|
Radio Research Laboratory (Harvard)
The Radio Research Laboratory (RRL), located on the campus of Harvard University, was an 800-person secret research laboratory during World War II. Under the U.S. Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), it was a spinoff of the Radiation Laboratory (Rad Lab) at MIT, and set up to develop electronic countermeasures to enemy radars and communications, as well as electronic counter-countermeasures (ECCM) to circumvent enemy ECM. The RRL was directed by Frederick E. Terman and operated between 1942 and 1946. The RRL was engaged in both analysis and hardware development. They made significant contributions to the basic understanding of methods, theories, and circuits at very-high and ultra-high frequencies for radio systems, particularly in signals intelligence gear and statistical communications techniques. However, unlike the Rad Lab, the RRL never released significant details on its accomplishments; ECM and ECCM have always been closely guarded secrets by all nations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Scientific Research And Development
The Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) was an agency of the United States federal government created to coordinate scientific research for military purposes during World War II. Arrangements were made for its creation during May 1941, and it was created formally by Executive Order 8807 on June 28, 1941. It superseded the work of the National Defense Research Committee (NDRC), was given almost unlimited access to funding and resources, and was directed by Vannevar Bush, who reported only to President Franklin Delano Roosevelt. The research was widely varied, and included projects devoted to new and more accurate bombs, reliable detonators, work on the proximity fuze, guided missiles, radar and early-warning systems, lighter and more accurate hand weapons, more effective medical treatments (including work to make penicillin at scale, which was necessary for its use as a drug), more versatile vehicles, and, the most secret of all, the S-1 Section, which later be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Laboratory
The Radiation Laboratory, commonly called the Rad Lab, was a microwave and radar research laboratory located at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was first created in October 1940 and operated until 31 December 1945 when its functions were dispersed to industry, other departments within MIT, and in 1951, the newly formed MIT Lincoln Laboratory. The use of microwaves for various radio and radar uses was highly desired before the war, but existing microwave devices like the klystron were far too low powered to be useful. Alfred Lee Loomis, a millionaire and physicist who headed his own private laboratory, organized the Microwave Committee to consider these devices and look for improvements. In early 1940, Winston Churchill organized what became the Tizard Mission to introduce U.S. researchers to several new technologies the UK had been developing. Among these was the cavity magnetron, a leap forward in the creation of microwaves that made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Countermeasures
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting information to an enemy. The system may make many separate targets appear to the enemy, or make the real target appear to disappear or move about randomly. It is used effectively to protect aircraft from guided missiles. Most air forces use ECM to protect their aircraft from attack. It has also been deployed by military ships and recently on some advanced tanks to fool laser/IR guided missiles. It is frequently coupled with stealth advances so that the ECM systems have an easier job. Offensive ECM often takes the form of jamming. Self-protecting (defensive) ECM includes using blip enhancement and jamming of missile terminal homers. History The first example of electronic countermeasures being applied in a combat situation took place during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Counter-countermeasures
Electronic counter-countermeasures (ECCM) is a part of electronic warfare which includes a variety of practices which attempt to reduce or eliminate the effect of electronic countermeasures (ECM) on electronic sensors aboard vehicles, ships and aircraft and weapons such as missiles. ECCM is also known as electronic protective measures (EPM), chiefly in Europe. In practice, EPM often means resistance to jamming. A more detailed description defines it as the electronic warfare operations taken by a radar to offset the enemy's countermeasure. History Ever since electronics have been used in battle in an attempt to gain superiority over the enemy, effort has been spent on techniques to reduce the effectiveness of those electronics. More recently, sensors and weapons are being modified to deal with this threat. One of the most common types of ECM is radar jamming or spoofing. This originated with the Royal Air Force's use of what they codenamed ''Window'' during World War II, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick E
Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Nobility Anhalt-Harzgerode *Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) Austria * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederick II, Duke of Austria (1219–1246), last Duke of Austria from the Babenberg dynasty * Frederick the Fair (Frederick I of Austria (Habsburg), 1286–1330), Duke of Austria and King of the Romans Baden * Frederick I, Grand Duke of Baden (1826–1907), Grand Duke of Baden * Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden (1857–1928), Grand Duke of Baden Bohemia * Frederick, Duke of Bohemia (died 1189), Duke of Olomouc and Bohemia Britain * Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707–1751), eldest son of King George II of Great Britain Brandenburg/Prussia * Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg (1371–1440), also known as Frederick VI, Burgrave of Nuremberg * Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg (1413–1470), Margrave of Brandenburg * Frederick William, Elector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
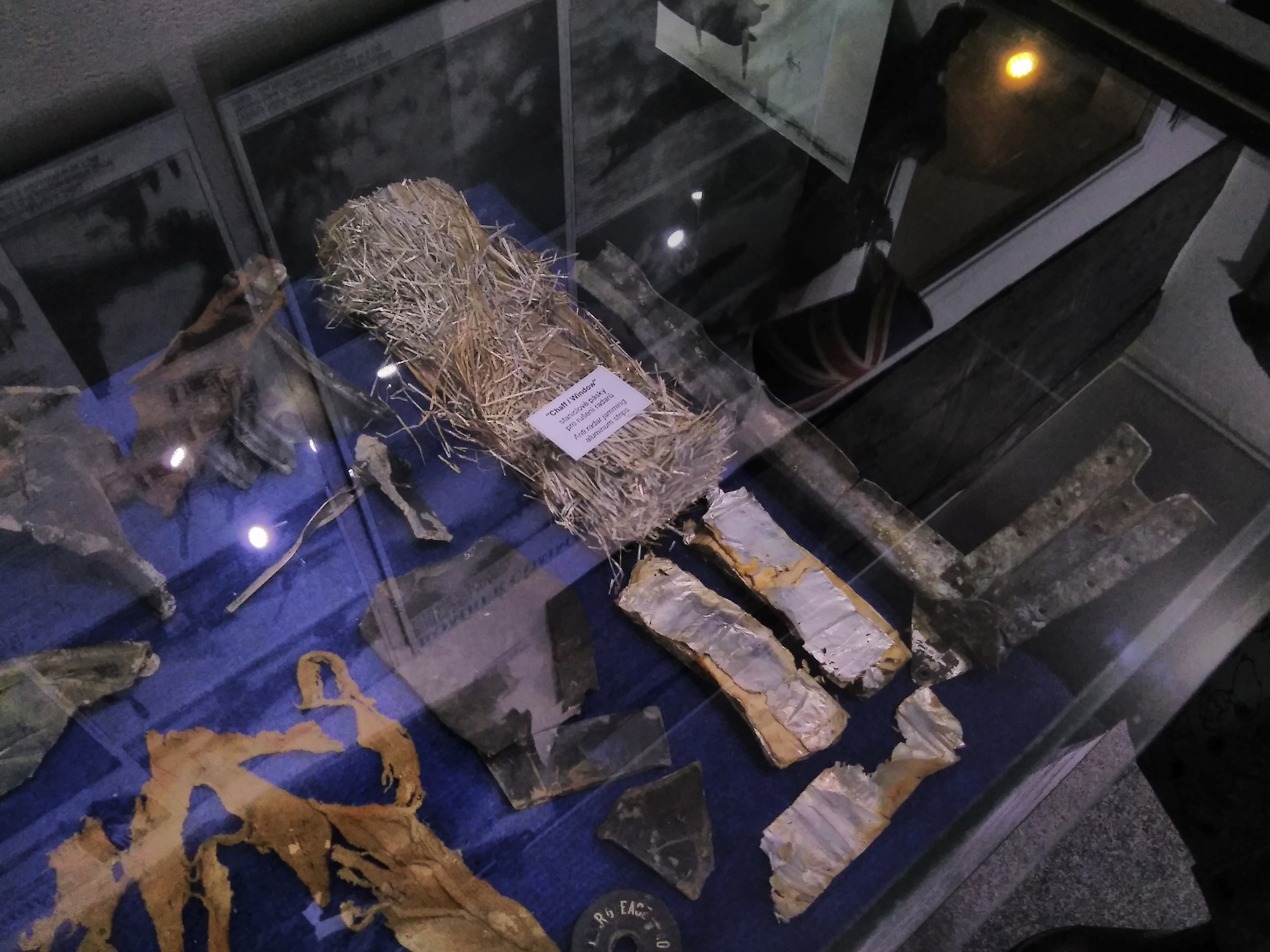
Chaff (countermeasure)
Chaff, originally called Window by the British and ''Düppel'' by the Second World War era German Luftwaffe (from the Berlin suburb where it was first developed), is a radar countermeasure in which aircraft or other targets spread a cloud of small, thin pieces of aluminium, metallized glass fibre or plastic, which either appears as a cluster of primary targets on radar screens or swamps the screen with multiple returns, in order to confuse and distract. Modern armed forces use chaff (in naval applications, for instance, using short-range SRBOC rockets) to distract radar-guided missiles from their targets. Most military aircraft and warships have chaff dispensing systems for self-defense. An intercontinental ballistic missile may release in its midcourse phase several independent warheads as well as penetration aids such as decoy balloons and chaff. Modern radar systems can distinguish chaff from target objects by measuring the Doppler shift; chaff quickly loses speed compared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred L
Fred may refer to: People * Fred (name), including a list of people and characters with the name Mononym * Fred (cartoonist) (1931–2013), pen name of Fred Othon Aristidès, French * Fred (footballer, born 1949) (1949–2022), Frederico Rodrigues de Oliveira, Brazilian * Fred (footballer, born 1979), Helbert Frederico Carreiro da Silva, Brazilian * Fred (footballer, born 1983), Frederico Chaves Guedes, Brazilian * Fred (footballer, born 1986), Frederico Burgel Xavier, Brazilian * Fred (footballer, born 1993), Frederico Rodrigues de Paula Santos, Brazilian * Fred Again (born 1993), British songwriter known as FRED Television and movies * ''Fred Claus'', a 2007 Christmas film * ''Fred'' (2014 film), a 2014 documentary film * Fred Figglehorn, a YouTube character created by Lucas Cruikshank ** ''Fred'' (franchise), a Nickelodeon media franchise ** '' Fred: The Movie'', a 2010 independent comedy film * '' Fred the Caveman'', French Teletoon production from 2002 * Fred Flint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Cross-section
Radar cross-section (RCS), also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected. An object reflects a limited amount of radar energy back to the source. The factors that influence this include: *the material with which the target is made; *the size of the target relative to the wavelength of the illuminating radar signal; *the absolute size of the target; *the incident angle (angle at which the radar beam hits a particular portion of the target, which depends upon the shape of the target and its orientation to the radar source); *the reflected angle (angle at which the reflected beam leaves the part of the target hit; it depends upon incident angle); *the polarization of the transmitted and the received radiation with respect to the orientation of the target. While important in detecting targets, strength of emitter and distance are not factors that affect the calculation of an RCS becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
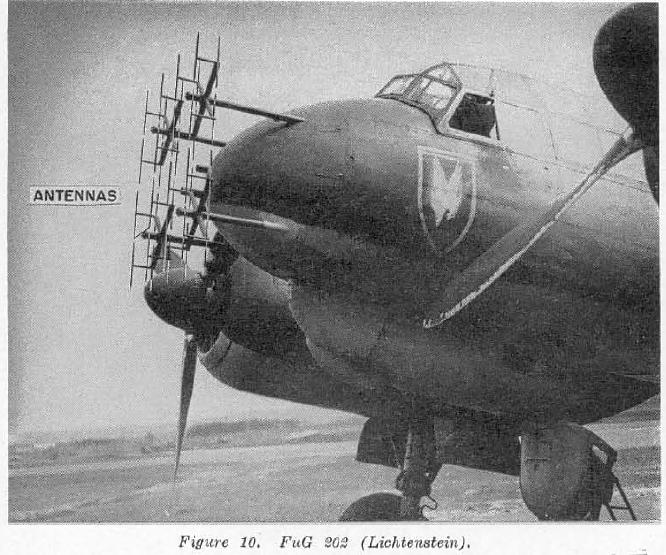
Lichtenstein Radar
The Lichtenstein radar was among the earliest airborne radars available to the Luftwaffe in World War II and the first one used exclusively for air interception. Developed by Telefunken, it was available in at least four major revisions, called FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C, FuG 212 Lichtenstein C-1, FuG 220 Lichtenstein SN-2 and the very rarely used FuG 228 Lichtenstein SN-3. (FuG is short for ''Funk-Gerät'', radio set). The Lichtenstein series remained the only widely deployed airborne interception radar used by the Germans on their night fighters during the war — the competing FuG 216 through 218 ''Neptun'' mid- VHF band radar systems were meant as a potentially more versatile stop-gap system through 1944, until the microwave-based FuG 240 "Berlin" could be mass-produced; the ''Berlin'' system was still being tested when the war ended. FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C Early FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C units were not deployed until 1942. They operated at a maximum RF output power o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horn Antenna
A horn antenna or microwave horn is an antenna that consists of a flaring metal waveguide shaped like a horn to direct radio waves in a beam. Horns are widely used as antennas at UHF and microwave frequencies, above 300 MHz. They are used as feed antennas (called feed horns) for larger antenna structures such as parabolic antennas, as standard calibration antennas to measure the gain of other antennas, and as directive antennas for such devices as radar guns, automatic door openers, and microwave radiometers. Their advantages are moderate directivity, low standing wave ratio (SWR), broad bandwidth, and simple construction and adjustment. One of the first horn antennas was constructed in 1897 by Bengali-Indian radio researcher Jagadish Chandra Bose in his pioneering experiments with microwaves. reprinted in The modern horn antenna was invented independently in 1938 by Wilmer Barrow and G. C. Southworth The development of radar in World War 2 stimulated horn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |