|
Rancho Castac
Rancho Castac or Rancho Castec was a Mexican land grant in present-day Kern and Los Angeles counties, California, made by Governor Manuel Micheltorena to Jose Maria Covarrubias in 1843. The rancho in the Tehachapi Mountains lay between Castac Lake on the south and the present Grapevine on the north and included what is now the community of Lebec. The rancho is now a part of the Tejon Ranch. The word Castac is derived from Kashtiq, the Chumash-language name that the Chumash people gave to the area nearby. The title to Rancho Castac was granted by Governor Micheltorena in 1843 to schoolteacher and government official José María Covarrubias. With the cession of California to the United States after the Mexican-American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that existing land grants would be honored. As required by the Land Act of 1851, a claim for Rancho Castac was filed with the U.S. Public Land Commission in 1853, and the grant was patented to Covarrubi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchos Of California
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Patent
A land patent is a form of letters patent assigning official ownership of a particular tract of land that has gone through various legally-prescribed processes like surveying and documentation, followed by the letter's signing, sealing, and publishing in public records, made by a sovereign entity. It is the highest evidence of right, title, and interest to a defined area. It is usually granted by a central, federal, or state government to an individual, partnership, trust, or private company. The land patent is not to be confused with a land grant. Patented lands may be lands that had been granted by a sovereign authority in return for services rendered or accompanying a title or otherwise bestowed ''gratis'', or they may be lands privately purchased by a government, individual, or legal entity from their prior owners. "Patent" is both a process and a term. As a process, it is somewhat parallel to gaining a patent for intellectual property, including the steps of uniquely def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
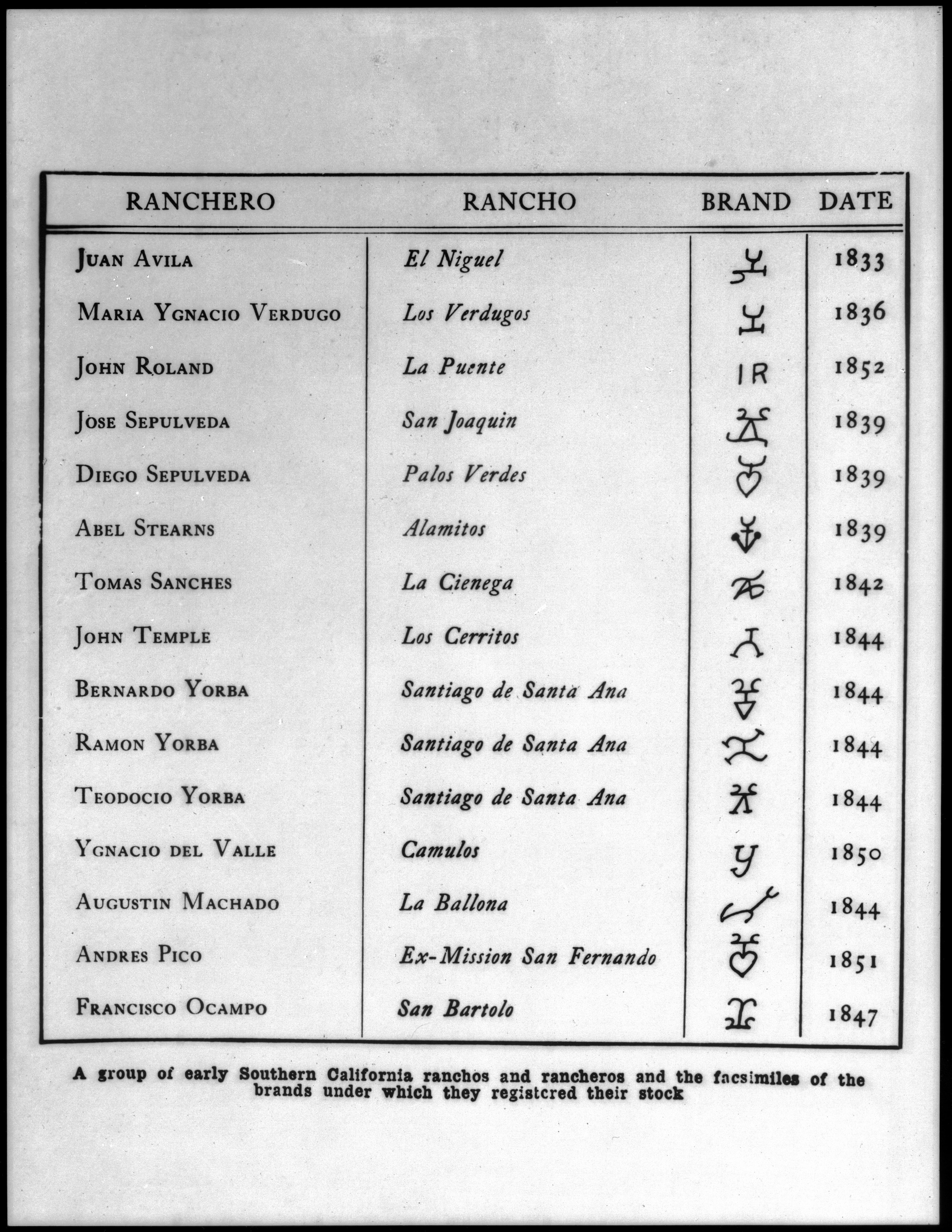
Ranchos Of Los Angeles County, California
Rancho or Ranchos may refer to: Settlements and communities *Rancho, Aruba, former fishing village and neighbourhood of Oranjestad *Ranchos of California, 19th century land grants in Alta California **List of California Ranchos *Ranchos, Buenos Aires in Argentina Schools *Rancho Christian School in Temecula, California *Rancho High School in North Las Vegas, Nevada * Rancho San Joaquin Middle School in Irvine, California *Rancho Solano Preparatory School in Scottsdale, Arizona *Rancho Verde High School in Moreno Valley, California Film *Rancho, a character in the Bollywood film ''3 Idiots'' *Rancho (monkey), an Indian monkey animal actor Other *Rancho, a shock absorber brand by Tenneco Automotive * Rancho carnavalesto or Rancho, a type of dance club from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *Rancho Los Amigos National Rehabilitation Center or Rancho *Rancho Point, a rock headland in the South Shetland Islands *Matra Rancho or Rancho, an early French leisure activity vehicle See also * * *E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchos Of Kern County, California
Rancho or Ranchos may refer to: Settlements and communities *Rancho, Aruba, former fishing village and neighbourhood of Oranjestad *Ranchos of California, 19th century land grants in Alta California **List of California Ranchos *Ranchos, Buenos Aires in Argentina Schools *Rancho Christian School in Temecula, California *Rancho High School in North Las Vegas, Nevada *Rancho San Joaquin Middle School in Irvine, California *Rancho Solano Preparatory School in Scottsdale, Arizona *Rancho Verde High School in Moreno Valley, California Film *Rancho, a character in the Bollywood film ''3 Idiots'' *Rancho (monkey), an Indian monkey animal actor Other *Rancho, a shock absorber brand by Tenneco Automotive * Rancho carnavalesto or Rancho, a type of dance club from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *Rancho Los Amigos National Rehabilitation Center or Rancho *Rancho Point, a rock headland in the South Shetland Islands *Matra Rancho or Rancho, an early French leisure activity vehicle See also * * *El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Ranchos
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ranchos Of California
These California land grants were made by Spanish (1784–1821) and Mexican (1822–1846) authorities of Las Californias and Alta California to private individuals before California became part of the United States of America.Shumway, Burgess M.,1988, ''California Ranchos: Patented Private Land Grants Listed by County'', The Borgo Press, San Bernardino, CA, Under Spain, no private land ownership was allowed, so the grants were more akin to free leases. After Mexico achieved independence, the Spanish grants became actual land ownership grants. Following the Mexican–American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. Alta California ranchos in Mexico From 1773 to 1836, the border between Alta California and Baja California was about 30 miles south of the Mexico–United States border drawn by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo that ended the Mexican–American War in 1848. Under the Siete Leyes constitutional reforms of 1836, the Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Communities Of The Tejon Pass
The Mountain Communities of the Tejon Pass, or the Frazier Mountain Communities, in the San Emigdio Mountains is a region of California that includes Lebec, Frazier Park, Lake of the Woods, Pinon Pines, and Pine Mountain Club, in Kern County, Gorman in Los Angeles County and Lockwood Valley within Kern and Ventura counties. They are all within or near the Tejon Pass, which links Southern California with the San Joaquin Valley. Also sometimes included within the communities are Cuddy Valley, Grapevine, Neenach and New Cuyama. Although the communities are divided among three counties (four, if New Cuyama, which is in Santa Barbara County, is included), they are tied together by the local newspaper, the ''Mountain Enterprise'', the Mountain Communities Chamber of Commerce, and the Ridge Route Communities Museum and Historical Society. All the communities are unincorporated areas, and all are served by their respective county agencies, such as sheriff's departments and county ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1857 Fort Tejon Earthquake
The 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake occurred at about 8:20 a.m. (Pacific time) on January 9 in central and Southern California. One of the largest recorded earthquakes in the United States, with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9, it ruptured the southern part of the San Andreas Fault for a length of about 225 miles (350 km), between Parkfield and Wrightwood. Though the shock was centered near Parkfield, the event is referred to as the Fort Tejon earthquake, because that was the location of the greatest damage. Fort Tejon is just north of the junction of the San Andreas and Garlock Faults, where the Tehachapi, San Emigdio, and Sierra Pelona Transverse Ranges come together. The earthquake is the most recent large event to occur along that portion of the San Andreas Fault, and is estimated to have had a maximum perceived intensity of IX (''Violent'') on the Modified Mercalli scale (MMI) near Fort Tejon in the Tehachapi Mountains, and along the San Andreas Fault from Mil Potre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho La Liebre
Rancho La Liebre was a Mexican land grant in present-day Kern County, California and Los Angeles County, given in 1846 by Governor Pío Pico to José María Flores. Liebre means "Hare" in Spanish and the rancho was named as such because of the abundance of jack rabbits in the area. The rancho was mostly in the mountainous terrain of the Tehachapi Mountains and Sierra Pelona Mountains, in the northwest part of Los Angeles County, west of the Antelope Valley and Mojave Desert. The rancho is now a part of the Tejon Ranch. History Flores was the commander and chief of the Mexican forces in California during the Mexican-American War. With the cession of California to the United States following the Mexican-American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. Flores nearly lost his entitlement to the rancho when the Public Land Commission declared the grant to be fraudulently obtained. The Land Commission contended that Pico back dated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho El Tejon
Rancho or Ranchos may refer to: Settlements and communities *Rancho, Aruba, former fishing village and neighbourhood of Oranjestad *Ranchos of California, 19th century land grants in Alta California **List of California Ranchos *Ranchos, Buenos Aires in Argentina Schools *Rancho Christian School in Temecula, California *Rancho High School in North Las Vegas, Nevada *Rancho San Joaquin Middle School in Irvine, California *Rancho Solano Preparatory School in Scottsdale, Arizona *Rancho Verde High School in Moreno Valley, California Film *Rancho, a character in the Bollywood film ''3 Idiots'' *Rancho (monkey), an Indian monkey animal actor Other *Rancho, a shock absorber brand by Tenneco Automotive * Rancho carnavalesto or Rancho, a type of dance club from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *Rancho Los Amigos National Rehabilitation Center or Rancho *Rancho Point, a rock headland in the South Shetland Islands *Matra Rancho or Rancho, an early French leisure activity vehicle See also * * *El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Los Alamos Y Agua Caliente
Rancho Los Alamos y Agua Caliente was a Mexican land grant in present day Kern County, California given in 1846 by Governor Pio Pico to Francisco Lopes, Luis Jordan and Vicente Botiller. The name means "Cottonwoods and Hot Springs Ranch" in Spanish. The native riparian Fremont Cottonwood ''(Populus fremontii)'' grow around natural springs. Rancho Los Alamos y Agua Caliente lay between two other Mexican Land Grants in the Tehachapi Mountains, Rancho El Tejon and Rancho Castac. The rancho is now a part of the Tejon Ranch. History A grant was made to Pedro Carrillo by Governor Manuel Micheltorena in 1843, that included Hungry Valley, Cañada de los Alamos and Peace Valley, the later area of the Hungry Valley State Vehicular Recreation Area, Gorman and the Tejon Pass (then called Portezuela de Castac or Castac Pass), but Carrillo failed to comply with any of its conditions. In 1846, Governor Pío Pico declared that, "Taking into consideration the seven months granted to citi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Fitzgerald Beale
Edward Fitzgerald "Ned" Beale (February 4, 1822 – April 22, 1893) was a national figure in the 19th-century United States. He was a naval officer, military general, explorer, frontiersman, Indian affairs superintendent, California rancher, diplomat, and friend of Kit Carson, Buffalo Bill Cody and Ulysses S. Grant. He fought in the United States-Mexican War, emerging as a hero of the Battle of San Pasqual in 1846. He achieved national fame in 1848 in carrying to the east the first gold samples from California, contributing to the gold rush. In the late 1850s, Beale surveyed and built Beale's Wagon Road, which many settlers used to move to the West, and which became part of Route 66 and the route for the Transcontinental railroad. As California's first Superintendent of Indian Affairs, Beale helped charter a humanitarian policy towards Native Americans in the 1850s. He also founded the Tejon Ranch, the largest private landholding in California, and became a millionaire severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |