|
Rancho Feliz
Rancho Feliz was a Ranchos of California, Mexican land grant in present day San Mateo County, California given in 30 April 1844 by Governor Manuel Micheltorena to Domingo Féliz. The grant extended north from Rancho Cañada de Raymundo along the San Andreas Valley, west of San Andreas Lake up to Sweeney Ridge. History Domingo Féliz (1820–??), born in San Francisco, received the one square league grant in 1844. This was also known as ''Cañada de las Auras''. With the Mexican Cession, cession of California to the United States following the Mexican–American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. As required by the Land Act of 1851, a claim for Rancho Feliz was filed with the Public Land Commission in 1852, and the grant was Land patent, patented to Domingo Féliz in 1873. In 1854 Agoston Haraszthy acquired of Rancho Feliz.Brian McGinty, 1998, ''Strong Wine: The Life and Legend of Agoston Haraszthy'', Stanford University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feliz Diseño
Feliz is a municipality ''(Municipalities of Brazil, município)'' in the Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. (Municipalities, in this case, are sections of cities/villages in Brazil, which are like counties in the United States of America.) The population of Feliz was 13,640 as of 2020. Feliz was founded in February 1959. The area of Feliz is approximately . Feliz is in the Brazilian region of South Region, Brazil, Sul, which is the southernmost region of Brazil. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchos Of California
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Mateo County, California
San Mateo County ( ), officially the County of San Mateo, is a county (United States), county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the population was 764,442. Redwood City, California, Redwood City is the county seat, and the third most populated city following Daly City, California, Daly City and San Mateo, California, San Mateo. San Mateo County is included in the San Francisco-Oakland-Berkeley, CA MSA (metropolitan statistical area), Silicon Valley, and is part of the San Francisco Bay Area, the nine counties bordering San Francisco Bay. It covers most of the San Francisco Peninsula. San Francisco International Airport is located in the northeastern area of the county and is approximately 7 miles south of the city and county limits of San Francisco, even though the airport itself is assigned a San Francisco United States Postal Service, postal address. The county's built-up areas are mostly suburban, and are home to sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel Micheltorena
Joseph Manuel María Joaquin Micheltorena y Llano (8 June 1804 – 7 September 1853) was a brigadier general of the Mexican Army, adjutant-general of the same, governor, commandant-general and inspector of the department of Las Californias, then within Mexico. Micheltorena was the last non-Californian Mexican governor before Californian native son Pío Pico took office. Personal life Micheltorena was born in 1804 in Oaxaca de Juárez, Oaxaca, Mexico, into a prominent Basque family. His parents were Army Captain Joseph Eusebio Micheltorena (who in 1819 was included among a list of notable foreigners in Mexico), and Catarina Gertrudis Llano. He was baptized at five days old at Oaxaca Cathedral. His grandparents were Joseph de Micheltorena (Mitxeltorena) and María Encarnación de Herrera (paternal), and Joseph Augustín de Llano and María Romero (maternal). Career Micheltorena was appointed governor of California by Mexican President Antonio López de Santa Anna and served from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
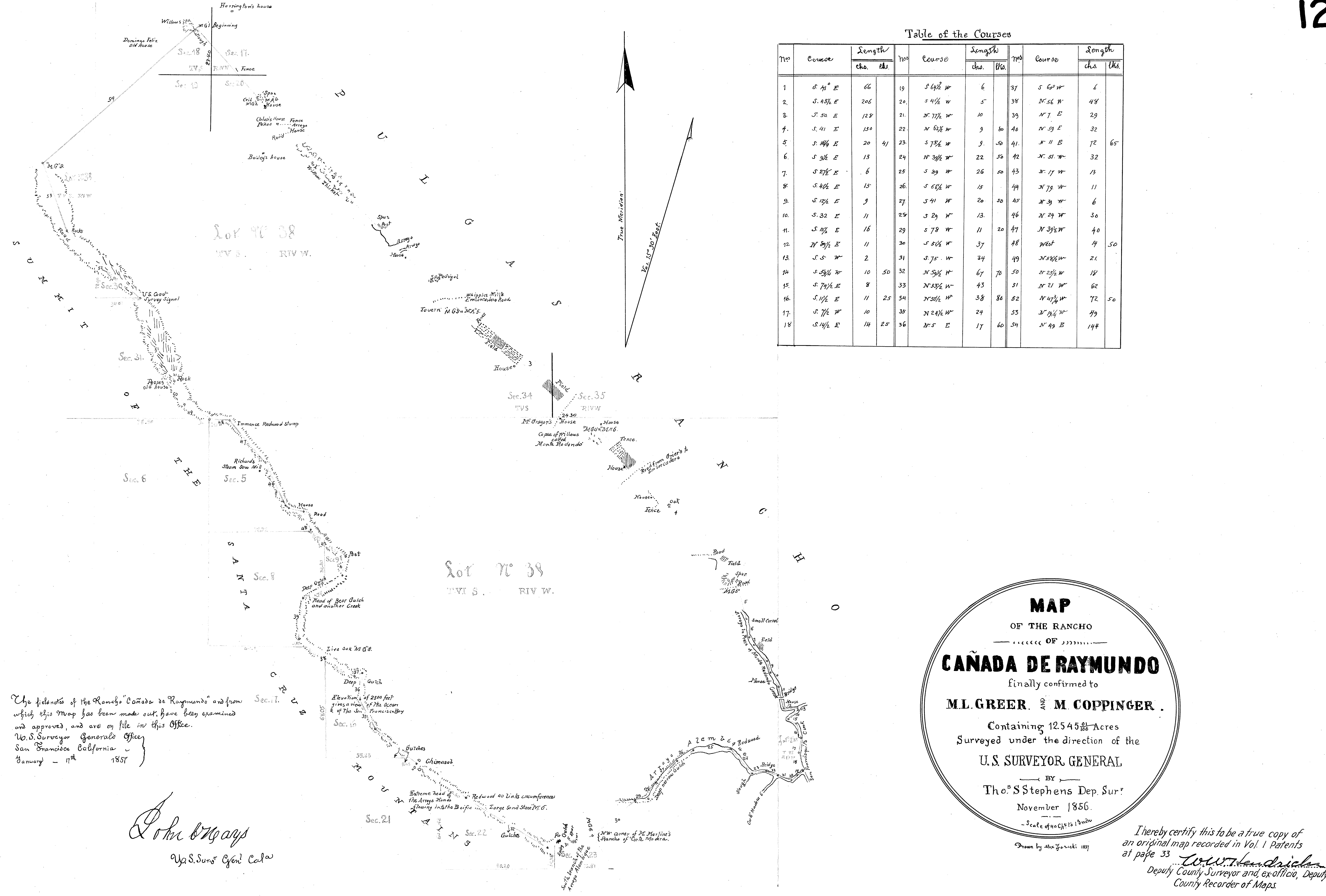
Rancho Cañada De Raymundo
Rancho Cañada de Raymundo was a Mexican land grant in present-day San Mateo County, California given August 4, 1840 to Raimundo (also known as Raymundo), a native of Baja California, who was sent out by the padres of Mission Santa Clara to capture runaway Mission Indians in 1797. On the 1856 Rancho de las Pulgas and 1868 Easton maps, the valley of Laguna Creek was referred to as the ''Cañada de Raymundo''. Laguna Creek was also alternatively known as ''Cañada Raimundo Creek''. In 1841 Rancho Cañada de Raymundo was granted to John Coppinger by Governor Juan Alvarado for helping in the revolt led by Alvarado against the Mexican authorities in Monterey. The two and one half league long by three-quarter league wide grant consisted the eastern slopes and valleys in the present-day Woodside area. The grant began at Alambique Creek, the north border of Rancho Corte de Madera, and extended north to Rancho Feliz. Rancho Cañada de Raymundo was bounded on the east by Rancho de las P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Andreas Lake
San Andreas Lake is a reservoir adjacent to the San Francisco Peninsula cities of Millbrae and San Bruno in San Mateo County, California. It is situated directly on the San Andreas Fault, which is named after the valley it is in. History After discovering San Francisco Bay from Sweeney Ridge on November 4, 1769, the Portolá expedition descended what Portolà called the ''Cañada de San Francisco'', now San Andreas Creek, to camp in the vicinity of today's San Andreas Lake. The next day they reached a "Laguna Grande" which today is covered by the Upper Crystal Springs Reservoir. The campsite is marked by California Historical Marker No. 94 "Portola Expedition Camp", located at Crystal Springs Dam, on Skyline Boulevard, 0.1 mi south of Crystal Springs Road. They camped here a second time on November 12, on their return trip. Padre Palóu, on an expedition from Monterey to explore the western side of San Francisco Bay led by Captain Fernando Rivera y Moncada, renamed Por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweeney Ridge
Sweeney Ridge, is a hilly hiking area of ridges and ravines between San Bruno, California, San Bruno and Pacifica, California, about a 25-minute drive south from San Francisco. The ridge's 1,200-foot-high summit, covered with coastal scrub and grassland, slopes down to San Francisco Bay on the east and to the Pacific Ocean on the west. The ridge is part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. Historically, the ridge is the location of the San Francisco Bay Discovery Site, commemorating the Portolá expedition's first sighting of San Francisco Bay on November 4, 1769 (expedition scouts actually made the discovery a few days earlier). Description Hiking trail access to Sweeney Ridge is available, on the Pacifica side, from the Shelldance Nursery site (Mori Ridge trail), and from the east end of Fassler Avenue (Baquiano Trail). On the San Bruno side, access the area from parking lots #2 and #4 at Skyline College (Sweeney Ridge Trail), and via a paved trail from the end of Sneath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Cession
The Mexican Cession ( es, Cesión mexicana) is the region in the modern-day southwestern United States that Mexico originally controlled, then ceded to the United States in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. This region had not been part of the areas east of the Rio Grande that had been claimed by the Republic of Texas, though the Texas annexation resolution two years earlier had not specified the southern and western boundary of the new state of Texas. At roughly , the Mexican Cession was the third-largest acquisition of territory in U.S. history, surpassed only by the Louisiana Purchase and the Alaska Purchase. Most of the area had been the Mexican territory of Alta California, while a southeastern strip on the Rio Grande had been part of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, most of whose area and population were east of the Rio Grande on land that had been claimed by the Republic of Texas since 1835, but never controlled or even approached aside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1845 American annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered its territory. Mexico refused to recognize the Velasco treaty, because it was signed by President Antonio López de Santa Anna while he was captured by the Texan Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was ''de facto'' an independent country, but most of its Anglo-American citizens wanted to be annexed by the United States. Sectional politics over slavery in the United States were preventing annexation because Texas would have been admitted as a slave state, upsetting the balance of power between Northern free states and Southern slave states. In the 1844 United States presidential election, Democrat James K. Polk was elected on a platform of expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 February 1848, in the Villa de Guadalupe Hidalgo (now a neighborhood of Mexico City) between the United States and Mexico that ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). The treaty was ratified by the United States on 10 March and by Mexico on 19 May. The ratifications were exchanged on 30 May, and the treaty was proclaimed on 4 July 1848. With the defeat of its army and the fall of its capital in September 1847, Mexico entered into negotiations with the U.S. peace envoy, Nicholas Trist, to end the war. On the Mexican side, there were factions that did not concede defeat or seek to engage in negotiations. The treaty called for the United States to pay US$15 million to Mexico and to pay off the claims of American citizens against Mex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Land Commission
The California Land Act of 1851 (), enacted following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo and the admission of California as a state in 1850, established a three-member Public Land Commission to determine the validity of prior Spanish and Mexican land grants. It required landowners who claimed title under the Mexican government to file their claim with a commission within two years. Contrary to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which guaranteed full protection of all property rights for Mexican citizens, it placed the burden on landholders to prove their title. While the commission eventually confirmed 604 of the 813 claims, almost all of the claims went to court and resulted in protracted litigation. The expense of the long court battles required many land holders to sell portions of the property or even trade it in payment for legal services. A few cases were litigated into the 1940s. Legislation California Senator William M. Gwin presented a bill that was approved by the Senate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

