|
Rancho Carne Humana
Rancho Carne Humana was a Mexican land grant in present-day Napa County, California, given in 1841 by Governor Juan Alvarado to Edward Turner Bale. The name means "human flesh" in Spanish. There is speculation as to why the name was chosen. The grant was originally known to the native residents as "Huilic Noma" and also "Colijolmanoc". One naming theory speculates that Bale, in a bit of black humor, twisted "Colijolmanoc" into the similar-sounding Spanish "Carne Humana". Rancho Carne Humana was at the northern end of the Napa Valley, stretching from present-day Rutherford northward to Calistoga, ending at Tubbs Lane and including present-day St. Helena. History Dr. Edward Turner Bale (1810-1849), an English physician, landed at Monterey in 1837, and practiced medicine there for five or six years. In 1840–43 he was surgeon of the California forces by General Mariano Vallejo's appointment. He married Maria Ygnacia Soberanes, the niece of both General Mariano Vallejo and Mari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchos Of California
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 February 1848, in the Villa de Guadalupe Hidalgo (now a neighborhood of Mexico City) between the United States and Mexico that ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). The treaty was ratified by the United States on 10 March and by Mexico on 19 May. The ratifications were exchanged on 30 May, and the treaty was proclaimed on 4 July 1848. With the defeat of its army and the fall of its capital in September 1847, Mexico entered into negotiations with the U.S. peace envoy, Nicholas Trist, to end the war. On the Mexican side, there were factions that did not concede defeat or seek to engage in negotiations. The treaty called for the United States to pay US$15 million to Mexico and to pay off the claims of American citizens against Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
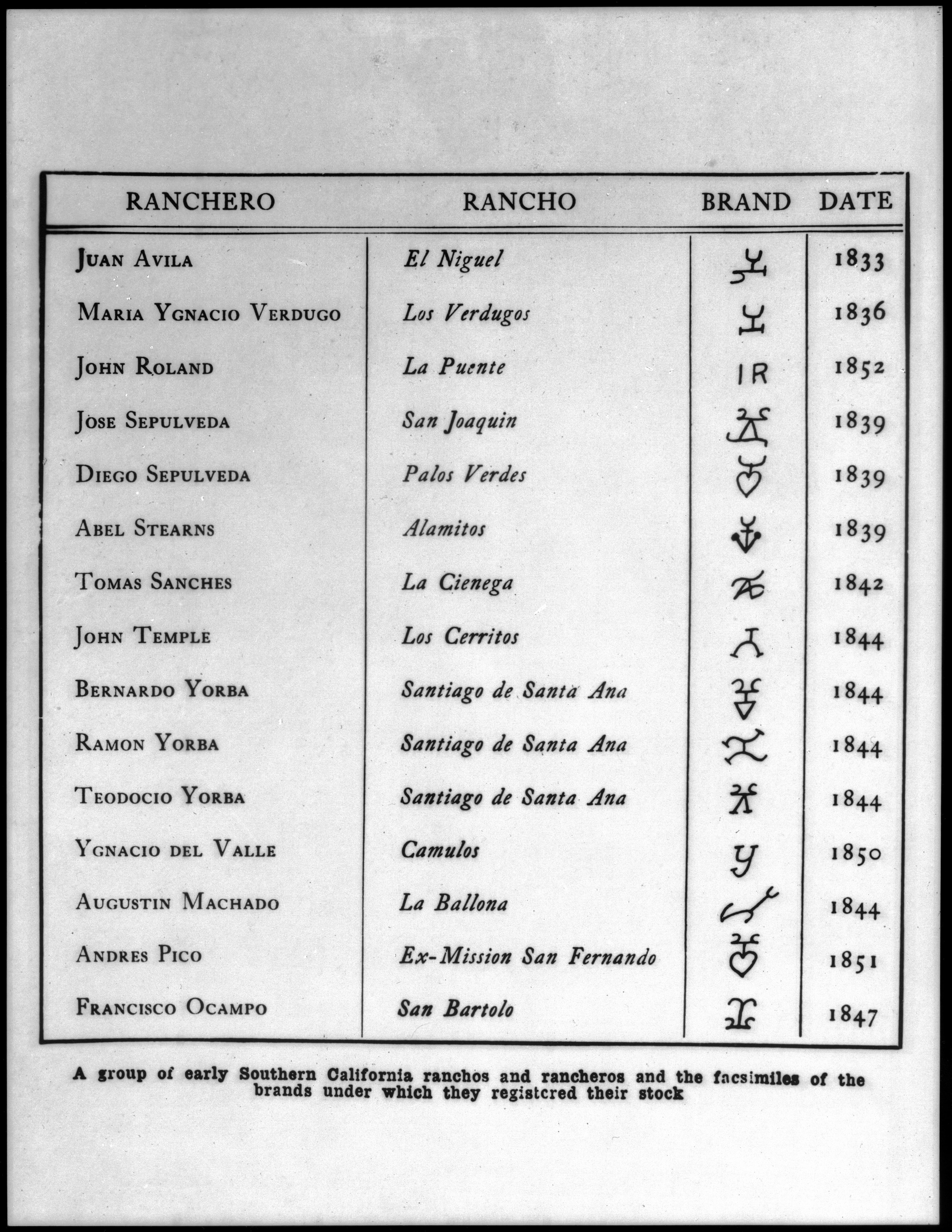
Ranchos Of Napa County, California
Rancho or Ranchos may refer to: Settlements and communities *Rancho, Aruba, former fishing village and neighbourhood of Oranjestad *Ranchos of California, 19th century land grants in Alta California **List of California Ranchos *Ranchos, Buenos Aires in Argentina Schools *Rancho Christian School in Temecula, California *Rancho High School in North Las Vegas, Nevada *Rancho San Joaquin Middle School in Irvine, California *Rancho Solano Preparatory School in Scottsdale, Arizona *Rancho Verde High School in Moreno Valley, California Film *Rancho, a character in the Bollywood film ''3 Idiots'' *Rancho (monkey), an Indian monkey animal actor Other *Rancho, a shock absorber brand by Tenneco Automotive * Rancho carnavalesto or Rancho, a type of dance club from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *Rancho Los Amigos National Rehabilitation Center or Rancho *Rancho Point, a rock headland in the South Shetland Islands *Matra Rancho or Rancho, an early French leisure activity vehicle See also * * *El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Ranchos
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ranchos Of California
These California land grants were made by Spanish (1784–1821) and Mexican (1822–1846) authorities of Las Californias and Alta California to private individuals before California became part of the United States of America.Shumway, Burgess M.,1988, ''California Ranchos: Patented Private Land Grants Listed by County'', The Borgo Press, San Bernardino, CA, Under Spain, no private land ownership was allowed, so the grants were more akin to free leases. After Mexico achieved independence, the Spanish grants became actual land ownership grants. Following the Mexican–American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. Alta California ranchos in Mexico From 1773 to 1836, the border between Alta California and Baja California was about 30 miles south of the Mexico–United States border drawn by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo that ended the Mexican–American War in 1848. Under the Siete Leyes constitutional reforms of 1836, the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Pacific Railroad
The California Pacific Railroad Company (abbreviated Cal. P. R. R. or Cal-P) was incorporated in 1865 at San Francisco, California as the California Pacific ''Rail Road'' Company. It was renamed the California Pacific Railroad ''Extension'' Company in the spring of 1869, then renamed the California Pacific Railroad later that same year. Its main railroad from Vallejo to Sacramento was completed six months prior to the May 1869 golden spike ceremony of the Central Pacific/Union Pacific Transcontinental Railway. Beginning January 1869, the company operated a passenger ferryboat (''New World'') from San Francisco to Vallejo and thence a railroad to Sacramento. It also had a branch from Adelante (later Napa Junction, now American Canyon) to Calistoga and another from Davis to Marysville. The Cal-P operated independently from 1865 to 1876. It was then operated by the Central Pacific and was finally sold to the Southern Pacific. Amtrak's ''Capitol Corridor'' follows the original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartleson–Bidwell Party
In 1841, the Bartleson–Bidwell Party, led by Captain John Bartleson and John Bidwell, became the first American emigrants to attempt a wagon crossing from Missouri to California. Beginnings In the winter of 1840, the Western Emigration Society was founded in Missouri, with 500 pledging to trek west into Mexican California. Members included Baldridge, Barnett, Bartleson, Bidwell and Nye. Organized on 18 May 1841, Talbot H. Green was elected president, John Bidwell secretary, and John Bartleson captain. The group joined Father Pierre Jean De Smet's Jesuit missionary group, led by Thomas F. Fitzpatrick, westward across South Pass along the Oregon Trail. That trail took them past Courthouse and Jail Rocks, Chimney Rock, Scotts Bluff, Fort Laramie, and Independence Rock. The Bartleson-Bidwell party separated from Fitzpatrick, and the missionary group, at Soda Springs on 11 Aug. The Trail The western Emigration Society had resolved to follow the route suggested by Dr. John Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Brannan
Samuel Brannan (March 2, 1819 – May 5, 1889) was an American settler, businessman, journalist, and prominent Mormon who founded the '' California Star'', the first newspaper in San Francisco, California. He is considered the first to publicize the California Gold Rush and was its first millionaire. He used the profits from his stores to buy large tracts of real estate. He helped form the first vigilance committee in San Francisco and was disfellowshiped from the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) because of his actions within the vigilance committee. Brannan's wife divorced him and he was forced to liquidate much of his real estate to pay her one-half of their assets. He died poor and in relative obscurity. Early life Brannan was born in Saco, Maine, to Thomas and Sara Emery Brannan. In order to escape his abusive father, Brannan moved with his sister (Mary Ann) and her husband (Alexander) to Painesville, Ohio when he was fourteen years old. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bale Grist Mill State Historic Park
Bale Grist Mill State Historic Park is a California state park located in Napa County between St. Helena and Calistoga. The park is the site of a water-powered grist mill that was built in 1846 is one of only two water-driven mills remaining west of the Mississippi River. History The mill was established in 1846 by Dr. Edward Turner Bale on property in Rancho Carne Humana land grant. Bale lived near the site until his death in 1849. The gristmill and granary were built with local materials, Douglas firs and coast redwoods. Some timbers were cut to length with the bark left on, while others were roughed out with hand tools. The timbers were notched and held in place with wooden pegs as well as nails and screws. The foundation of the structure is native stone. The mill was powered by a waterwheel, with water diverted from Mill Creek nearby. A ditch carried the water from a millpond to a wooden flume, which brought the water to the top of the waterwheel. The first wheel did no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Krug
Charles Krug (1825–1892) was among the pioneers of winemaking in the Napa Valley, California, and was the founder of the Charles Krug Winery. Biography Charles Krug visited the United States from Prussia in 1847, and became a citizen in 1852. In 1851 he served as an apprentice winemaker for Agoston Haraszthy and then John Patchett before establishing his own winery. Krug married Carolina Bale, the daughter of early Napa Valley pioneer and miller Edward Turner Bale and granddaughter of María Isidora Vallejo of the prominent Californio Vallejo family, on December 26, 1860. Krug was inducted into the Culinary Institute of America's Vintner's Hall of Fame in 2007. Winemaking The dowry Bale left for her included of land north of St. Helena, California, on which Krug planted a vineyard and founded his winery in 1861. Charles Krug introduced innovative ideas in winemaking to California. He began making wine using a cider press for pressing, carefully selected rootstocks, variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Patent
A land patent is a form of letters patent assigning official ownership of a particular tract of land that has gone through various legally-prescribed processes like surveying and documentation, followed by the letter's signing, sealing, and publishing in public records, made by a sovereign entity. It is the highest evidence of right, title, and interest to a defined area. It is usually granted by a central, federal, or state government to an individual, partnership, trust, or private company. The land patent is not to be confused with a land grant. Patented lands may be lands that had been granted by a sovereign authority in return for services rendered or accompanying a title or otherwise bestowed ''gratis'', or they may be lands privately purchased by a government, individual, or legal entity from their prior owners. "Patent" is both a process and a term. As a process, it is somewhat parallel to gaining a patent for intellectual property, including the steps of uniquely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Land Commission
The California Land Act of 1851 (), enacted following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo and the admission of California as a state in 1850, established a three-member Public Land Commission to determine the validity of prior Spanish and Mexican land grants. It required landowners who claimed title under the Mexican government to file their claim with a commission within two years. Contrary to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which guaranteed full protection of all property rights for Mexican citizens, it placed the burden on landholders to prove their title. While the commission eventually confirmed 604 of the 813 claims, almost all of the claims went to court and resulted in protracted litigation. The expense of the long court battles required many land holders to sell portions of the property or even trade it in payment for legal services. A few cases were litigated into the 1940s. Legislation California Senator William M. Gwin presented a bill that was approved by the Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |