|
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired electron, unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemical reaction, chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimer (chemistry), dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and methylene radical, triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, Plasma (ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
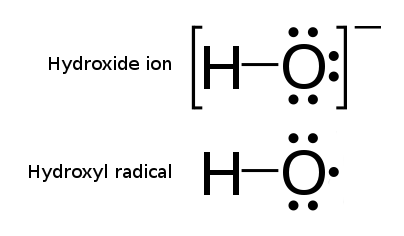
Hydroxyl Radical
The hydroxyl radical is the diatomic molecule . The hydroxyl radical is very stable as a dilute gas, but it decays very rapidly in the condensed phase. It is pervasive in some situations. Most notably the hydroxyl radicals are produced from the decomposition of hydroperoxides (ROOH) or, in atmospheric chemistry, by the reaction of excited atomic oxygen with water. It is also important in the field of radiation chemistry, since it leads to the formation of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, which can enhance corrosion and SCC in coolant systems subjected to radioactive environments. In organic synthesis, hydroxyl radicals are most commonly generated by photolysis of 1-hydroxy-2(1''H'')-pyridinethione. Notation The unpaired electron of the hydroxyl radical is officially represented by a middle dot, •, beside the O. Biology Hydroxyl radicals can occasionally be produced as a byproduct of immune action. Macrophages and microglia most frequently generate this compound wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma ()πλάσμα , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek English Lexicon'', on Perseus is one of the four fundamental states of matter. It contains a significant portion of charged particles – ions and/or s. The presence of these charged particles is what primarily sets plasma apart from the other fundamental states of matter. It is the most abundant form of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Atom Abstraction
In chemistry, a hydrogen atom abstraction or hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) is any chemical reaction in which a hydrogen free radical (neutral hydrogen atom) is abstracted from a substrate according to the general equation: :X^\bullet + H-Y -> X-H + Y^\bullet Examples of HAT reactions are oxidative reactions in general, hydrocarbon combustion, and reactions involving cytochrome P450 containing an iron(V)-oxo unit. The abstractor (X•) is usually a radical species itself, but it may also be a closed-shell In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom ... species such as chromyl chloride. HAT can take place through proton-coupled electron transfer. A synthetic example is found in iron zeolites, which stabilize alpha-oxygen. References {{Reflist Chemical reactions Reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstraction
Abstraction in its main sense is a conceptual process wherein general rules and concepts are derived from the usage and classification of specific examples, literal ("real" or " concrete") signifiers, first principles, or other methods. "An abstraction" is the outcome of this process—a concept that acts as a common noun for all subordinate concepts and connects any related concepts as a ''group'', ''field'', or ''category''.Suzanne K. Langer (1953), ''Feeling and Form: a theory of art developed from Philosophy in a New Key'' p. 90: " Sculptural form is a powerful abstraction from actual objects and the three-dimensional space which we construe ... through touch and sight." Conceptual abstractions may be formed by filtering the information content of a concept or an observable phenomenon, selecting only those aspects which are relevant for a particular purpose. For example, abstracting a leather soccer ball to the more general idea of a ball selects only the information o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond-dissociation Energy
The bond-dissociation energy (BDE, ''D''0, or ''DH°'') is one measure of the strength of a chemical bond . It can be defined as the standard enthalpy change when is cleaved by homolysis to give fragments A and B, which are usually radical species. The enthalpy change is temperature-dependent, and the bond-dissociation energy is often defined to be the enthalpy change of the homolysis at 0 K ( absolute zero), although the enthalpy change at 298 K ( standard conditions) is also a frequently encountered parameter. As a typical example, the bond-dissociation energy for one of the C−H bonds in ethane () is defined as the standard enthalpy change of the process : , : ''DH''°298() = Δ''H°'' = 101.1(4) kcal/mol = 423.0 ± 1.7 kJ/mol = 4.40(2) eV (per bond). To convert a molar BDE to the energy needed to dissociate the bond ''per molecule'', the conversion factor 23.060 kcal/mol (96.485 kJ/mol) for each eV can be used. A variety of exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homolysis (chemistry)
In chemistry, homolysis () or homolytic fission is the dissociation of a molecular bond by a process where each of the fragments (an atom or molecule) retains one of the originally bonded electrons. During homolytic fission of a neutral molecule with an even number of electrons, two free radicals will be generated. That is, the two electrons involved in the original bond are distributed between the two fragment species. Bond cleavage is also possible by a process called heterolysis. The energy involved in this process is called bond dissociation energy (BDE). BDE is defined as the " enthalpy (per mole) required to break a given bond of some specific molecular entity by homolysis," symbolized as ''D''. BDE is dependent on the strength of the bond, which is determined by factors relating to the stability of the resulting radical species. Because of the relatively high energy required to break bonds in this manner, homolysis occurs primarily under certain circumstances: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homolysis2
The term homolysis generally means breakdown (''lysis'') to equal pieces (''homo'' = same). There are separate meanings for the word in chemistry and biology: * Homolysis (biology), the fact that the dividing cell gives two equal-size daughter cells * Homolysis (chemistry), a chemical bond dissociation of a neutral molecule generating two free radicals See also * Heterolysis (other) Heterolysis may refer to: * Heterolysis (biology), the apoptosis induced by hydrolytic enzymes from surrounding cells * Heterolysis (chemistry) In chemistry, heterolysis or heterolytic fission () is the process of cleaving/breaking a covalent b ... Science disambiguation pages {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cage Effect (chemistry)
In chemistry, the cage effect (also known as geminate recombination) describes how the properties of a molecule are affected by its surroundings. First introduced by Franck and Rabinowitch in 1934, the cage effect suggests that instead of acting as an individual particle, molecules in solvent are more accurately described as an encapsulated particle. The encapsulated molecules or radicals are called cage pairs or geminate pairs. In order to interact with other molecules, the caged particle must diffuse from its solvent cage. The typical lifetime of a solvent cage is 10 seconds. Many manifestations of the cage effect exist. In free radical polymerization, radicals formed from the decomposition of an initiator molecule are surrounded by a cage consisting of solvent and/or monomer molecules. Within the cage, the free radicals undergo many collisions leading to their recombination or mutual deactivation. This can be described by the following reaction: : R\!-\!R \;\;\unders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox Signaling
''Antioxidants & Redox Signaling '' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering reduction–oxidation (redox) signaling and antioxidant research. It covers topics such as reactive oxygen species/ reactive nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) as messengers gaseous signal transducers, hypoxia and tissue oxygenation, microRNA, prokaryotic systems, and lessons from plant biology. Abstracting and indexing This journal is indexed by the following services: According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 7.407. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Antioxidants and Redox Signaling Biology journals Journals published between 27 and 51 times per year Mary Ann Liebert academic journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |