|
Radar, Anti-Aircraft
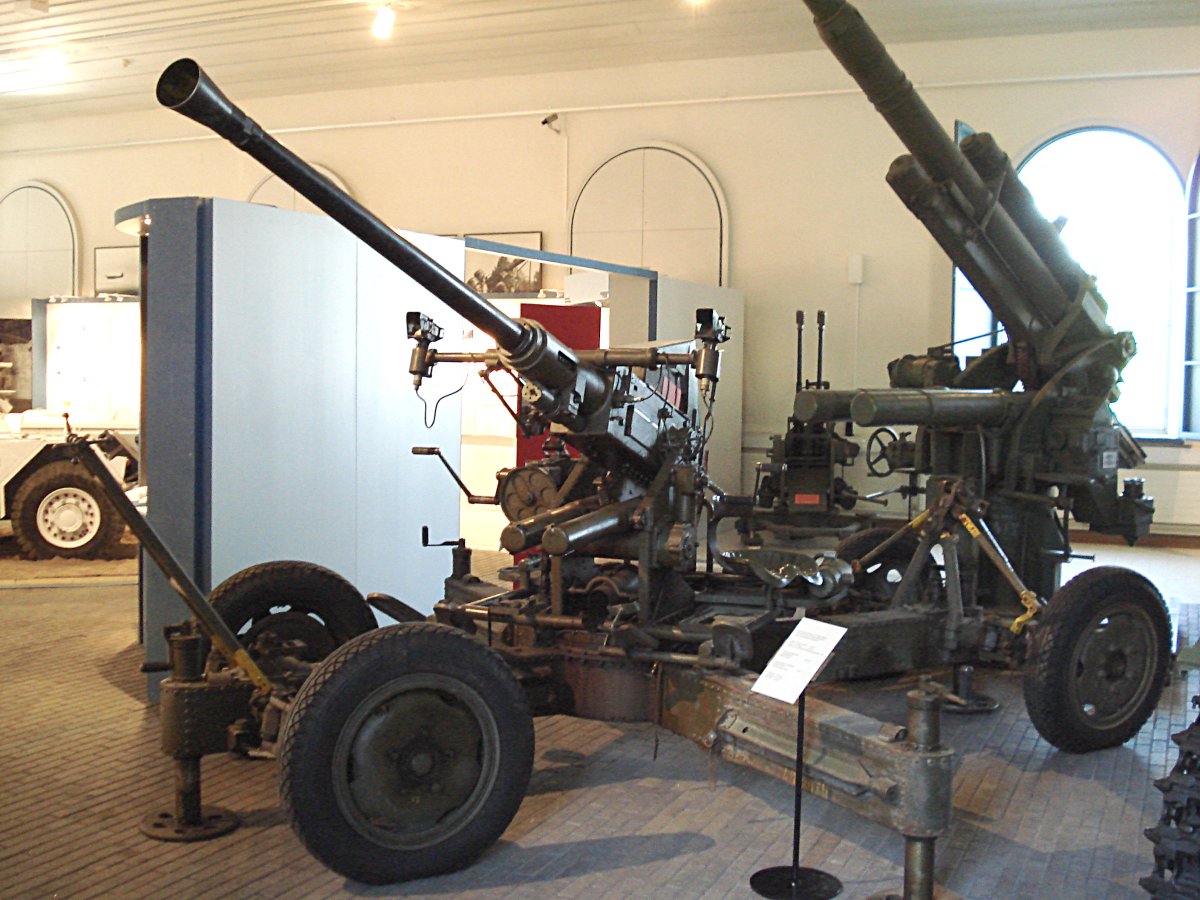
Radar, Anti-Aircraft, or simply AA radar for short, was a classification system for British Army radars introduced in 1943 and used into the 1960s when these systems were replaced by missiles with their own integral radar systems. The classification included subcategories, Number 1 through 8, as well as the many individual systems which were assigned Marks. Some of the Army radars pre-date the introduction of this classification system and had their own nomenclature that tended to remain in use even after they officially received new names. Notable among these are the Gun Laying and Searchlight Control categories. Additionally, equipment introduced after the classification system often have rainbow codes that they are well known by. Some were also used by the Royal Air Force and thus also had an AMES number. Number 1 AA Number 1 was assigned to the early gun laying radars operating in the 1.5 m VHF band. They were almost always referred to by their original name, GL Mk. I ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel. The modern British Army traces back to 1707, with antecedents in the English Army and Scots Army that were created during the Restoration in 1660. The term ''British Army'' was adopted in 1707 after the Acts of Union between England and Scotland. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the monarch as their commander-in-chief, but the Bill of Rights of 1689 and Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Therefore, Parliament approves the army by passing an Armed Forces Act at least once every five years. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence and commanded by the Chief of the General Staff. The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
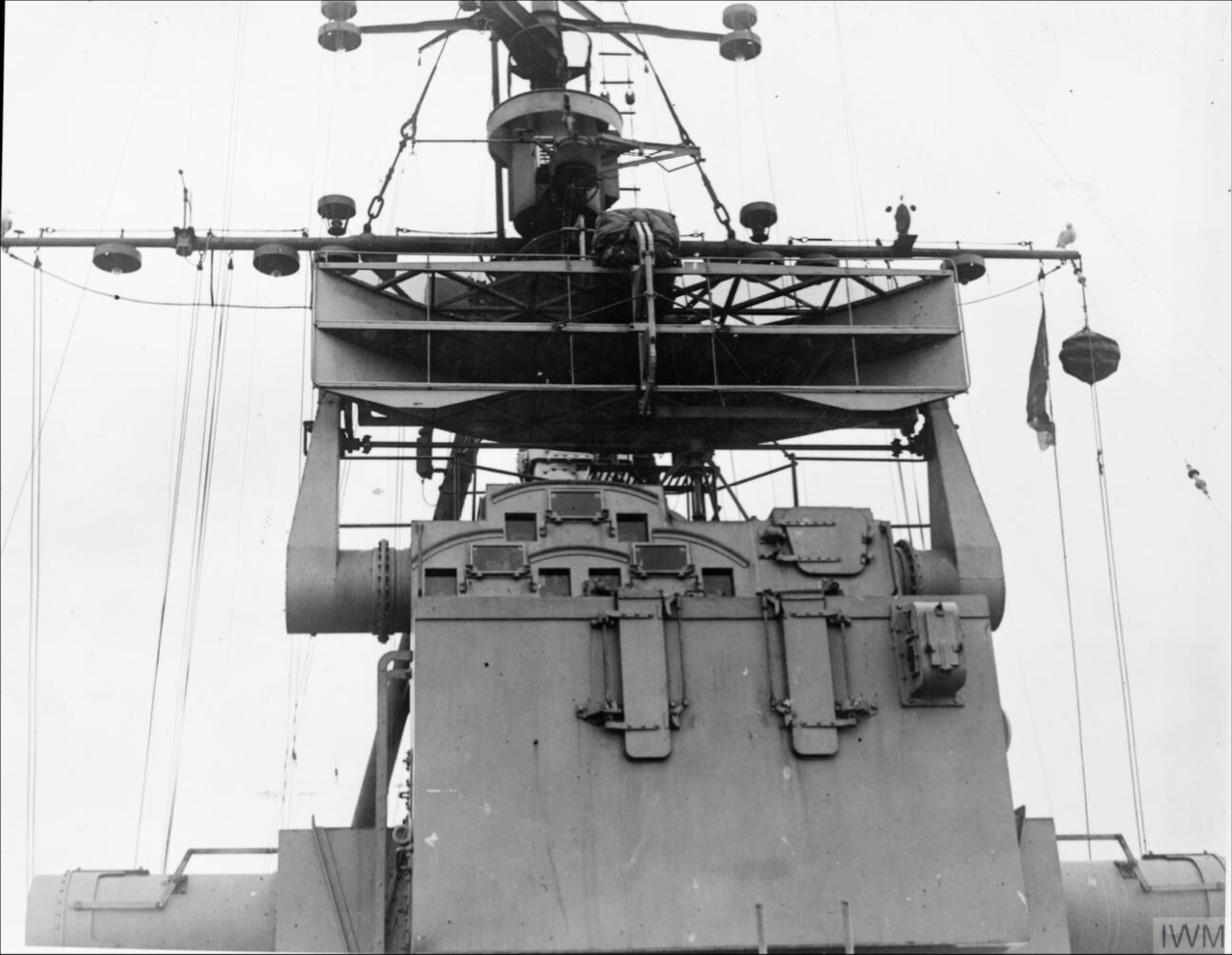
Tactical Control Radar
Tactical Control is a term originating in the British Army to refer to a class of medium-range radar systems. They are generally used for controlling the airspace around a set location on the ground, sometimes a dispersed battery of anti-aircraft artillery or surface-to-air missiles, but they also found use as air traffic control systems around airbases. They generally have a high pulse repetition frequency and rotate quickly in order to provide rapid updates at the expense of reduced range. In the Army, these radars were initially grouped into the Radar, AA, No. 4 classification, with several Marks of such systems being used from the early World War II period into the early 1960s. The main purpose of these radars was to provide early warning to weapons crews, as well as "putting on" information so they could aim their gun laying radars in the general direction of the target. In the post-war era, this data was handed off electronically. When the RAF took over many of the Army's ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Laying Radars
A gun is a ranged weapon designed to use a shooting tube (gun barrel) to launch projectiles. The projectiles are typically solid, but can also be pressurized liquid (e.g. in water guns/cannons, spray guns for painting or pressure washing, projected water disruptors, and technically also flamethrowers), gas (e.g. light-gas gun) or even charged particles (e.g. plasma gun). Solid projectiles may be free-flying (as with bullets and artillery shells) or tethered (as with Taser guns, spearguns and harpoon guns). A large-caliber gun is also called a ''cannon''. The means of projectile propulsion vary according to designs, but are traditionally effected pneumatically by a high gas pressure contained within the barrel tube, produced either through the rapid exothermic combustion of propellants (as with firearms), or by mechanical compression (as with air guns). The high-pressure gas is introduced behind the projectile, pushing and accelerating it down the length of the tube, imparti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bofors 40 Mm Automatic Gun L/60
The Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60 (often referred to simply as the "Bofors 40 mm gun", the "Bofors gun" and the like, see name) is an anti-aircraft autocannon, designed in the 1930s by the Swedish arms manufacturer AB Bofors. The gun was designed as an intermediate anti-aircraft gun, filling the gap between fast firing close-range small calibre anti-aircraft guns and slower firing long-range high calibre anti-aircraft guns, a role which previously was filled by older outdated guns. The Bofors 40 mm L/60 was for its time perfectly suited for this role and outperformed competing designs in the years leading up to World War II in both effectiveness and reliability. It entered the export market around 1932 and was in service with 18 countries by 1939. Throughout World War II it became one of the most popular and widespread medium-weight anti-aircraft guns. It was used by the majority of the western Allies and some Axis powers such as Nazi Germany and Hungary. In the pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange Yeoman
Orange most often refers to: *Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis'' ** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower * Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum *Some other citrus or citrus-like fruit, see ''list of plants known as orange'' * ''Orange'' (word), both a noun and an adjective in the English language Orange may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Game of Life'' (film), a 2007 film originally known as ''Oranges'' * ''Orange'' (2010 film), a Telugu-language film * ''The Oranges'' (film), a 2011 American romantic comedy starring Hugh Laurie * ''Orange'' (2012 film), a Malayalam-language film * ''Orange'' (2015 film), a Japanese film * ''Orange'' (2018 film), a Kannada-language film Music Groups and labels * Orange (band), an American punk rock band, who formed in 2002 from California * Orange Record Label, a Canadian independent record label, founded 2003 A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheese Antenna
The cheese antenna, also known as a pillbox antenna and a parallel-plate antenna, is a type of microwave-frequency radio antenna found in certain types of radar. The antenna consists of a suitable microwave source, almost always some sort of feed horn, positioned in front of a reflector consisting of a thin two-dimensional parabolic curve with metal plates on either side. The name comes from the resulting antenna looking like a segment that has been cut from a wheel of cheese. Cheese antennas produce a signal that is highly focused in one dimension, and almost entirely unfocused in the other. The result is a broad fan-shaped (or sector) transmission pattern. These are used when the location in a single plane is desired, which is often the case for horizon-scanning radars seen on ships. The first example of the cheese was developed for the Royal Navy's Type 271 radar, allowing it to accurately measure the bearing to a target while having a wide vertical coverage so the reflectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Band
The S band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a part of the microwave band of the electromagnetic spectrum covering frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). Thus it crosses the conventional boundary between the UHF and SHF bands at 3.0 GHz. The S band is used by airport surveillance radar for air traffic control, weather radar, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites, especially those used by NASA to communicate with the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station. The 10 cm radar short-band ranges roughly from 1.55 to 5.2 GHz. The S band also contains the 2.4–2.483 GHz ISM band, widely used for low power unlicensed microwave devices such as cordless phones, wireless headphones (Bluetooth), wireless networking (WiFi), garage door openers, keyless vehicle locks, baby monitors as well as for medical diathermy machines and microwave ovens (typically at 2.495 GHz). India's re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-Sea Vessel Radar
Radar, Air-to-Surface Vessel, or ASV radar for short, is a classification used by the Royal Air Force (RAF) to refer to a series of aircraft-mounted radar systems used to scan the surface of the ocean to locate ships and surfaced submarines. The first examples were developed just before the opening of World War II and they have remained a major instrument on patrol aircraft since that time. It is part of the wider surface search radar classification, which includes similar radars in ground and ship mountings. The first ASV was developed after the accidental detection of wharves and cranes while testing an air-to-air radar in 1937. For a variety of reasons, ASV was easier to develop than the air-to-air variety of the same systems, and the first operational use of the Mark I followed in early 1940. A cleaned-up and repackaged version, ASV Mark II, replaced it at the end of the year, but the system was not widespread until late in 1941. ASV was useful for detecting U-boats at night ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Code
The Rainbow Codes were a series of code names used to disguise the nature of various British military research projects. They were mainly used by the Ministry of Supply from the end of the Second World War until 1958, when the ministry was broken up and its functions distributed among the forces. The codes were replaced by an alphanumeric code system. History During WWII, British intelligence was able to glean details of new German technologies simply by considering their code names. For instance, when they heard of a new system known as ''Wotan'', Reginald Victor Jones asked around and found that Wotan was a one-eyed god. Based on this, he guessed it was a radio navigation system using a single radio beam. This proved correct, and the Royal Air Force was able to quickly render it useless through jamming. Wishing to avoid making this sort of mistake, Ministry of Supply (MoS) initiated a system that would be entirely random and deliberately unrelated to the program in any way, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AA No
AA, Aa, Double A, or Double-A may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * ''America's Army'', a 2002 computer game published by the U.S. Army * '' Ancient Anguish'', a computer game in existence since 1992 * Aa!, a J-Pop musical group * Double-A (band), stylised as AA, South Korean boy band * ''Aa'' (album), a 2016 album by Baauer * AA (song), a 2021 single by Walker Hayes * Ace Attorney, a series of video games developed by Capcom. *AA Films, an Indian film distribution company * AA Book (other) *AA, the production code for the 1966 ''Doctor Who'' serial '' The Savages'' Brands, organizations and enterprises * Alcoholics Anonymous, an international fellowship dedicated to helping alcoholics peer to peer in sobriety * A. A. Arms, a defunct firearms manufacturer * Aerolíneas Argentinas, an Argentine airline (logo used to consist of two A's) * Air Asia, an Asian multinational low cost carrier * Alcoa, an American aluminum-producing company (stock symbol AA) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |