|
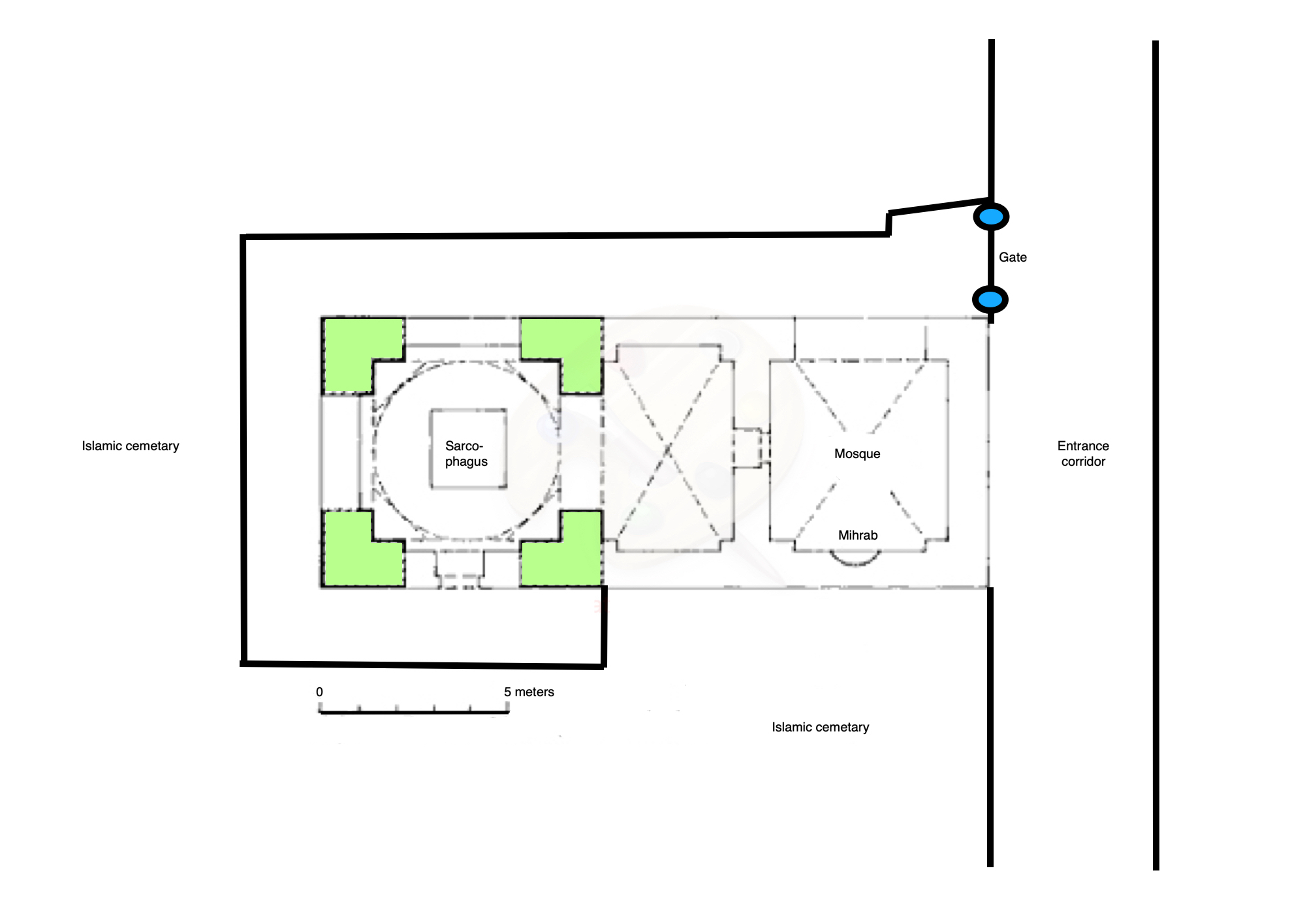
Rachel's Tomb
Rachel's Tomb ( ''Qǝbūrat Rāḥēl''; Modern he, קבר רחל ''Qever Raḥel;'' ar, قبر راحيل ''Qabr Rāḥīl'') is a site revered as the burial place of the Bible, Biblical matriarch Rachel. The site is also referred to as the Bilal bin Rabah mosque ( ar, مسجد بلال بن رباح). The tomb is held in esteem by Jews, Christians, and Muslims.: “Rather than being content with half a dozen or even a full dozen witnesses, we have tried to compile as many sources as possible. During the Roman and Byzantine era, when Christians dominated there was really not much attention given to Rachel's Tomb in Bethlehem. It was only when the Muslims took control that the shrine became an important site. Yet it was rarely considered a shrine exclusive to one religion. To be sure, most of the witnesses were Christian, yet there were also Jewish and Muslim visitors to the tomb. Equally important, the Christian witnesses call attention to the devotion shown to the shrine thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rachel
Rachel () was a Biblical figure, the favorite of Jacob's two wives, and the mother of Joseph and Benjamin, two of the twelve progenitors of the tribes of Israel. Rachel's father was Laban. Her older sister was Leah, Jacob's first wife. Her aunt Rebecca was Jacob's mother. After Leah conceived again, Rachel was finally blessed with a son, Joseph, who would become Jacob's favorite child. Children Rachel's son Joseph was destined to be the leader of Israel's tribes between exile and nationhood. This role is exemplified in the Biblical story of Joseph, who prepared the way in Egypt for his family's exile there. After Joseph's birth, Jacob decided to return to the land of Canaan with his family. Fearing that Laban would deter him, he fled with his two wives, Leah and Rachel, and twelve children without informing his father-in-law. Laban pursued him and accused him of stealing his idols. Indeed, Rachel had taken her father's idols, hidden them inside her camel's seat cushion, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antechamber
A vestibule (also anteroom, antechamber, or foyer) is a small room leading into a larger space such as a lobby, entrance hall or passage, for the purpose of waiting, withholding the larger space view, reducing heat loss, providing storage space for outdoor clothing, etc. The term applies to structures in both modern and classical architecture since ancient times. In modern architecture, a vestibule is typically a small room next to the outer door and connecting it with the interior of the building. In ancient Roman architecture, a vestibule ( la, vestibulum) was a partially enclosed area between the interior of the house and the street. Ancient usage Ancient Greece Vestibules were common in ancient Greek temples. Due to the construction techniques available at the time, it was not possible to build large spans. Consequently, many entranceways had two rows of columns that supported the roof and created a distinct space around the entrance. In ancient Greek houses, the prothyru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the northeast, Syria to the north, and the Palestinian West Bank, Israel, and the Dead Sea to the west. It has a coastline in its southwest on the Gulf of Aqaba's Red Sea, which separates Jordan from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as its economic, political, and cultural centre. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three stable kingdoms emerged there at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their Kingdom with Petra as the capital. Later rulers of the Transjordan region include the Assyrian, Babylonian, Roman, Byzantine, Rashidun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordanian Annexation Of The West Bank
The Jordanian annexation of the West Bank formally occurred on 24 April 1950, after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, during which Transjordan occupied territory that had previously been part of Mandatory PalestineRaphael Israeli, Jerusalem divided: the armistice regime, 1947–1967, Volume 23 of Cass series – Israeli history, politics, and society, Psychology Press, 2002, p. 23. and had been earmarked by the UN General Assembly Resolution 181 of 29 November 1947 for an independent Arab state to be established there alongside a Jewish state mainly to its west. The annexation tripled the population of Transjordan, from 400,000 to 1,300,000, and the country became a dualistic society with the Palestinian and Transjordanian communities remaining distinct. During the war, Jordan's Arab Legion took control of territory on the western side of the Jordan River, including the cities of Jericho, Bethlehem, Hebron, Nablus and eastern Jerusalem, including the Old City. Following th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Separatum (Jerusalem)
''Corpus separatum'' (Latin for " separated body") was the internationalization proposal for Jerusalem and its surrounding area as part of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine. It was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly with a two-thirds majority in November 1947. According to the Partition Plan, the city of Jerusalem would be brought under international governance, conferring it a special status due to its shared importance for the Abrahamic religions. The ''corpus separatum'' was one of the main issues of the Lausanne Conference of 1949, besides the borders of Israel and the question of the Palestinian right of return. The Partition Plan was not implemented, being firstly rejected by Palestinians, Palestinian and Arab League, other Arab leaders and then overtaken by the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, which left Jerusalem split between Israel (West Jerusalem) and Jordan (East Jerusalem). Presently, there is generally wide international support for Status of Jerusa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Partition Plan For Palestine
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Resolution 181 (II). The resolution recommended the creation of independent Arab and Jewish States and a Special International Regime for the city of Jerusalem. The Partition Plan, a four-part document attached to the resolution, provided for the termination of the Mandate, the progressive withdrawal of British armed forces and the delineation of boundaries between the two States and Jerusalem. Part I of the Plan stipulated that the Mandate would be terminated as soon as possible and the United Kingdom would withdraw no later than 1 August 1948. The new states would come into existence two months after the withdrawal, but no later than 1 October 1948. The Plan sought to address the conflicting objectives and claims of two competing movements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Berlin (1878)
The Treaty of Berlin (formally the Treaty between Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Great Britain and Ireland, Italy, Russia, and the Ottoman Empire for the Settlement of Affairs in the East) was signed on 13 July 1878. In the aftermath of the Russian victory against the Ottoman Empire in the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, the major powers restructured the map of the Balkan region. They reversed some of the extreme gains claimed by Russia in the preliminary Treaty of San Stefano, but the Ottomans lost their major holdings in Europe. It was one of three major peace agreements in the period after the 1815 Congress of Vienna. It was the final act of the Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) and included Great Britain and Ireland, Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Italy, Russia and the Ottoman Empire. Chancellor of Germany Otto von Bismarck was the chairman and dominant personality. The most important task of the Congress was to decide the fate of Bulgaria, but Bulgaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Status Quo (Holy Land Sites)
is a Latin phrase meaning the existing state of affairs, particularly with regard to social, political, religious or military issues. In the sociological sense, the ''status quo'' refers to the current state of social structure and/or values. With regard to policy debate, it means how conditions are, contrasted with a possible change. For example: "The countries are now trying to maintain the ''status quo'' with regard to their nuclear arsenals." To maintain the ''status quo'' is to keep things the way they presently are. The related phrase ''status quo ante'', literally "the status before", refers to the state of affairs that existed previously. Political usage Via social movements the status quo might be overhauled. These seek to alleviate or prevent a particular issue and often to shape social feeling and cultural expression of a society or nation. The status quo is at least in part rejected by their protagonists – progressives – leading the movement. Advocat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meron Benvenisti
Meron Benvenisti ( he, מירון בנבנשתי, 21 April 193420 September 2020) was an Israeli political scientist who was deputy mayor of Jerusalem under Teddy Kollek from 1971 to 1978, during which he administered East Jerusalem and served as Jerusalem's chief planning officer. He supported a binational Israeli–Palestinian state.Ofer Aderet "Israeli Columnist Meron Benvenisti, Vocal Supporter of a Binational State, Dies at 86" ''Haaretz'' 20 September 2020. Early life Benvenisti was born in 1934 in Jerusalem, his father was David Benvenisti, a Greek Jew originally from Thessaloniki and recipient of the Israel Prize, while his mother Leah (née Friedman) was Lithuanian Jews, Lithuanian Jewish. He was the brother of Refael (Rafi) Benvenisti, and father of Eyal Benvenisti. He graduated from the Hebrew University Secondary School, Leyada and served his compulsory military service in a Nahal unit near the Northern District (Israel), Israeli–Lebanese border at Kibbutz Gesher Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Christianity
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish diaspora. The first followers of Christianity were Jews or proselytes, commonly referred to as Jewish Christians and God-fearers. The Apostolic sees claim to have been founded by one or more of the apostles of Jesus, who are said to have dispersed from Jerusalem sometime after the crucifixion of Jesus, c. 26–36, perhaps following the Great Commission. Early Christians gathered in small private homes, known as house churches, but a city's whole Christian community would also be called a church – the Greek noun ἐκκλησία (''ekklesia'') literally means assembly, gathering, or congregation but is translated as church in most English translations of the New Testament. Many early Christians were merchants and others who had prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Gilbert
Sir Martin John Gilbert (25 October 1936 – 3 February 2015) was a British historian and honorary Fellow of Merton College, Oxford. He was the author of eighty-eight books, including works on Winston Churchill, the 20th century, and Jewish history including the Holocaust. He was a member of the Chilcot Inquiry into Britain's role in the Iraq War. Early life Martin Gilbert was born in London, the first child of Peter Gilbert, a north London jeweller, and his wife Miriam; their original family name was Goldberg.The Papers of Sir Martin Gilbert, Churchill Archives Centre,https://archivesearch.lib.cam.ac.uk/repositories/9/resources/1585 All four of his grandparents had been born in the Pale of Settlement in Tsarist Russia (today's Poland and Lithuania). Nine months after the outbreak of the Second World War, he was evacuated to Canada as part of the British efforts to safeguard children. Vivid memories of the transatlantic crossing from Liverpool to Quebec sparked his curiosity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susan Starr Sered
Susan Starr Sered (born 1955) is Professor of Sociology at Suffolk University and Senior Researcher at Suffolk University's Center for Women's Health and Human Rights. Previously, she was the director of the "Religion, Health and Healing Initiative" at the Harvard University Center for the Study of World Religions, and a Professor of Sociology and Anthropology at Bar-Ilan University, Israel. Her interests include both research and advocacy/activism. Professor Sered works closely with the Massachusetts Women's Justice Network and other organizations advocating for women's human rights and against mass incarceration. Published works Professor Sered is the author of seven books, nearly one hundred scholarly articles, and numerous op-eds and shorter articles focusing on women's health, mass incarceration, and a variety of religious issues. Professor Sered's work ''Women of the Sacred Groves'' was severely criticized by Okinawan Studies related scholars in "Declaration of Concern"p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

