|
Radioactive Contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is unintended or undesirable (from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) definition). Such contamination presents a hazard because the radioactive decay of the contaminants, produces ionizing radiation (namely alpha, beta, gamma rays and free neutrons). The degree of hazard is determined by the concentration of the contaminants, the energy of the radiation being emitted, the type of radiation, and the proximity of the contamination to organs of the body. It is important to be clear that the contamination gives rise to the radiation hazard, and the terms "radiation" and "contamination" are not interchangeable. The sources of radioactive pollution can be classified into two groups: natural and man-made. Following an atmospheric nuclear weapon discharge or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanford N Reactor Adjusted
Hanford may refer to: Places *Hanford (constituency), a constituency in Tuen Mun, People's Republic of China *Hanford, Dorset, a village and parish in England *Hanford, Staffordshire, England *Hanford, California, United States *Hanford, Iowa, United States *Hanford, Washington, a community depopulated by the U.S. government in March 1943 Schools * Hanford School, a school in Hanford, Dorset * Hanford High School, a high school in Richland, Washington Other uses *Hanford (surname) *Hanford Site, a nuclear complex *Hanford Tri-State Airlines or Mid-Continent Airlines *USS Hanford, USS ''Hanford'' People with the given name * Hanford Dixon (born 1958), American football player and sports announcer * Hanford MacNider (1889–1968), American diplomat and US Army General See also *Handford, a surname *Hanford Carnegie Museum *Hanford Reach, a free-flowing section of the Columbia River *Hanford Reach National Monument {{disambiguation, geo, given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fission Product
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release of heat energy (kinetic energy of the nuclei), and gamma rays. The two smaller nuclei are the ''fission products''. (See also Fission products (by element)). About 0.2% to 0.4% of fissions are ternary fissions, producing a third light nucleus such as helium-4 (90%) or tritium (7%). The fission products themselves are usually unstable and therefore radioactive. Due to being relatively neutron-rich for their atomic number, many of them quickly undergo beta decay. This releases additional energy in the form of beta particles, antineutrinos, and gamma rays. Thus, fission events normally result in beta and gamma radiation, even though this radiation is not produced directly by the fission event itself. The produced radionuclides have varyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinides In The Environment
Environmental radioactivity is not limited to actinides; non-actinides such as radon and radium are of note. While all actinides are radioactive, there are a lot of actinides or actinide-relating minerals in the Earth's crust such as uranium and thorium. These minerals are helpful in many ways, such as carbon-dating, most detectors, X-rays, and more. Inhalation versus ingestion Generally, ingested insoluble actinide compounds, such as high-fired uranium dioxide and mixed oxide (MOX) fuel, will pass through the digestive system with little effect since they cannot dissolve and be absorbed by the body. Inhaled actinide compounds, however, will be more damaging as they remain in the lungs and irradiate the lung tissue. Ingested low-fired oxides and soluble salts such as nitrate can be absorbed into the blood stream. If they are inhaled then it is possible for the solid to dissolve and leave the lungs. Hence, the dose to the lungs will be lower for the soluble form. Actinium Actin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing is the chemical separation of fission products and actinides from spent nuclear fuel. Originally, reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing nuclear weapons. With commercialization of nuclear power, the reprocessed plutonium was recycled back into MOX nuclear fuel for thermal reactors. The reprocessed uranium, also known as the spent fuel material, can in principle also be re-used as fuel, but that is only economical when uranium supply is low and prices are high. A breeder reactor is not restricted to using recycled plutonium and uranium. It can employ all the actinides, closing the nuclear fuel cycle and potentially multiplying the energy extracted from natural uranium by about 60 times. Reprocessing must be highly controlled and carefully executed in advanced facilities by highly specialized personnel. Fuel bundles which arrive at the sites from nuclear power plants (after having cooled down for several years) are completely dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in flash lamps and arc lamps, and as a general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft. Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System. Radioactive xenon-135 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goiânia Accident
The Goiânia accident was a radioactive contamination accident that occurred on September 13, 1987, in Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil, after a forgotten radiotherapy source was stolen from an abandoned hospital site in the city. It was subsequently handled by many people, resulting in four deaths. About 112,000 people were examined for radioactive contamination and 249 of them were found to have been contaminated. In the consequent cleanup operation, topsoil had to be removed from several sites, and several houses were demolished. All the objects from within those houses, including personal possessions, were seized and incinerated. ''Time'' magazine has identified the accident as one of the world's "worst nuclear disasters" and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) called it "one of the world's worst radiological incidents". Description of the source The radiation source in the Goiânia accident was a small capsule containing about of highly radioactive caesium chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitting from within the body rather than radiation that is generated by external sources like X-rays. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine. Diagnostic medical imaging Diagnostic In nuclear medicine imaging, radiopharmaceuticals are taken internally, for example, through inhalation, intravenously or orally. Then, external detectors (gamma cameras) capture and form images from the radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceuticals. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Bomb Spike
Carbon-14, C-14, or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic materials is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and colleagues (1949) to date archaeological, geological and hydrogeological samples. Carbon-14 was discovered on February 27, 1940, by Martin Kamen and Sam Ruben at the University of California Radiation Laboratory in Berkeley, California. Its existence had been suggested by Franz Kurie in 1934. There are three naturally occurring isotopes of carbon on Earth: carbon-12 (), which makes up 99% of all carbon on Earth; carbon-13 (), which makes up 1%; and carbon-14 (), which occurs in trace amounts, making up about 1 or 1.5 atoms per 1012 atoms of carbon in the atmosphere. Carbon-12 and carbon-13 are both stable, while carbon-14 is unstable and has a half-life of 5,730 ± 40 years. Carbon-14 decays into nitrogen-14 () through beta decay. A gram of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayak Disaster
The Kyshtym disaster, sometimes referred to as the Mayak disaster or Ozyorsk disaster in newer sources, was a radioactive contamination accident that occurred on 29 September 1957 at Mayak, a plutonium production site for nuclear weapons and nuclear fuel reprocessing plant located in the closed city of Chelyabinsk-40 (now Ozyorsk) in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union. The disaster is the third-worst nuclear incident (by radioactivity released) after the Chernobyl disaster and the Fukushima Daiichi disaster. It measured as a Level 6 disaster on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES), making it the third-highest on the INES (which ranks by population impact), behind the Chernobyl disaster, which resulted in the evacuation of 335,000 people, and the Fukushima Daiichi disaster, which resulted in the evacuation of 154,000 people; the Chernobyl disaster and the Fukushima Daiichi disaster are both Level 7 disasters on the INES. At least 22 villages were exposed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chernobyl Disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuclear energy accidents rated at seven—the maximum severity—on the International Nuclear Event Scale, the other being the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan. The initial emergency response, together with later decontamination of the environment, involved more than 500,000 personnel and cost an estimated 18 billion roubles—roughly US$68 billion in 2019, adjusted for inflation. The accident occurred during a safety test meant to measure the ability of the steam turbine to power the emergency feedwater pumps of an RBMK-type nuclear reactor in the event of a simultaneous loss of external power and major coolant leak. During a planned decrease of reactor power in preparation for the test, the operators accidentally dropp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
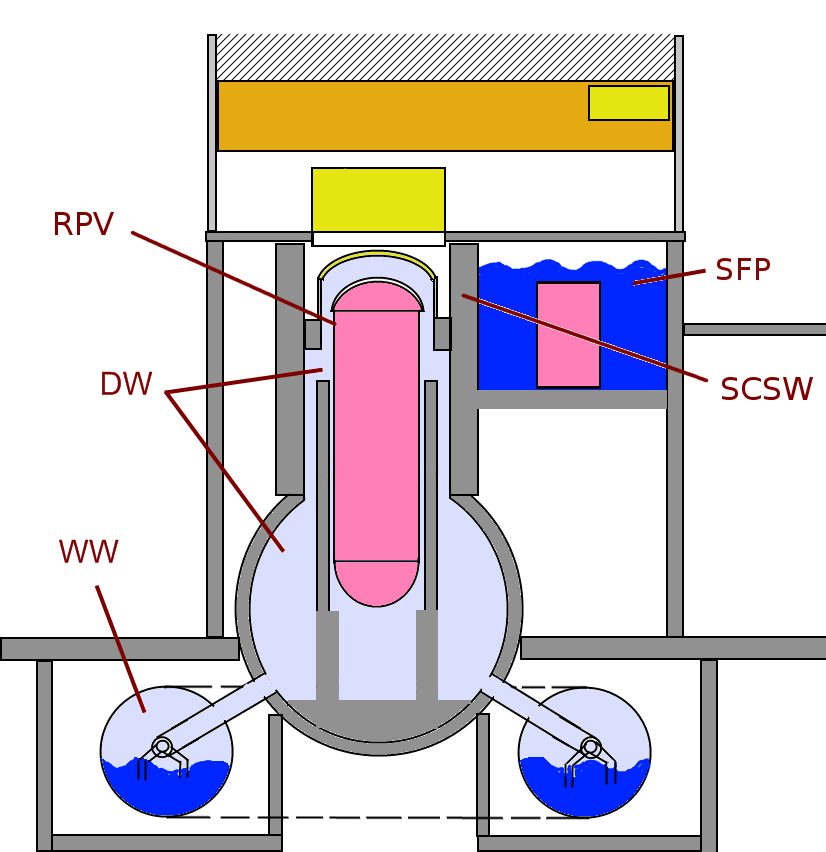
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and remains the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan. The earthquake triggered a powerful tsunami, with 13–14-meter-high waves damaging the nuclear power plant's emergency diesel generators, leading to a loss of electric power. The result was the most severe nuclear accident since the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, classified as level seven on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES) after initially being classified as level five, and thus joining Chernobyl as the only other accident to receive such classification. While the 1957 explosion at the Mayak facility was the second worst by radioactivity released, the INES ranks incidents by impact on population, so Chernobyl (335,000 people evacuated) and Fukushima (154,000 evacuate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Contamination From The Rocky Flats Plant
The Rocky Flats Plant, a former U.S. nuclear weapons production facility located about 15 miles northwest of Denver, caused radioactive (primarily plutonium, americium, and uranium) contamination within and outside its boundaries. The contamination primarily resulted from two major plutonium fires in 1957 and 1969 (plutonium is pyrophoric, and shavings can spontaneously combust) and from wind-blown plutonium that leaked from barrels of radioactive waste. Much lower concentrations of radioactive isotopes were released throughout the operational life of the plant from 1952 to 1992, from smaller accidents and from normal operational releases of plutonium particles too small to be filtered. Prevailing winds from the plant carried airborne contamination south and east, into populated areas northwest of Denver. The contamination of the Denver area by plutonium from the fires and other sources was not publicly reported until the 1970s. According to a 1972 study coauthored by Edward Marte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |