult to use reliably and Software portability, portably. Many hardware floating-point units use the IEEE 754 standard. The standard defines: * ''arithmetic formats:'' sets of Binary code, binary and decimal floating-point data, which consist of finite numbers (including signed zeros and subnormal numbers), infinity, infinities, and special "not a number" values (NaNs) * ''interchange formats:'' encodings (bit strings) that may be used to exchange floating-point data in an efficient and compact form * ''rounding rules:'' properties to be satisfied when rounding numbers during arithmetic and conversions * ''operations:'' arithmetic and other operatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hexadecimal Number
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbols, hexadecimal uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols "0"–"9" to represent values 0 to 9 and "A"–"F" to represent values from ten to fifteen. Software developers and system designers widely use hexadecimal numbers because they provide a convenient representation of binary-coded values. Each hexadecimal digit represents four bits (binary digits), also known as a nibble (or nybble). For example, an 8-bit byte is two hexadecimal digits and its value can be written as to in hexadecimal. In mathematics, a subscript is typically used to specify the base. For example, the decimal value would be expressed in hexadecimal as . In programming, several notations denote hexadecimal numbers, usually involving a prefix. The prefix 0x is used in C, which would denote this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
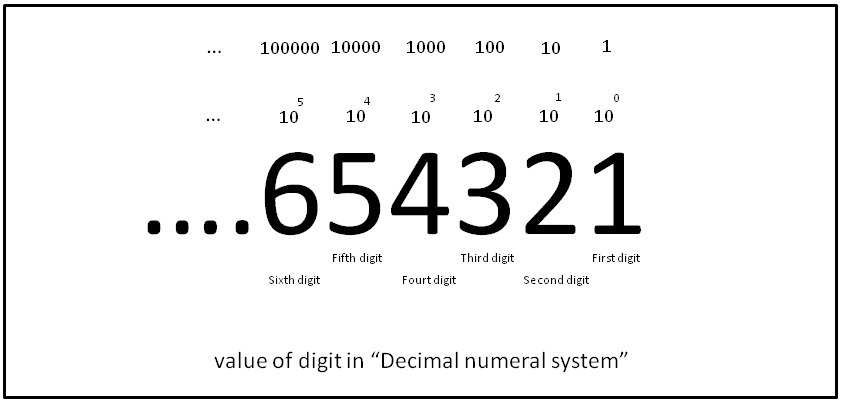
Decimal Number
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the #Decimal fractions, decimal fractions. That is, fraction ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Binary Number
A binary number is a number expressed in the Radix, base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" (zero) and "1" (one). A ''binary number'' may also refer to a rational number that has a finite representation in the binary numeral system, that is, the quotient of an integer by a power of two. The base-2 numeral system is a positional notation with a radix of 2. Each digit is referred to as a bit, or binary digit. Because of its straightforward implementation in digital electronic circuitry using logic gates, the binary system is used by almost all modern computer, computers and computer-based devices, as a preferred system of use, over various other human techniques of communication, because of the simplicity of the language and the noise immunity in physical implementation. History The modern binary number system was studied in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries by Thoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Power Of 10
In mathematics, a power of 10 is any of the integer powers of the number ten; in other words, ten multiplied by itself a certain number of times (when the power is a positive integer). By definition, the number one is a power (the zeroth power) of ten. The first few non-negative powers of ten are: : 1, 10, 100, 1,000, 10,000, 100,000, 1,000,000, 10,000,000... Positive powers In decimal notation the ''n''th power of ten is written as '1' followed by ''n'' zeroes. It can also be written as 10''n'' or as 1E''n'' in E notation. See order of magnitude and orders of magnitude (numbers) for named powers of ten. There are two conventions for naming positive powers of ten, beginning with 109, called the long and short scales. Where a power of ten has different names in the two conventions, the long scale name is shown in parentheses. The positive 10 power related to a short scale name can be determined based on its Latin name-prefix using the following formula: 10 prefix-n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative integers. The set (mathematics), set of all integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the set of natural numbers, the set of integers \mathbb is Countable set, countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fraction, fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , 5/4, and Square root of 2, are not. The integers form the smallest Group (mathematics), group and the smallest ring (mathematics), ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Power Of Two
A power of two is a number of the form where is an integer, that is, the result of exponentiation with number 2, two as the Base (exponentiation), base and integer as the exponent. In the fast-growing hierarchy, is exactly equal to f_1^n(1). In the Hardy hierarchy, is exactly equal to H_(1). Powers of two with Sign (mathematics)#Terminology for signs, non-negative exponents are integers: , , and is two multiplication, multiplied by itself times. The first ten powers of 2 for non-negative values of are: :1, 2, 4, 8, 16 (number), 16, 32 (number), 32, 64 (number), 64, 128 (number), 128, 256 (number), 256, 512 (number), 512, ... By comparison, powers of two with negative exponents are fractions: for positive integer , is one half multiplied by itself times. Thus the first few negative powers of 2 are , , , , etc. Sometimes these are called ''inverse powers of two'' because each is the multiplicative inverse of a positive power of two. Base of the binary numeral sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to Execution (computing), execute. It is one component of software, which also includes software documentation, documentation and other intangible components. A ''computer program'' in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to Execution (computing), execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be Translator (computing), translated to machine instructions using a compiler written for the language. (Assembly language programs are translated using an Assembler (computing), assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within an interpreter (computing), interpreter written for the language. If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system Loader (computing), loads it into Random-access memory, memory and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Xerox Corporation
Xerox Holdings Corporation (, ) is an American corporation that sells print and digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox was the pioneer of the photocopier market, beginning with the introduction of the Xerox 914 in 1959, so much so that the word ''xerox'' is commonly used as a synonym for ''photocopy''. Xerox is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut, though it is incorporated in New York with its largest group of employees based around Rochester, New York, the area in which the company was founded. As a large developed company, it is consistently placed in the list of Fortune 500 companies. The company purchased Affiliated Computer Services for $6.4 billion in early 2010. On December 31, 2016, Xerox separated its business process service operations, essentially those operations acquired with the purchase of Affiliated Computer Services, into a new publicly traded company, Conduent. Xerox focuses on its document technology and document out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Interpress
Interpress is a page description language developed at Xerox PARC, based on the Forth programming language and an earlier graphics language called JaM. PARC failed to commercialize it, so its creators, Chuck Geschke and John Warnock, founded Adobe Systems in 1982, and developed PostScript. Interpress is used in some Xerox printers, notably the DocuTech Network Production Publisher, and is supported in Xerox Ventura Publisher. It also serves as the output format for PARC's InterScript, a rich text word processor A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features. Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word .... Interpress describes the desired or ideal appearance of a document that has been completely composed by some other process (emitter). All line ending, hyphenation, and line justification decisions, and in fact all deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |