|
Rayleigh Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Rayleigh distribution is a continuous probability distribution for nonnegative-valued random variables. Up to rescaling, it coincides with the chi distribution with two degrees of freedom. The distribution is named after Lord Rayleigh (). A Rayleigh distribution is often observed when the overall magnitude of a vector is related to its directional components. One example where the Rayleigh distribution naturally arises is when wind velocity is analyzed in two dimensions. Assuming that each component is uncorrelated, normally distributed with equal variance, and zero mean, then the overall wind speed (vector magnitude) will be characterized by a Rayleigh distribution. A second example of the distribution arises in the case of random complex numbers whose real and imaginary components are independently and identically distributed Gaussian with equal variance and zero mean. In that case, the absolute value of the complex number is Rayle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh DistributionPDF
Rayleigh may refer to: Science *Rayleigh scattering * Rayleigh–Jeans law *Rayleigh waves *Rayleigh (unit), a unit of photon flux named after the 4th Baron Rayleigh * Rayl, rayl or Rayleigh, two units of specific acoustic impedance and characteristic acoustic impedance, named after the 3rd Baron Rayleigh *Rayleigh criterion in angular resolution *Rayleigh distribution *Rayleigh fading * Rayleigh law on low-field magnetization *Rayleigh length *Rayleigh number, a dimensionless number for a fluid associated with buoyancy driven flow *Rayleigh quotient *Rayleigh–Ritz method *Plateau–Rayleigh instability explains why a falling stream of fluid breaks up into smaller packets *Rayleigh–Taylor instability an instability of an interface between two fluids Title of nobility *Baron Rayleigh ** Charlotte Mary Gertrude Strutt, 1st Baroness Rayleigh **John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh, physicist, winner of a Nobel Prize in 1904 **Robert John Strutt, 4th Baron Rayleigh, physici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Density Function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) can be interpreted as providing a ''relative likelihood'' that the value of the random variable would be close to that sample. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the ''absolute likelihood'' for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0 (since there is an infinite set of possible values to begin with), the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample. In a more precise sense, the PDF is used to specify the probability of the random variable falling ''within a particular range of values'', as opposed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Function
In mathematics, the gamma function (represented by , the capital letter gamma from the Greek alphabet) is one commonly used extension of the factorial function to complex numbers. The gamma function is defined for all complex numbers except the non-positive integers. For every positive integer , \Gamma(n) = (n-1)!\,. Derived by Daniel Bernoulli, for complex numbers with a positive real part, the gamma function is defined via a convergent improper integral: \Gamma(z) = \int_0^\infty t^ e^\,dt, \ \qquad \Re(z) > 0\,. The gamma function then is defined as the analytic continuation of this integral function to a meromorphic function that is holomorphic in the whole complex plane except zero and the negative integers, where the function has simple poles. The gamma function has no zeroes, so the reciprocal gamma function is an entire function. In fact, the gamma function corresponds to the Mellin transform of the negative exponential function: \Gamma(z) = \mathcal M \ (z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment (mathematics)
In mathematics, the moments of a function are certain quantitative measures related to the shape of the function's graph. If the function represents mass density, then the zeroth moment is the total mass, the first moment (normalized by total mass) is the center of mass, and the second moment is the moment of inertia. If the function is a probability distribution, then the first moment is the expected value, the second central moment is the variance, the third standardized moment is the skewness, and the fourth standardized moment is the kurtosis. The mathematical concept is closely related to the concept of moment in physics. For a distribution of mass or probability on a bounded interval, the collection of all the moments (of all orders, from to ) uniquely determines the distribution (Hausdorff moment problem). The same is not true on unbounded intervals (Hamburger moment problem). In the mid-nineteenth century, Pafnuty Chebyshev became the first person to think systematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system in which each point on a plane is determined by a distance from a reference point and an angle from a reference direction. The reference point (analogous to the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system) is called the ''pole'', and the ray from the pole in the reference direction is the ''polar axis''. The distance from the pole is called the ''radial coordinate'', ''radial distance'' or simply ''radius'', and the angle is called the ''angular coordinate'', ''polar angle'', or ''azimuth''. Angles in polar notation are generally expressed in either degrees or radians (2 rad being equal to 360°). Grégoire de Saint-Vincent and Bonaventura Cavalieri independently introduced the concepts in the mid-17th century, though the actual term "polar coordinates" has been attributed to Gregorio Fontana in the 18th century. The initial motivation for the introduction of the polar system was the study of circula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotelling's T-squared Distribution
In statistics, particularly in hypothesis testing, the Hotelling's ''T''-squared distribution (''T''2), proposed by Harold Hotelling, is a multivariate probability distribution that is tightly related to the ''F''-distribution and is most notable for arising as the distribution of a set of sample statistics that are natural generalizations of the statistics underlying the Student's ''t''-distribution. The Hotelling's ''t''-squared statistic (''t''2) is a generalization of Student's ''t''-statistic that is used in multivariate hypothesis testing. Motivation The distribution arises in multivariate statistics in undertaking tests of the differences between the (multivariate) means of different populations, where tests for univariate problems would make use of a ''t''-test. The distribution is named for Harold Hotelling, who developed it as a generalization of Student's ''t''-distribution. Definition If the vector d is Gaussian multivariate-distributed with zero mean and unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multivariate T-distribution
In statistics, the multivariate ''t''-distribution (or multivariate Student distribution) is a multivariate probability distribution. It is a generalization to random vectors of the Student's ''t''-distribution, which is a distribution applicable to univariate random variables. While the case of a random matrix could be treated within this structure, the matrix ''t''-distribution is distinct and makes particular use of the matrix structure. Definition One common method of construction of a multivariate ''t''-distribution, for the case of p dimensions, is based on the observation that if \mathbf y and u are independent and distributed as N(,) and \chi^2_\nu (i.e. multivariate normal and chi-squared distributions) respectively, the matrix \mathbf\, is a ''p'' × ''p'' matrix, and /\sqrt = -, then has the density : \frac\left +\frac(-)^T^(-)\right and is said to be distributed as a multivariate ''t''-distribution with parameters ,,\nu. Note that \mathbf\Sigma is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoyt Distribution
The Nakagami distribution or the Nakagami-''m'' distribution is a probability distribution related to the gamma distribution. The family of Nakagami distributions has two parameters: a shape parameter m\geq 1/2 and a second parameter controlling spread \Omega>0. Characterization Its probability density function (pdf) is : f(x;\,m,\Omega) = \fracx^\exp\left(-\fracx^2\right), \forall x\geq 0. where (m\geq 1/2,\text\Omega>0) Its cumulative distribution function is : F(x;\,m,\Omega) = P\left(m, \fracx^2\right) where ''P'' is the regularized (lower) incomplete gamma function. Parametrization The parameters m and \Omega are : m = \frac , and : \Omega = \operatorname \left ^2 \right Parameter estimation An alternative way of fitting the distribution is to re-parametrize \Omega and ''m'' as ''σ'' = Ω/''m'' and ''m''. Given independent observations X_1=x_1,\ldots,X_n=x_n from the Nakagami distribution, the likelihood function is : L( \sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
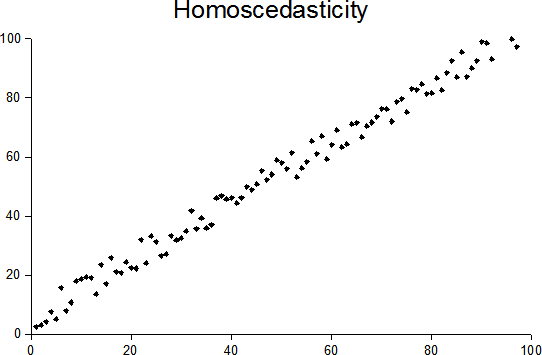
Unequal Variance
In statistics, a sequence (or a vector) of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in unbiased but inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit The goodness of fit of a statistical model describes how well it fits a set of observations. Measures of goodness of fit typically summarize the discrepancy between observed values and the values expected under the model in question. Such measure ... as measured by the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus
The fundamental theorem of calculus is a theorem that links the concept of differentiating a function (calculating its slopes, or rate of change at each time) with the concept of integrating a function (calculating the area under its graph, or the cumulative effect of small contributions). The two operations are inverses of each other apart from a constant value which depends on where one starts to compute area. The first part of the theorem, the first fundamental theorem of calculus, states that for a function , an antiderivative or indefinite integral may be obtained as the integral of over an interval with a variable upper bound. This implies the existence of antiderivatives for continuous functions. Conversely, the second part of the theorem, the second fundamental theorem of calculus, states that the integral of a function over a fixed interval is equal to the change of any antiderivative between the ends of the interval. This greatly simplifies the calculation of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Coordinate System
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system in which each point on a plane is determined by a distance from a reference point and an angle from a reference direction. The reference point (analogous to the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system) is called the ''pole'', and the ray from the pole in the reference direction is the ''polar axis''. The distance from the pole is called the ''radial coordinate'', ''radial distance'' or simply ''radius'', and the angle is called the ''angular coordinate'', ''polar angle'', or ''azimuth''. Angles in polar notation are generally expressed in either degrees or radians (2 rad being equal to 360°). Grégoire de Saint-Vincent and Bonaventura Cavalieri independently introduced the concepts in the mid-17th century, though the actual term "polar coordinates" has been attributed to Gregorio Fontana in the 18th century. The initial motivation for the introduction of the polar system was the study of circula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Integral
In mathematics (specifically multivariable calculus), a multiple integral is a definite integral of a function of several real variables, for instance, or . Integrals of a function of two variables over a region in \mathbb^2 (the real-number plane) are called double integrals, and integrals of a function of three variables over a region in \mathbb^3 (real-number 3D space) are called triple integrals. For multiple integrals of a single-variable function, see the Cauchy formula for repeated integration. Introduction Just as the definite integral of a positive function of one variable represents the area of the region between the graph of the function and the -axis, the double integral of a positive function of two variables represents the volume of the region between the surface defined by the function (on the three-dimensional Cartesian plane where ) and the plane which contains its domain. If there are more variables, a multiple integral will yield hypervolumes of multidimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |