|
Rabbet
A rabbet (American English) or rebate (British English) is a recess or groove cut into the edge of a piece of machinable material, usually wood. When viewed in cross-section, a rabbet is two-sided and open to the edge or end of the surface into which it is cut. An example of the use of a rabbet is in a glazing bar where it makes provision for the insertion of the pane of glass and putty. It may also accommodate the edge of the back panel of a cabinet. It is also used in door and casement window jambs, and for shiplap planking. A rabbet can be used to form a joint with another piece of wood (often containing a dado). Rabbet joints are easy to construct and have good appeal to them. They are simple to use in carpentry based work but can be doubtful when it comes to the strength of the joint. Nails and screws can be added to help increase the overall strength. Etymology The word ''rabbet'' is from Old French ''rabbat'', "a recess into a wall", and ''rabattre'' "to beat down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
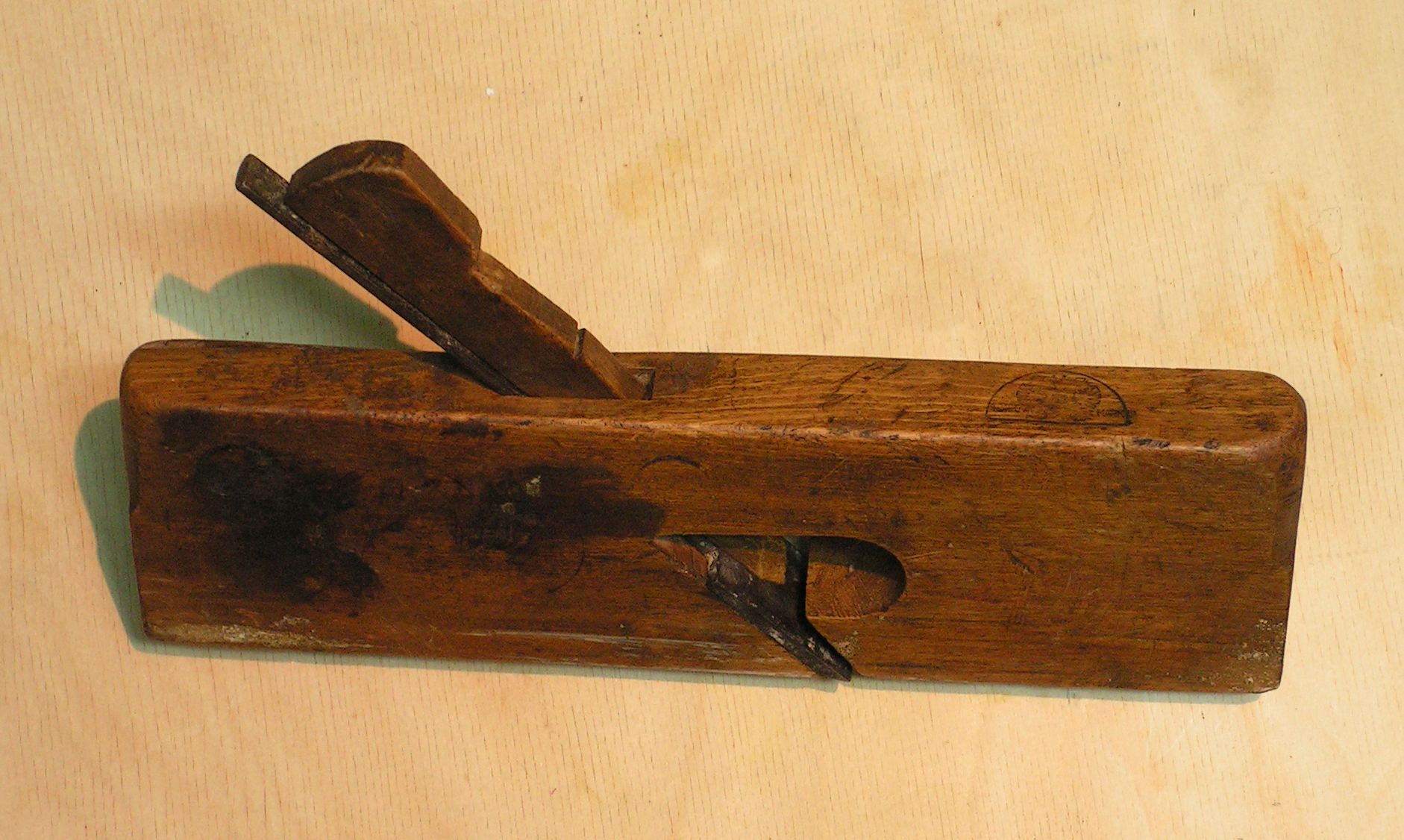
Rebate Plane
The rebate plane (British English) or rabbet plane (American English) is a hand plane designed for cutting rebates/rabbets in wood. It's a simple tool used in many Western countries with hundreds of years of history. It was in use in England at least as early as the 11th century. The rebate plane is one of a group of planes, including the shoulder plane, bullnose plane and carriage makers plane, in which the blade protrudes by a very small amount—usually less than half a millimetre—from the sides of the plane body on both sides. The blade is very slightly wider than the body of the plane. The reason for the slight protrusion of the blade is so that the plane body does not bind on the side of the cut, which would result in the side wall of the rabbet not being perpendicular to the bottom. Rebate planes are intended for long grain Wood grain is the longitudinal arrangement of wood fibers or the pattern resulting from such an arrangement. Definition and meanings R. Bruce H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
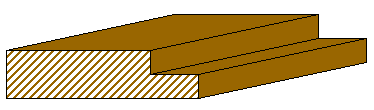
Shiplap
Shiplap is a type of wooden board used commonly as exterior siding in the construction of residences, barns, sheds, and outbuildings. Exterior walls Shiplap is either rough-sawn or milled pine or similarly inexpensive wood between wide with a rabbet on opposite sides of each edge. The rabbet allows the boards to overlap in this area. The profile of each board partially overlaps that of the board next to it creating a channel that gives shadow line effects, provides excellent weather protection and allows for dimensional movement. Useful for its strength as a supporting member, and its ability to form a relatively tight seal when lapped, shiplap is usually used as a type of siding for buildings that do not require extensive maintenance and must withstand cold and aggressive climates. Rough-sawn shiplap is attached vertically in post and beam construction, usually with 51–65 mm (6d–8d) common nails, while milled versions, providing a tighter seal, are more commonly p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dado (joinery)
A dado (US and Canada), housing (UK) or trench (Europe) is a slot or trench cut into the surface of a piece of machinable material, usually wood. When viewed in cross-section, a dado has three sides. A dado is cut across, or perpendicular to, the grain and is thus differentiated from a groove which is cut with, or parallel to the grain. Dados are often used to affix shelves to cabinetry bodies. Similar to the dado, see rabbet (rebate). Variations * A ''through'' dado involves cuts which run between both edges of the surface, leaving both ends open. * A ''stopped'' or ''blind'' dado ends before one (stopped) or both (blind) of the cuts meets the edge of the surface. * A ''half dado'' is formed with a narrow dado cut into one part, coupled with a rabbet of another piece. This joint tends to be used because of its ability to hide unattractive gaps due to varying material thicknesses. See also * Dado set * Woodworking joints Joinery is a part of woodworking that involves joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dado (joinery)
A dado (US and Canada), housing (UK) or trench (Europe) is a slot or trench cut into the surface of a piece of machinable material, usually wood. When viewed in cross-section, a dado has three sides. A dado is cut across, or perpendicular to, the grain and is thus differentiated from a groove which is cut with, or parallel to the grain. Dados are often used to affix shelves to cabinetry bodies. Similar to the dado, see rabbet (rebate). Variations * A ''through'' dado involves cuts which run between both edges of the surface, leaving both ends open. * A ''stopped'' or ''blind'' dado ends before one (stopped) or both (blind) of the cuts meets the edge of the surface. * A ''half dado'' is formed with a narrow dado cut into one part, coupled with a rabbet of another piece. This joint tends to be used because of its ability to hide unattractive gaps due to varying material thicknesses. See also * Dado set * Woodworking joints Joinery is a part of woodworking that involves joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casement Window
A casement window is a window that is attached to its frame by one or more hinges at the side. They are used singly or in pairs within a common frame, in which case they are hinged on the outside. Casement windows are often held open using a casement stay. Windows hinged at the top are referred to as awning windows, and ones hinged at the bottom are called hoppers. Overview Throughout Britain and Ireland, casement windows were common before the sash window was introduced. They were usually metal with leaded glass, which refers to glass panes held in place with strips of lead called cames (leaded glass should not be confused with lead glass, which refers to the manufacture of the glass itself). These casement windows usually were hinged on the side, and opened inward. By the start of the Victorian era, opening casements and frames were constructed from timber in their entirety. The windows were covered by functional exterior shutters, which opened outward. Variants of casement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jointer
A jointer or in some configurations, a jointer-planer (also known in the UK and Australia as a planer or surface planer, and sometimes also as a buzzer or flat top) is a woodworking machine used to produce a flat surface along a board's length. As a jointer, the machine operates on the narrow edge of boards, preparing them for use as butt joint or gluing into panels. A planer-jointer setup has the width that enables smoothing ''('surface planing')'' and leveling the faces (widths) of boards small enough to fit the tables. Name The jointer derives its name from its primary function of producing flat edges on boards prior to joining them edge-to-edge to produce wider boards. The use of this term probably arises from the name of a type of hand plane, the jointer plane, which is also used primarily for this purpose. "Planer" is the normal term in the UK and Australia for what is called a "jointer" in North America, where the former term refers exclusively to a thickness planer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand Saw
In woodworking and carpentry, hand saws, also known as "panel saws", are used to cut pieces of wood into different shapes. This is usually done in order to join the pieces together and carve a wooden object. They usually operate by having a series of sharp points of some substance that is harder than the wood being cut. The hand saw is a bit like a tenon saw, but with one flat, sharp edge. Handsaws have been around for thousands of years. Egyptian hieroglyphics exist depicting ancient woodworkers sawing boards into pieces. Ancient bow saws have been found in Japan. The cut patterns on ancient boards may be observed sometimes to bear the unique cutting marks left by saw blades, particularly if the wood was not 'smoothed up' by some method. As for preservation of handsaws, twenty-four saws from eighteenth-century England are known to survive.Olmert, Michael (1996). ''Milton's Teeth and Ovid's Umbrella: Curiouser & Curiouser Adventures in History'', p.178. Simon & Schuster, New Yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamfer
A chamfer or is a transitional edge between two faces of an object. Sometimes defined as a form of bevel, it is often created at a 45° angle between two adjoining right-angled faces. Chamfers are frequently used in machining, carpentry, furniture, concrete formwork, mirrors, and to facilitate assembly of many mechanical engineering designs. Terminology In machining the word '' bevel'' is not used to refer to a chamfer. Machinists use chamfers to "ease" otherwise sharp edges, both for safety and to prevent damage to the edges. A ''chamfer'' may sometimes be regarded as a type of bevel, and the terms are often used interchangeably. In furniture-making, a lark's tongue is a chamfer which ends short of a piece in a gradual outward curve, leaving the remainder of the edge as a right angle. Chamfers may be formed in either inside or outside adjoining faces of an object or room. By comparison, a ''fillet'' is the rounding-off of an interior corner, and a ''round'' (or ''radiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bevel
A bevelled edge (UK) or beveled edge (US) is an edge of a structure that is not perpendicular to the faces of the piece. The words bevel and chamfer overlap in usage; in general usage they are often interchanged, while in technical usage they may sometimes be differentiated as shown in the image at right. A bevel is typically used to soften the edge of a piece for the sake of safety, wear resistance, or aesthetics; or to facilitate mating with another piece. Applications Cutting tools Most cutting tools have a bevelled edge which is apparent when one examines the grind. Bevel angles can be duplicated using a sliding T bevel. Graphic design Typographic bevels are shading and artificial shadows that emulate the appearance of a 3-dimensional letter. The bevel is a relatively common effect in graphic editors such as Photoshop. As such, it is in widespread use in mainstream logos and other design elements. Glass and mirrors Bevelled edges are a common aesthetic nicety added to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chisel
A chisel is a tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge (such that wood chisels have lent part of their name to a particular grind) of blade on its end, for carving or cutting a hard material such as wood, stone, or metal by hand, struck with a mallet, or mechanical power. The handle and blade of some types of chisel are made of metal or of wood with a sharp edge in it. Chiselling use involves forcing the blade into some material to cut it. The driving force may be applied by pushing by hand, or by using a mallet or hammer. In industrial use, a hydraulic ram or falling weight ('trip hammer') may be used to drive a chisel into the material. A gouge (one type of chisel) serves to carve small pieces from the material, particularly in woodworking, woodturning and sculpture. Gouges most frequently produce concave surfaces. A gouge typically has a 'U'-shaped cross-section. Etymology ''Chisel'' comes from the Old French ''cisel'', modern ''ciseau'', Late Latin ''cisel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
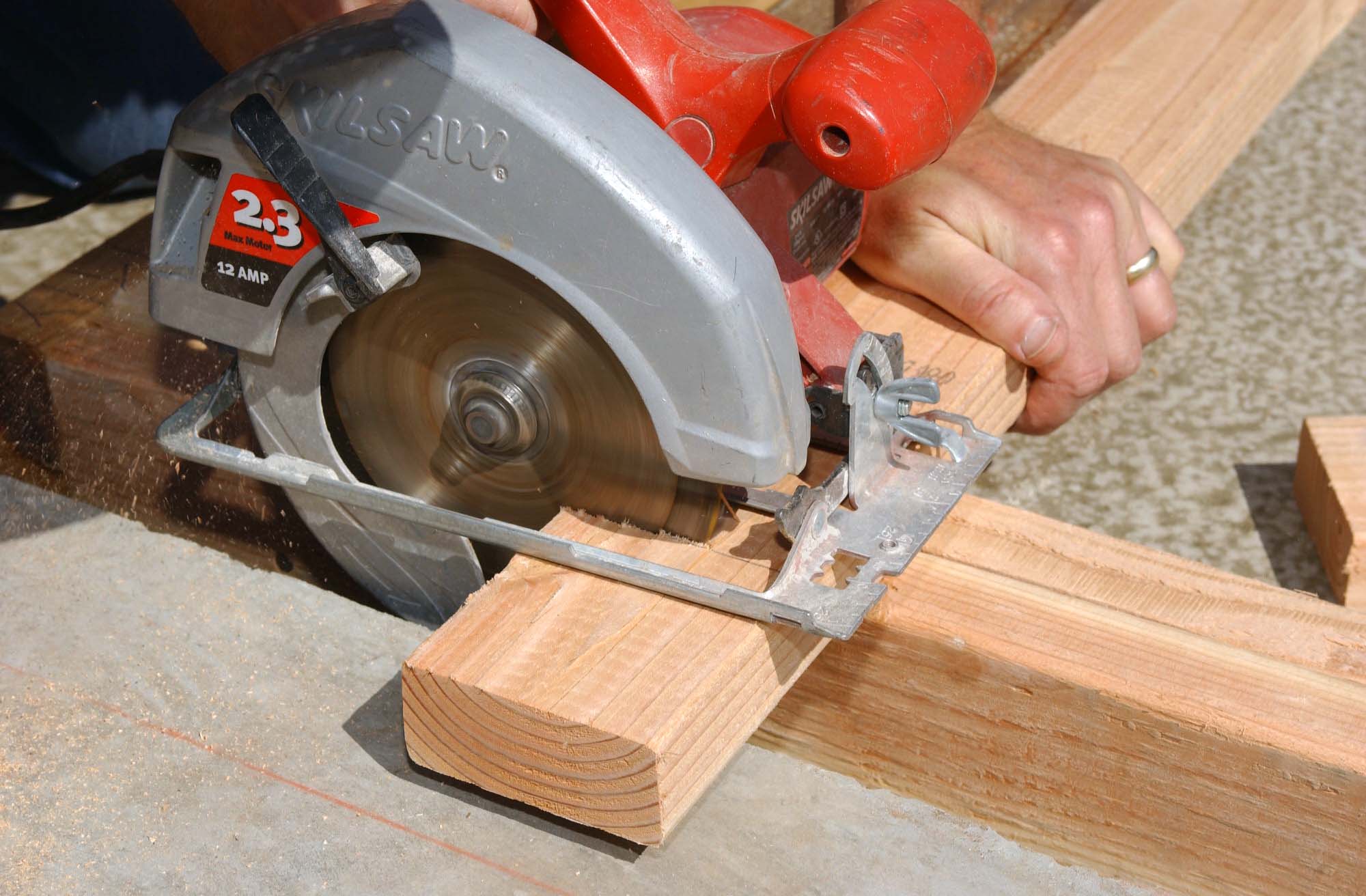
Circular Saw
A circular saw is a power-saw using a toothed or abrasive disc or blade to cut different materials using a rotary motion spinning around an arbor. A hole saw and ring saw also use a rotary motion but are different from a circular saw. ''Circular saws'' may also be loosely used for the blade itself. Circular saws were invented in the late 18th century and were in common use in sawmills in the United States by the middle of the 19th century. A circular saw is a tool for cutting many materials such as wood, masonry, plastic, or metal and may be hand-held or mounted to a machine. In woodworking the term "circular saw" refers specifically to the hand-held type and the table saw and chop saw are other common forms of circular saws. "Skilsaw" and "Skil saw" have become generic trademarks for conventional hand-held circular saws. Circular saw blades are specially designed for each particular material they are intended to cut and in cutting wood are specifically designed for making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Light.jpg)




