|
Rate–distortion Optimization
Rate-distortion optimization (RDO) is a method of improving video quality in video compression. The name refers to the optimization of the amount of ''distortion'' (loss of video quality) against the amount of data required to encode the video, the ''rate''. While it is primarily used by video encoders, rate-distortion optimization can be used to improve quality in any encoding situation (image, video, audio, or otherwise) where decisions have to be made that affect both file size and quality simultaneously. Background The classical method of making encoding decisions is for the video encoder to choose the result which yields the highest quality output image. However, this has the disadvantage that the choice it makes might require more bits while giving comparatively little quality benefit. One common example of this problem is in motion estimation, and in particular regarding the use of quarter pixel-precision motion estimation. Adding the extra precision to the motion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
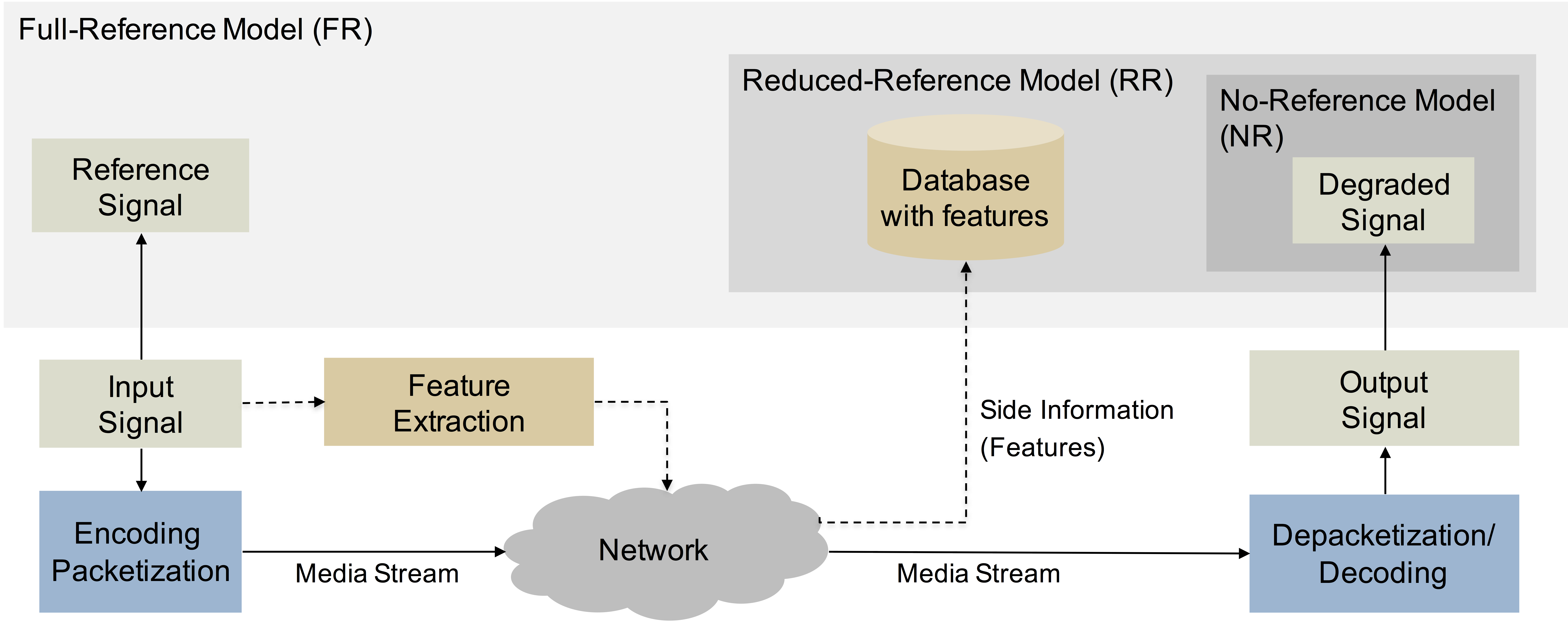
Video Quality
Video quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation (typically, compared to the original video). Video processing systems may introduce some amount of distortion or artifacts in the video signal that negatively impacts the user's perception of a system. For many stakeholders in video production and distribution, assurance of video quality is an important task. Video quality evaluation is performed to describe the quality of a set of video sequences under study. Video quality can be evaluated objectively (by mathematical models) or subjectively (by asking users for their rating). Also, the quality of a system can be determined offline (i.e., in a laboratory setting for developing new codecs or services), or in-service (to monitor and ensure a certain level of quality). From analog to digital video Since the world's first video sequence was recorded and transmitted, many video processing sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Compensation
Motion compensation in computing, is an algorithmic technique used to predict a frame in a video, given the previous and/or future frames by accounting for motion of the camera and/or objects in the video. It is employed in the encoding of video data for video compression, for example in the generation of MPEG-2 files. Motion compensation describes a picture in terms of the transformation of a reference picture to the current picture. The reference picture may be previous in time or even from the future. When images can be accurately synthesized from previously transmitted/stored images, the compression efficiency can be improved. Motion compensation is one of the two key video compression techniques used in video coding standards, along with the discrete cosine transform (DCT). Most video coding standards, such as the H.26x and MPEG formats, typically use motion-compensated DCT hybrid coding, known as block motion compensation (BMC) or motion-compensated DCT (MC DCT). Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 ASP
MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual (formally ISO/ IEC 14496-2) is a video compression format developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC standards. It uses block-wise motion compensation and a discrete cosine transform (DCT), similar to previous standards such as MPEG-1 Part 2 and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2. Several popular codecs including DivX, Xvid, and Nero Digital implement this standard. Note that MPEG-4 Part 10 defines a different format from MPEG-4 Part 2 and should not be confused with it. MPEG-4 Part 10 is commonly referred to as H.264 or AVC, and was jointly developed by ITU-T and MPEG. MPEG-4 Part 2 is H.263 compatible in the sense that a basic H.263 bitstream is correctly decoded by an MPEG-4 Video decoder. (MPEG-4 Video decoder is natively capable of decoding a basic form of H.263.) In MPEG-4 Visual, there are two types of video object layers: the video object layer that provides full MPEG-4 functionality, and a reduced functionali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xvid
Xvid (formerly "XviD") is a video codec library following the MPEG-4 video coding standard, specifically MPEG-4 Part 2 Advanced Simple Profile (ASP). It uses ASP features such as b-frames, global and quarter pixel motion compensation, lumi masking, trellis quantization, and H.263, MPEG and custom quantization matrices. Xvid is a primary competitor of the DivX Pro Codec. In contrast with the DivX codec, which is proprietary software developed by DivX, Inc., Xvid is free software distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License. This also means that unlike the DivX codec, which is only available for a limited number of platforms, Xvid can be used on all platforms and operating systems for which the source code can be compiled. History In January 2001, DivXNetworks founded ''OpenDivX'' as part of Project Mayo which was intended to be a home for open source multimedia projects. OpenDivX was an open-source MPEG-4 video codec based on a stripped-down version of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X265
x265 is a software codec for creating digital video streams in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) video compression format developed by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC). It is available as a command-line app or a software library, under the terms of GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2 or later; however, customers may request a commercial license. History x265 builds on source code from x264, an open-source video encoder for the previous MPEG video coding standard, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. The project has licensed the rights to use the x264 source code. Development on x265 began in March 2013. MulticoreWare made the source code for x265 publicly available on July 23, 2013. The x265 project was initially funded by a small group of charter licensee companies that direct the development requirements and receive commercial licenses to use x265 in their products without having to release their products under the GPL 2 license. In February 2014, x265 w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X264
x264 is a free and open-source software library and a command-line utility developed by VideoLAN for encoding video streams into the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video coding format. It is released under the terms of the GNU General Public License. History x264 was originally developed by Laurent Aimar, who stopped development in 2004 after being hired by ATEME. Loren Merritt then took over development. Later, in 2008, Fiona Glaser joined the project. They both stopped contributing in 2014. Today, x264 is primarily developed by Anton Mitrofanov and Henrik Gramner. Capabilities x264 provides a command line interface as well as an API. The former is used by many graphical user interfaces, such as Staxrip and MeGUI. The latter is used by many other interfaces, such as HandBrake and FFmpeg. x264 implements a large number of features compared to other H.264 encoders. x264 contains some psychovisual enhancements which aim to increase the subjective video quality of the encoded video. * Adapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theora
Theora is a free file format, free Lossy compression, lossy video compression format. It is developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation and distributed without licensing fees alongside their other free and open media projects, including the Vorbis audio format and the Ogg container. The libtheora video codec is the reference implementation (computing), reference implementation of the Theora video compression format being developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation. Theora is derived from the formerly Proprietary software, proprietary VP3 codec, released into the public domain by On2 Technologies. It is broadly comparable in design and bitrate efficiency to MPEG-4 Part 2, early versions of Windows Media Video, and RealVideo while lacking some of the features present in some of these other codecs. It is comparable in open standards philosophy to the BBC's Dirac (video compression format), Dirac codec. Theora is named after Theora Jones, Edison Carter's Controller on the ''Max Headroom (TV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TANDBERG Television
Ericsson Television, formerly Tandberg Television, is a company providing MPEG-4 AVC, MPEG-2 and HEVC encoding decoding and control solutions, plus stream processing, packaging, network adaption and related products, for Contribution & Distribution (C+D), IPTV, Cable, DTT, Satellite DTH and OTT. The global headquarters are located in Southampton, England, with additional offices in Rennes, France. The company was honored with its first Technology & Engineering Emmy Award in 2008 for the development of interactive Video-on-Demand infrastructure and signaling, leading to large scale VOD implementations. It was also awarded another Emmy® in 2009 for Pioneering Development of MPEG-4 AVC systems for HDTV. Then in 2011, for the Pioneering Development and Deployment of Active Format Description Technology and System. In 2013, the company acquired another Emmy® award for the Pioneering Development Of Video On Demand (VOD) Dynamic Advertising Insertion. Recently in 2014, Ericsson got ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VC-1
SMPTE 421, informally known as VC-1, is a video coding format. Most of it was initially developed as Microsoft's proprietary video format Windows Media Video 9 in 2003. With some enhancements including the development of a new Advanced Profile, it was officially approved as a SMPTE standard on April 3, 2006. It was primarily marketed as a lower-complexity competitor to the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard. After its development, several companies other than Microsoft asserted that they held patents that applied to the technology, including Panasonic, LG Electronics and Samsung Electronics. VC-1 is supported in the now-deprecated Microsoft Silverlight, the briefly-offered HD DVD disc format, and the Blu-ray Disc format. Format VC-1 is an evolution of the conventional block-based motion-compensated hybrid video coding design also found in H.261, MPEG-1 Part 2, H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2, H.263, and MPEG-4 Part 2. It was widely characterized as an alternative to the ITU-T and MPEG video cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office suite, and the Internet Explorer and Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, and Meta. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen on April 4, 1975, to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MainConcept
MainConcept GmbH is a software company founded in Germany by Markus Moenig and Thomas Zabel. They specialize in developing video/audio codecs and also applications and plug-ins related to video/audio encoding. They are a subsidiary of Endeavor Streaming, with employees in Germany, Russia, United States and Japan. History MainConcept is a video codec supplier founded in 1993 in Aachen, Germany and a board member of the MPEG Industry Forum. The Russian video codec company Elecard discussed an opportunity to become part of the company between April 2005 and August 2006. In November 2007 MainConcept became a wholly owned subsidiary of DivX, Inc. In June 2010, Sonic Solutions acquired DivX and its subsidiaries in a cash and stock deal valued at $323 million. Rovi Corporation acquired Sonic Solutions (including the MainConcept business) in February 2011 and later sold off the DivX and MainConcept businesses in April 2014. In February 2015, NeuLion, Inc. acquired DivX, LLC including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libavcodec
libavcodec is a free and open-source library of codecs for encoding and decoding video and audio data. libavcodec is an integral part of many open-source multimedia applications and frameworks. The popular MPV, xine and VLC media players use it as their main, built-in decoding engine that enables playback of many audio and video formats on all supported platforms. It is also used by the ffdshow tryouts decoder as its primary decoding library. libavcodec is also used in video editing and transcoding applications like Avidemux, MEncoder or Kdenlive for both decoding and encoding. libavcodec contains decoder and sometimes encoder implementations of several proprietary formats, including ones for which no public specification has been released. As such, a significant reverse engineering effort is part of libavcodec development. Having such codecs available within the standard libavcodec framework gives a number of benefits over using the original codecs, most notably increased po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |