|
Rachel Maxwell-Hyslop
Kathleen Rachel Maxwell-Hyslop, (''née'' Clay, 27 March 1914 – 9 May 2011) was an English archaeologist and scholar of the Ancient Near East. Early life Kathleen Rachel Clay was born in London to Sir Charles Travis Clay, an antiquarian and librarian at the House of Lords Library, and Hon. Alice Violet Robson (1892–1972), daughter of William Robson, Baron Robson. She attended Downe House School in Newbury, and graduated from University of Paris, Sorbonne, where she read French. In 1933, Clay joined Mortimer Wheeler's excavations at Verulamium and Maiden Castle, Dorset. She was inspired by Kathleen Kenyon to join the newly established UCL Institute of Archaeology, Institute of Archaeology at the University of London in 1934, one of its first three students. She studied under Sidney Smith and received a postgraduate diploma in Western Asian archaeology. In 1938, she married Aymer Robert Maxwell-Hyslop, a civil servant. They had three children. Career Maxwell-Hyslop was give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Parker-Mallowan
Barbara, Lady Mallowan, (born Barbara Hastings Parker; 14 July 1908 – 21 November 1993) was an English archaeologist, Assyriologist, and epigraphist who specialised in cylinder seals. Life and work Barbara Parker was born on 14 July 1908 to Reginald Francis Parker (1871–1946) and had a younger brother John Manwaring Parker (1911–1979). She worked in Baghdad and succeeded Robert Hamilton (1905–1995) as the secretary and librarian of the British School of Archaeology in Iraq from 1950 to 1961. She was its president from 1983 until her death in 1993. Her first assignment from director Max Mallowan was to build a "dig house" at Nimrud, which she did and maintained for many years. She was typically the only staff member to reside in Baghdad throughout the school year, from October to June. She was also a lecturer in Mesopotamian archaeology at the Institute of Archaeology, London, from 1961. She was not only involved in the excavations of Nimrud under Max Mallowan, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winifred Lamb
Winifred Lamb (3 November 1894 – 16 September 1963) was a British archaeologist, art historian, and museum curator who specialised in Greek, Roman, and Anatolian cultures and artefacts. The bulk of her career was spent as the honorary keeper (curator) of Greek antiquities at the University of Cambridge's Fitzwilliam Museum from 1920 to 1958, and the Fitzwilliam Museum states that she was a "generous benefactor ... raising the profile of the collections through groundbreaking research, acquisitions and publications." She directed archaeological excavations in Greece and Turkey; was a founding member of the British Institute of Archaeology at Ankara; and was the author of numerous books on Greek and Roman antiquities, including the 1929 publication ''Greek and Roman Bronzes'', which was standard reading for studies on the subject. Early life and education Lamb was born on 3 November 1894 at Holly Lodge, Campden Hill, London. She was the daughter of Edmund Lamb, who was a Membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1914 Births
This year saw the beginning of what became known as World War I, after Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir to the Austrian throne was assassinated by Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip. It also saw the first airline to provide scheduled regular commercial passenger services with heavier-than-air aircraft, with the St. Petersburg–Tampa Airboat Line. Events January * January 1 – The St. Petersburg–Tampa Airboat Line in the United States starts services between St. Petersburg and Tampa, Florida, becoming the first airline to provide scheduled regular commercial passenger services with heavier-than-air aircraft, with Tony Jannus (the first federally-licensed pilot) conveying passengers in a Benoist XIV flying boat. Abram C. Pheil, mayor of St. Petersburg, is the first airline passenger, and over 3,000 people witness the first departure. * January 11 – The Sakurajima volcano in Japan begins to erupt, becoming effusive after a very large earthquake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeologists From London
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Institute For The Study Of Iraq
The British Institute for the Study of Iraq (BISI) (formerly the British School of Archaeology in Iraq) is the only body in Britain devoted to research into the ancient civilizations and languages of Mesopotamia. It was founded in 1932 and its aims are to support and undertake research into the archaeology (and cognate subjects) of Iraq and the neighbouring countries from the earliest times to c. AD 1700, and to promote the cultural heritage of Iraq. Since 1934, the School has published a refereed journal, ''Iraq'', which is now published annually, in November/December of each year. It is a registered charity and has its headquarters in the office of the British Academy at Carlton House Terrace in London. History The School was founded in 1932 as a memorial to the life and works of Gertrude Bell. Bell was passionate about archaeology and bequeathed £6,000 for its founding when she died in 1926. Further fundraising in 1929 added £14,000, and although the Great Depression left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Tew
Great Tew is an English village and civil parish in Oxfordshire, about north-east of Chipping Norton and south-west of Banbury. The 2011 Census gave a parish population of 156. This qualifies it for an annual parish meeting, not a monthly parish council. The village has largely belonged since the 1980s to the Johnston family, as the Great Tew Estate, with renovations and improvements. A news report in 2020 stated that David Beckham and Victoria Beckham owned a "£6m Great Tew country home", Maplewood Barn, formerly Park Barn. Great Tew had 87 Grade II listed buildings in 2021. Toponym In Old English, the toponym ''Cyrictiwa'' – "Church Tew" – distinguishes the village from neighbouring Little Tew, which then lacked a church, and Nether Worton which seems not to have had a place of worship until the 12th century. Early history Evidence that the area has been inhabited since at least the Bronze Age includes a barrow about south of the village. Excavation of the site of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British School Of Archaeology In Iraq
The British Institute for the Study of Iraq (BISI) (formerly the British School of Archaeology in Iraq) is the only body in Britain devoted to research into the ancient civilizations and languages of Mesopotamia. It was founded in 1932 and its aims are to support and undertake research into the archaeology (and cognate subjects) of Iraq and the neighbouring countries from the earliest times to c. AD 1700, and to promote the cultural heritage of Iraq. Since 1934, the School has published a refereed journal, ''Iraq'', which is now published annually, in November/December of each year. It is a registered charity and has its headquarters in the office of the British Academy at Carlton House Terrace in London. History The School was founded in 1932 as a memorial to the life and works of Gertrude Bell. Bell was passionate about archaeology and bequeathed £6,000 for its founding when she died in 1926. Further fundraising in 1929 added £14,000, and although the Great Depression left th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Academy
The British Academy is the United Kingdom's national academy for the humanities and the social sciences. It was established in 1902 and received its royal charter in the same year. It is now a fellowship of more than 1,000 leading scholars spanning all disciplines across the humanities and social sciences and a funding body for research projects across the United Kingdom. The academy is a self-governing and independent registered charity, based at 10–11 Carlton House Terrace in London. The British Academy is funded with an annual grant from the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills (BIS). In 2014–15, the British Academy's total income was £33,100,000, including £27,000,000 from BIS. £32,900,000 was distributed during the year in research grants, awards and charitable activities. Purposes The academy states that it has five fundamental purposes: * To speak up for the humanities and the social sciences * To invest in the very best researchers and research * To i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Antiquaries Of London
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships (social relations) between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions; a given society may be described as the sum total of such relationships among its constituent of members. In the social sciences, a larger society often exhibits stratification or dominance patterns in subgroups. Societies construct patterns of behavior by deeming certain actions or concepts as acceptable or unacceptable. These patterns of behavior within a given society are known as societal norms. Societies, and their norms, undergo gradual and perpetual changes. Insofar as it is collaborative, a society can enable its members to benefit in ways that would otherwise be difficult on an individual b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pu-Abi
Puabi ( Akkadian: 𒅤𒀀𒉿 ''Pu-A-Bi'' "Word of my father"), also called Shubad or Shudi-Ad due to a misinterpretation by Sir Charles Leonard Woolley, was an important woman in the Sumerian city of Ur, during the First Dynasty of Ur (c. 2600 BCE). Commonly labeled as a "queen", her status is somewhat in dispute, although several cylinder seals in her tomb, labeled grave PG 800 at the Royal Cemetery at Ur, identify her by the title "'' nin''" or "eresh", a Sumerian word denoting a queen or a priestess. Puabi's seal does not place her in relation to any king or husband, possibly indicating that she ruled in her own right. It has been suggested that she was the second wife of king Meskalamdug. The fact that Puabi, herself a Semitic Akkadian, was an important figure among Sumerians, indicates a high degree of cultural exchange and influence among the ancient Sumerians and their Semitic neighbors. Although little is known about Puabi's life, the discovery of Puabi's tomb and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalbergia Sissoo
''Dalbergia sissoo'', known commonly as North Indian rosewood or ''shisham'', is a fast-growing, hardy, deciduous rosewood tree native to the Indian subcontinent and southern Iran. ''D. sissoo'' is a large, crooked tree with long, leathery leaves and whitish or pink flowers. Description ''Dalbergia sissoo'' is a medium to large deciduous tree with a light crown, which reproduces by seeds and suckers. It can grow up to in height and in diameter, but is usually smaller. Trunks are often crooked when grown in the open. Leaves are leathery, alternate, pinnately compound, and about long. Flowers are whitish to pink, fragrant, nearly sessile, up to long, and in dense clusters in length. Pods are oblong, flat, thin, strap-like, long, wide, and light brown. They contain one to five flat, bean-shaped seeds, long. They have a long taproot and numerous surface roots that produce suckers. Young shoots are downy and drooping; established stems have light brown to dark gray bark, up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
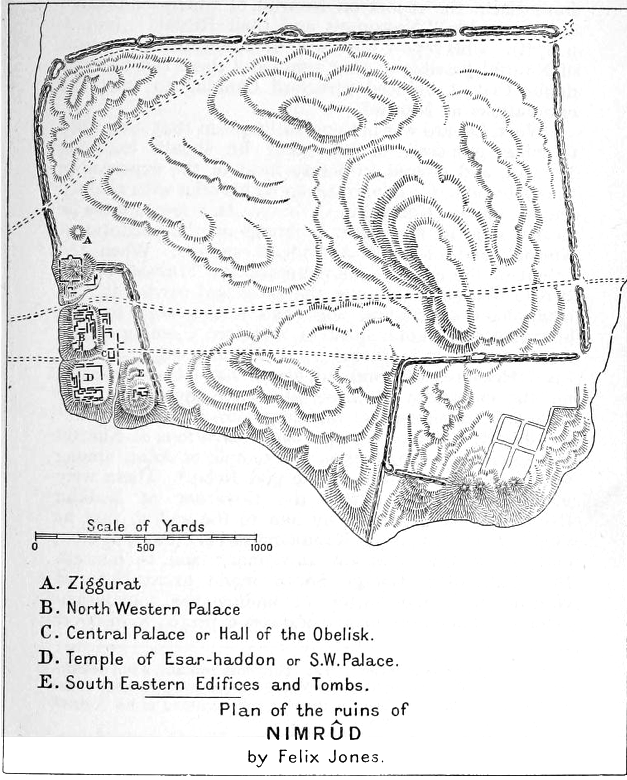
Nimrud
Nimrud (; syr, ܢܢܡܪܕ ar, النمرود) is an ancient Assyrian city located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah ( ar, السلامية), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a major Assyrian city between approximately 1350 BC and 610 BC. The city is located in a strategic position north of the point that the river Tigris meets its tributary the Great Zab.Brill's Encyclopedia of Islam 1913-36 p.923 The city covered an area of . The ruins of the city were found within of the modern-day village of |
.jpg)



_(14764273291).jpg)