|
Raymond Dingledine
Raymond J Dingledine (born December 17, 1948) is an American pharmacologist and neurobiologist who has made considerable contributions to the field of epilepsy. He serves as Professor in the School of Medicine at Emory University, Atlanta GA, where he chaired the pharmacology department for 25 years and served as Executive Associate Dean of Research for 10 years. Education Dingledine grew up in St. Marys, Ohio, a small town bordering Grand Lake St. Marys. He attended Michigan State University from 1967–1971 and graduated from Stanford University with a PhD in pharmacology in 1975. His PhD training was under Avram Goldstein. He then did postdoctoral stints with John Kelly and Leslie Iversen in Cambridge UK, and Per Andersen in Oslo Norway. It was in Per’s lab, working with Leif Gjerstad and Iver Langmoen, that he developed a lifelong interest in epilepsy. Career Dingledine joined the Department of Pharmacology at the University of North Carolina Chapel Hill in 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morehouse School Of Medicine
Morehouse School of Medicine is a private co-educational medical school in Atlanta, Georgia. Originally a part of Morehouse College, the school became independent in 1981. The school abbreviates its name with its initials "MSM." History Establishment Founded as a part of Morehouse College in 1975 during the tenure of college president Hugh M. Gloster, with Louis W. Sullivan, M.D. as dean, the School of Medicine at Morehouse College began as a two-year program in the basic sciences. The first students were admitted in 1978 and transferred to other medical schools for the clinical years of their training. Independent institution The institution became independent from Morehouse College in 1981, with Sullivan as President, and was fully accredited to award M.D. degrees in 1985. Initially, third year clinical courses were taught by faculty from Emory University's School of Medicine, but since 1990, the school has taught them itself. In 1989, Sullivan was appointed United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
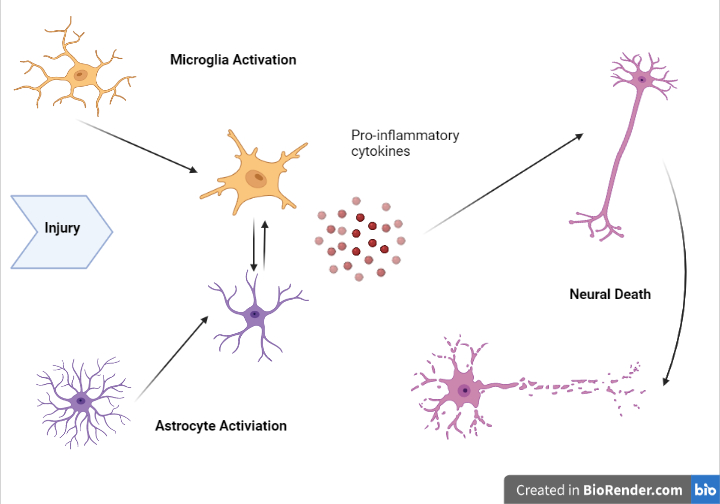
Neuroinflammation
Neuroinflammation is inflammation of the nervous tissue. It may be initiated in response to a variety of cues, including infection, traumatic brain injury,Ebert SE, Jensen P, Ozenne B, Armand S, Svarer C, Stenbaek DS ''et al.'' Molecular imaging of neuroinflammation in patients after mild traumatic brain injury: a longitudinal 123 I-CLINDE SPECT study. ''Eur J Neurol'' 2019. doi:10.1111/ene.13971. toxic metabolites, or autoimmunity. In the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain and spinal cord, microglia are the resident innate immune cells that are activated in response to these cues. The CNS is typically an immunologically privileged site because peripheral immune cells are generally blocked by the blood–brain barrier (BBB), a specialized structure composed of astrocytes and endothelial cells. However, circulating peripheral immune cells may surpass a compromised BBB and encounter neurons and glial cells expressing major histocompatibility complex molecules, perpetuat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifenprodil
Ifenprodil is an inhibitor of the NMDA receptor, specifically of GluN1 (glycine-binding NMDA receptor subunit 1) and GluN2B (glutamate-binding NMDA receptor subunit 2) subunits. Additionally, ifenprodil inhibits GIRK channels, and interacts with alpha1 adrenergic, serotonin, and sigma receptors. NMDA receptors are multimeric ionotropic glutamate receptors composed of four subunits. GluN1 is obligate for functional expression. Other subunits include GluN2A, GluN2B, and the more recently discovered GluN3 subunits. Ifenprodil selectively inhibits NMDA receptors containing the GluN2B subunit. As ifenprodil tartrate, it has been marketed in some countries, including Japan and France, as a cerebral vasodilator, under the trade names Cerocral, Dilvax, and Vadilex. Ifenprodil has been studied as a possible medication to prevent tinnitus after acoustic trauma. It is currently in phase III clinical trials to treat SARS-CoV2 infection and phase II Phase II, Phase 2 or Phase Two may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), and bind to and react with the receptors on the dendrites of another neuron (the postsynaptic neuron) a short distance away. A similar process occurs in retrograde neurotransmission, where the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron release retrograde neurotransmitters (e.g., endocannabinoids; synthesized in response to a rise in intracellular calcium levels) that signal through receptors that are located on the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, mainly at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses. Neurotransmission is regulated by several different factors: the availability and rate-of-synthesis of the neurotransmitter, the release of that neurotransmitter, the baseline activity of the postsynaptic cell, the number of available postsynapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamate Receptor
Glutamate receptors are synaptic and non synaptic receptors located primarily on the membranes of neuronal and glial cells. Glutamate (the conjugate base of glutamic acid) is abundant in the human body, but particularly in the nervous system and especially prominent in the human brain where it is the body's most prominent neurotransmitter, the brain's main excitatory neurotransmitter, and also the precursor for GABA, the brain's main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Glutamate receptors are responsible for the glutamate-mediated postsynaptic excitation of neural cells, and are important for neural communication, memory formation, learning, and regulation. Glutamate receptors are implicated in a number of neurological conditions. Their central role in excitotoxicity and prevalence in the central nervous system has been linked or speculated to be linked to many neurodegenerative diseases, and several other conditions have been further linked to glutamate receptor gene mutations o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (mood)
Depression is a mental state of low mood and aversion to activity, which affects more than 280 million people of all ages (about 3.5% of the global population). Classified medically as a mental and behavioral disorder, the experience of depression affects a person's thoughts, behavior, motivation, feelings, and sense of well-being. The core symptom of depression is said to be anhedonia, which refers to loss of interest or a loss of feeling of pleasure in certain activities that usually bring joy to people. Depressed mood is a symptom of some mood disorders such as major depressive disorder and dysthymia; it is a normal temporary reaction to life events, such as the loss of a loved one; and it is also a symptom of some physical diseases and a side effect of some drugs and medical treatments. It may feature sadness, difficulty in thinking and concentration and a significant increase or decrease in appetite and time spent sleeping. People experiencing depression may have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." In medical diagnosis, pain is regarded as a symptom of an underlying condition. Pain motivates the individual to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general functioning. Simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Ischemia
Brain ischemia is a condition in which there is insufficient bloodflow to the brain to meet metabolic demand. This leads to poor oxygen supply or cerebral hypoxia and thus leads to the death of brain tissue or cerebral infarction/ischemic stroke. It is a sub-type of stroke along with subarachnoid hemorrhage and intracerebral hemorrhage. Ischemia leads to alterations in brain metabolism, reduction in metabolic rates, and energy crisis. There are two types of ischemia: focal ischemia, which is confined to a specific region of the brain; and global ischemia, which encompasses wide areas of brain tissue. The main symptoms of brain ischemia involve impairments in vision, body movement, and speaking. The causes of brain ischemia vary from sickle cell anemia to congenital heart defects. Symptoms of brain ischemia can include unconsciousness, blindness, problems with coordination, and weakness in the body. Other effects that may result from brain ischemia are stroke, cardiorespiratory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMDA Receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA receptor, AMPA and kainate receptors. Depending on its subunit composition, its Ligand (biochemistry), ligands are glutamate and glycine (or D-Serine, D-serine). However, the binding of the ligands is typically not sufficient to open the channel as it may be blocked by Magnesium, Mg2+ ions which are only removed when the neuron is sufficiently depolarized. Thus, the channel acts as a “coincidence detector” and only once both of these conditions are met, the channel opens and it allows cation, positively charged ions (cations) to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is thought to be very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and mediating learning and memory functions. The NMDA receptor is ionotropic, meaning it is a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society For Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics
The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (ASPET) is a scientific society founded in late 1908 by John Jacob Abel of Johns Hopkins University (also the founder of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), with the aim of promoting the growth of pharmacological research. Many society members are researchers in basic and clinical pharmacology who help develop disease-fighting medications and therapeutics. ASPET is one of the constituent societies of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB). The society's headquarters are in Rockville, MD. The current president is Michael F. Jarvis. Publications The society publishes three research journals and a review journal: the ''Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics'', ''Drug Metabolism and Disposition'', ''Molecular Pharmacology'', and ''Pharmacological Reviews'' Starting in 2012 these publications are only offered online. The society copublishes a who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |