|
Rabbit Fever (2006 Film)
Rabbit fever may refer to: * ''Rabbit Fever'' (film), a documentary about the National Rabbit Show circuit * Tularemia, a disease * Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus Rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD), also known as viral hemorrhagic disease (VHD), is a highly infectious and lethal form of viral hepatitis that affects European rabbits. Some viral strains also affect hares and cottontail rabbits. Mortality rate ... (RHDV), a disease {{disambig Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbit Fever (film)
''Rabbit Fever'' is a 2010 feature-length documentary film directed by Amy Do, about the competition at the 2005 National Convention of the American Rabbit Breeders' Association (ARBA), the largest assemblage of rabbits in the world. The film has found support from, among others, the Ignatz Awards, Ignatz Award-winning artist Jeffrey Brown (comics), Jeffrey Brown, who illustrated the movie poster. It was shown at the 8th San Francisco Documentary Film Festival in October 2009 as a work-in-progress. The final work officially Premiere, premiered in 2010. Production notes ''Rabbit Fever'' was originally developed as a 20-minute project for Do's film class at the University of Southern California. Do was encouraged by her instructor, director Charles Braverman to expand it into a feature-length film. After much demand from her fans in the Rabbit Show community, Amy Do has made a Limited Release of her film which was and currently can be purchased on her website. It was released ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tularemia
Tularemia, also known as rabbit fever, is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium ''Francisella tularensis''. Symptoms may include fever, skin ulcers, and enlarged lymph nodes. Occasionally, a form that results in pneumonia or a throat infection may occur. The bacterium is typically spread by ticks, deer flies, or contact with infected animals. It may also be spread by drinking contaminated water or breathing in contaminated dust. It does not spread directly between people. Diagnosis is by blood tests or cultures of the infected site. Prevention is by using insect repellent, wearing long pants, rapidly removing ticks, and not disturbing dead animals. Treatment is typically with the antibiotic streptomycin. Gentamicin, doxycycline, or ciprofloxacin may also be used. Between the 1970s and 2015, around 200 cases were reported in the United States a year. Males are affected more often than females. It occurs most frequently in the young and the middle aged. In the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
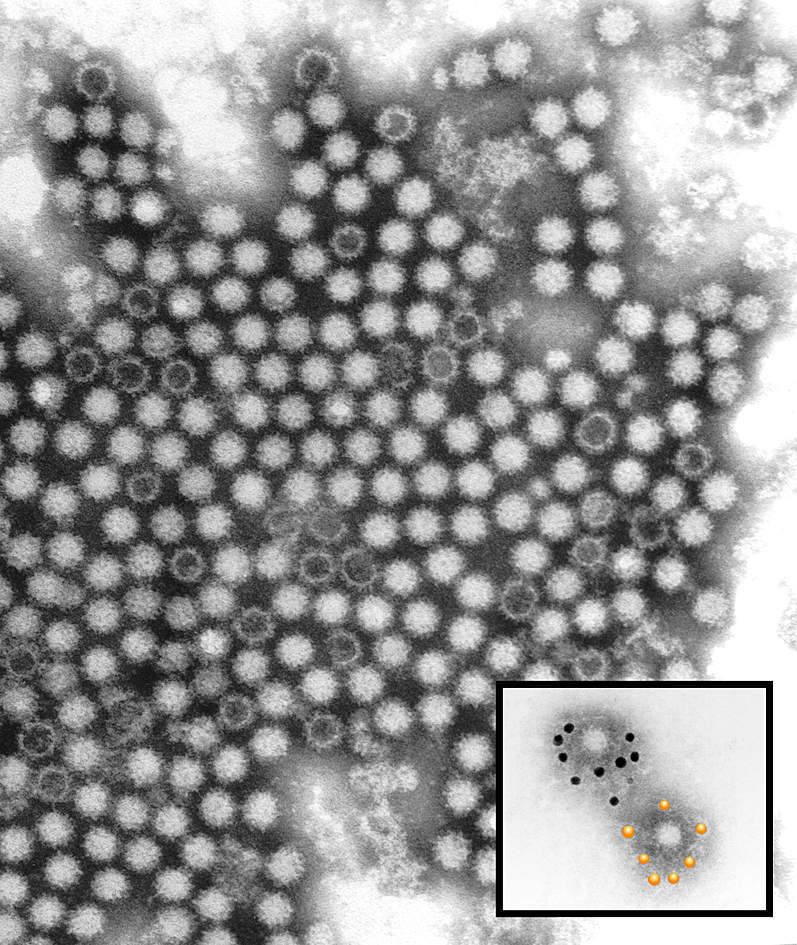
Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus
Rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD), also known as viral hemorrhagic disease (VHD), is a highly infectious and lethal form of viral hepatitis that affects European rabbits. Some viral strains also affect hares and cottontail rabbits. Mortality rates generally range from 70 to 100 percent. The disease is caused by strains of ''rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus'' (RHDV), a lagovirus in the family ''Caliciviridae''. ''Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus'' ''Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus'' (RHDV) is a virus in the genus ''Lagovirus'' and the family ''Caliciviridae''. It is a nonenveloped virus with a diameter around 35–40 nm, icosahedral symmetry, and a linear positive-sense RNA genome of 6.4–8.5 kb. RHDV causes a generalized infection in rabbits that is characterized by liver necrosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and rapid death. Division into serotypes has been defined by a lack of cross-neutralization using specific antisera. Rabbit lagoviruses also include rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |