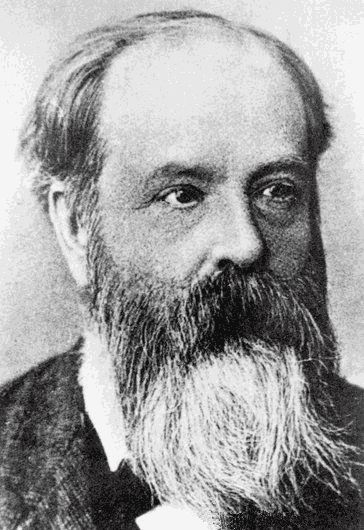|
Ralph Kenna
Professor Ralph Kenna (born 27 August 1964 – died 26 October 2023) was an Irish mathematician and theoretical physicist who was head of the statistical physics research group at Coventry University. He was a specialist in statistical physics, complex systems and Irish mythology. Early life and education Kenna was born in Athlone, on the border between counties Roscommon and Westmeath, Ireland, on 27 August 1964. He attended Marist College, Athlone (best leaving certificate, class of 1981) and obtained his B.A. (mod) degree in Theoretical Physics from Trinity College Dublin in 1985. He also obtained his M.Sc. (1988) from Trinity College Dublin. He completed his PhD (Dr. rer. nat.) at the University of Graz under Professor Christian Lang in 1993. Career Kenna was an EU Marie Curie Research Fellow at the University of Liverpool from 1994 to 1997 and at Trinity College Dublin from 1997 to 1999. He lectured at Trinity from 1998 to 2002, when he moved to Coventry Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coventry University
, mottoeng = By Art and Industry , established = , type = Public , endowment = £28 million (2015) , budget = £787.5 million , chancellor = Margaret Casely-Hayford , vice_chancellor = John Latham , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Coventry , country = England , campus = Urban, CU London , coordinates = , former_names = Coventry Polytechnic (1987–1992)Lanchester Polytechnic (1970–1987) , colours = Coventry Blue , website = , logo = File:Coventry_University_logo.svg , image_name = File:Coventry_University_coat_of_arms_(updated).png , image_size = 150px , caption = Coat of arms of Coventry University , faculty = 1,890 , affiliations = Coventry University is a public research university in Coventry, England. The origins of Coventry University can be linked to the founding of the Coventry School of Design in 1843. It was known as Lanchester Polytechnic from 1970 until 1987, and then as Coventry Polytechnic until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Poetry
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. Etymology The English word ''epic'' comes from Latin ''epicus'', which itself comes from the Ancient Greek adjective (''epikos''), from (''epos''), "word, story, poem." In ancient Greek, 'epic' could refer to all poetry in dactylic hexameter (''epea''), which included not only Homer but also the wisdom poetry of Hesiod, the utterances of the Delphic oracle, and the strange theological verses attributed to Orpheus. Later tradition, however, has restricted the term 'epic' to ''heroic epic'', as described in this article. Overview Originating before the invention of writing, primary epics, such as those of Homer, were composed by bards who used complex rhetorical and metrical schemes by which they could memorize the epic as received i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Mass
In nuclear engineering, a critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties (specifically, its nuclear fission cross-section), density, shape, enrichment, purity, temperature, and surroundings. The concept is important in nuclear weapon design. Explanation of criticality When a nuclear chain reaction in a mass of fissile material is self-sustaining, the mass is said to be in a ''critical'' state in which there is no increase or decrease in power, temperature, or neutron population. A numerical measure of a critical mass is dependent on the effective neutron multiplication factor , the average number of neutrons released per fission event that go on to cause another fission event rather than being absorbed or leaving the material. When ''k'' = 1, the mass is critical, and the chain reaction is self-sustaining. A ''subcritical'' mass is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Physics
The Institute of Physics (IOP) is a UK-based learned society and professional body that works to advance physics education, research and application. It was founded in 1874 and has a worldwide membership of over 20,000. The IOP is the Physical Society for the UK and Ireland and supports physics in education, research and industry. In addition to this, the IOP provides services to its members including careers advice and professional development and grants the professional qualification of Chartered Physicist (CPhys), as well as Chartered Engineer (CEng) as a nominated body of the Engineering Council. The IOP's publishing company, IOP Publishing, publishes 85 academic titles. History The Institute of Physics was formed in 1960 from the merger of the Physical Society, founded as the Physical Society of London in 1874, and the Institute of Physics, founded in 1918. The Physical Society of London had been officially formed on 14 February 1874 by Frederick Guthrie, following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale-free Network
A scale-free network is a network whose degree distribution follows a power law, at least asymptotically. That is, the fraction ''P''(''k'') of nodes in the network having ''k'' connections to other nodes goes for large values of ''k'' as : P(k) \ \sim \ k^\boldsymbol where \gamma is a parameter whose value is typically in the range 2<\gamma<3 (wherein the second moment () of is infinite but the first moment is finite), although occasionally it may lie outside these bounds. Many networks have been reported to be scale-free, although statistical analysis has refuted many of these claims and seriously questioned others. Additionally, some have argued that simply knowing that a degree-distribution is [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Model
A spin model is a mathematical model used in physics primarily to explain magnetism. Spin models may either be classical or quantum mechanical in nature. Spin models have been studied in quantum field theory as examples of integrable models. Spin models are also used in quantum information theory and computability theory in theoretical computer science. The theory of spin models is a far reaching and unifying topic that cuts across many fields. Introduction In ordinary materials, the magnetic dipole moments of individual atoms produce magnetic fields that cancel one another, because each dipole points in a random direction. Ferromagnetic materials below their Curie temperature, however, exhibit magnetic domains in which the atomic dipole moments are locally aligned, producing a macroscopic, non-zero magnetic field from the domain. These are the ordinary "magnets" with which we are all familiar. The study of the behavior of such "spin models" is a thriving area of research in con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percolation Theory
In statistical physics and mathematics, percolation theory describes the behavior of a network when nodes or links are added. This is a geometric type of phase transition, since at a critical fraction of addition the network of small, disconnected clusters merge into significantly larger connected, so-called spanning clusters. The applications of percolation theory to materials science and in many other disciplines are discussed here and in the articles network theory and percolation. Introduction A representative question (and the source of the name) is as follows. Assume that some liquid is poured on top of some porous material. Will the liquid be able to make its way from hole to hole and reach the bottom? This physical question is modelled mathematically as a three-dimensional network of vertices, usually called "sites", in which the edge or "bonds" between each two neighbors may be open (allowing the liquid through) with probability , or closed with probability , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review E
''Physical Review E'' is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal, published monthly by the American Physical Society. The main field of interest is collective phenomena of many-body systems. It is currently edited by Uwe C. Täuber. While original research content requires subscription, editorials, news, and other non-research content is openly accessible. Scope Although the focus of this journal is many-body phenomena, the broad scope of the journal includes quantum chaos, soft matter physics, classical chaos, biological physics and granular materials. Also emphasized are statistical physics, equilibrium and transport properties of fluids, liquid crystals, complex fluids, polymers, chaos, fluid dynamics, plasma physics, classical physics, and computational physics. About Physical Review E APS. July 2010 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theories to develop mathematical models. The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koppa (letter)
Koppa or qoppa (; as a modern numeral sign: ) is a letter that was used in early forms of the Greek alphabet, derived from Phoenician qoph (). It was originally used to denote the sound, but dropped out of use as an alphabetic character in favor of Kappa (Κ). It has remained in use as a numeral symbol (90) in the system of Greek numerals, although with a modified shape. Koppa is the source of Latin Q, as well as the Cyrillic numeral sign of the same name ( Koppa). Alphabetic In Phoenician, qoph was pronounced ; in Greek, which lacked such a sound, it was instead used for before back vowels Ο, Υ and Ω. In this function, it was borrowed into the Italic alphabets and ultimately into Latin. However, as the sound had two redundant spellings, koppa was eventually replaced by kappa (Κ) in Greek. It remained in use as a letter in some Doric regions into the 5th century BC. The koppa was used as a symbol for the city of Corinth, which had the early spelling of . Numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Exponent
Critical or Critically may refer to: *Critical, or critical but stable, medical states **Critical, or intensive care medicine *Critical juncture, a discontinuous change studied in the social sciences. *Critical Software, a company specializing in mission and business critical information systems * Critical theory, a school of thought that critiques society and culture by applying knowledge from the social sciences and the humanities * Critically endangered, a risk status for wild species *Criticality (status), the condition of sustaining a nuclear chain reaction Art, entertainment, and media * ''Critical'' (novel), a medical thriller written by Robin Cook * ''Critical'' (TV series), a Sky 1 TV series * "Critical" (''Person of Interest''), an episode of the American television drama series ''Person of Interest'' *"Critical", a 1999 single by Zion I People *Cr1TiKaL (born 1994), an American YouTuber and Twitch streamer See also * Critic *Criticality (other) *Critical Condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Physics B
Nuclear may refer to: Physics Relating to the nucleus of the atom: *Nuclear engineering *Nuclear physics *Nuclear power Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ... *Nuclear reactor *Nuclear weapon *Nuclear medicine *Radiation therapy *Nuclear warfare Mathematics *Nuclear space *Nuclear operator *Nuclear congruence *Nuclear C*-algebra Biology Relating to the Cell nucleus, nucleus of the cell: * Nuclear DNA Society *Nuclear family, a family consisting of a pair of adults and their children Music *Nuclear (band), "Nuclear" (band), group music. *Nuclear (Ryan Adams song), "Nuclear" (Ryan Adams song), 2002 *"Nuclear", a song by Mike Oldfield from his ''Man on the Rocks'' album *Nu.Clear (EP), ''Nu.Clear'' (EP) by South Korean girl group CLC See also *Nucleus (disambigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |