|
RW Trianguli
This is a list of notable stars in the constellation Triangulum, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also * List of stars by constellation All stars but one can be associated with an IAU constellation. IAU constellations are areas of the sky. Although there are only 88 IAU constellations, the sky is actually divided into 89 irregularly shaped boxes as the constellation Serpens is spli ... References * * * * * * {{Stars of Triangulum *List Triangulum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Trianguli
Alpha Trianguli (α Trianguli, abbreviated Alpha Tri, α Tri) is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation of Triangulum. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately distant from the Sun. The brighter or primary component is named Mothallah . Nomenclature ''α Trianguli'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Trianguli'') is the system's Bayer designation. The system bore the traditional names ''Ras al Muthallah'' or ''Mothallah'' and ''Caput Trianguli'' derived from the Arabic رأس المثلث' ''raʼs al-muthallath'' "the head of the triangle" and its Latin translation. The International Astronomical Union Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) has approved the name ''Mothallah'' for this star. For members of multiple star systems, and where a component letter (e.g. from the Washington Double Star Catalog) is not explicitly shown in the namelist, the WGSN says that the name should be understood to be attribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R Trianguli
R Trianguli (abbreviated as R Tri) is a short-period oxygen-rich Mira variable in Triangulum with a period of 266.9 days, discovered by T. H. E. C. Espin in 1890. It is losing about , close to average for a short-period Mira variable. While most short-period Mira variables reside in the Galactic halo, R Trianguli is a member of the thick disk, and its proper motion is fairly high for its distance. Its angular diameter in the K band (infrared), K band was measured in 2002 to be, on average, , with a shape suggesting that there is an optically thin disk structure surrounding the star. References {{Triangulum Mira variables M-type giants Objects with variable star designations, Trianguli, R Triangulum Astronomical objects discovered in 1890 Bright Star Catalogue objects, 0758 Henry Draper Catalogue objects, 016210 2MASS objects, J02370234+3415513 Emission-line stars Hipparcos objects, 012193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Irregular Variable
A slow irregular variable (ascribed the GCVS types L, LB and LC) is a variable star that exhibit no or very poorly defined periodicity in their slowly changing light emissions. These stars have often been little-studied, and once more is learnt about them, they are reclassified into other categories such as semiregular variables. Nomenclature Irregular variable stars were first given acronyms based on the letter "I": ''Ia'', ''Ib''. and ''Ic''. These were later refined so that the I codes were used "nebular" or "rapidly irregular" variable stars such as T Tauri and Orion variables. The remaining irregular stars, cool slowly varying giants and supergiants of type Ib or Ic were reassigned to Lb and Lc. When the General Catalogue of Variable Stars standardised its acronyms to be all uppercase, the codes LB and LC were used. Type Lb ''Slow irregular variables of late spectral types ( K, M, C, S); as a rule, they are giants'' The GCVS also claims to give this type to slow irregular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15 Trianguli
15 Trianguli is a suspected variable star located in the northern constellation Triangulum, with an apparent magnitude of 5.4 making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions, although it is suspected of being an irregular variable with a range of 0.14 magnitudes. The star is situated about 480 light years away but is approaching with a heliocentric radial velocity of . 15 Trianguli has a stellar classification of M3 III. It has 1.7 times the mass of the Sun and 118 times the radius of the Sun. It has an effective temperature of and shines at 1,668 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere, giving it an orange glow. It is an asymptotic giant branch The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) lat ... star, which means it is fusing hydrogen and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12 Trianguli
12 Trianguli is a solitary star located in the northern constellation Triangulum, with an apparent magnitude of 5.37, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. The star is situated 160 light years away but is approaching with a heliocentric radial velocity of . It is calculated to be about old with a stellar classification of F0 III, making it an F-type giant. It has 1.6 times the mass of the Sun and shines at 14 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of . Together with ι Trianguli and 10 Trianguli, it forms part of the obsolete Triangulum Minus Triangulum Minus (Latin for the ''Smaller Triangle'') was a constellation created by Johannes Hevelius. Its name is sometimes wrongly written as Triangulum Min''or''. It was formed from the southern parts of his ''Triangulum, Triangula'' (plural f .... References {{Triangulum F-type giants Triangulum (constellation) Trianguli, 12 15257 11486 0717 Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10 Trianguli
10 Trianguli is a solitary star located in the northern constellation Triangulum. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.28, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. The star is situated 363 light years away and is thought to be moving further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of , although this value varies widely depending on the study. 10 Trianguli has a stellar classification of A2 V. It has 2.326 times the mass of the Sun and 3.651 times the radius of the Sun. It shines at 85.4 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 9183 K, giving it a blueish white glow. Together with ι Trianguli and 12 Trianguli, it forms part of the obsolete Triangulum Minus Triangulum Minus (Latin for the ''Smaller Triangle'') was a constellation created by Johannes Hevelius. Its name is sometimes wrongly written as Triangulum Min''or''. It was formed from the southern parts of his ''Triangulum, Triangula'' (plural f . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7 Trianguli
7 Trianguli is a solitary star located in the northern constellation Triangulum. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.25, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. The star is situated at distance of 360 light years but is approaching with a heliocentric radial velocity of , which is poorly constrained. 7 Trianguli has a stellar classification of A0 V or B9.5 V, depending on the study. At present it has 2.77 times the mass of the Sun and 3.24 times the radius of the Sun. It shines at 89.1 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 10,685 K, giving it a blueish white glow. 7 Trianguli is a young star, with an age of 283 million years and spins rapidly with a projected rotational velocity Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface. The rotation of a star pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14 Trianguli
14 Trianguli (14 Tri), also known as HD 15656, is a spectroscopic binary located in the northern constellation Triangulum. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.14, making it faintly visible to the naked eye in ideal conditions. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements place the system 433 light years away, and it is currently approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of . At its current distance, 14 Tri's brightness is diminished by 0.21 magnitude due to interstellar dust. It has an absolute magnitude of −0.46. The visible component is an evolved red giant with a stellar classification of K5 III. It has 1.85 times the mass of the Sun, but it has expanded to 40.5 times its girth. It radiates 373 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of , giving it an orangish-red hue. 14 Tri is slightly metal-deficient with e/H= −0.16, and spins modestly with a projected rotational velocity of . This is a single-lined spectroscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
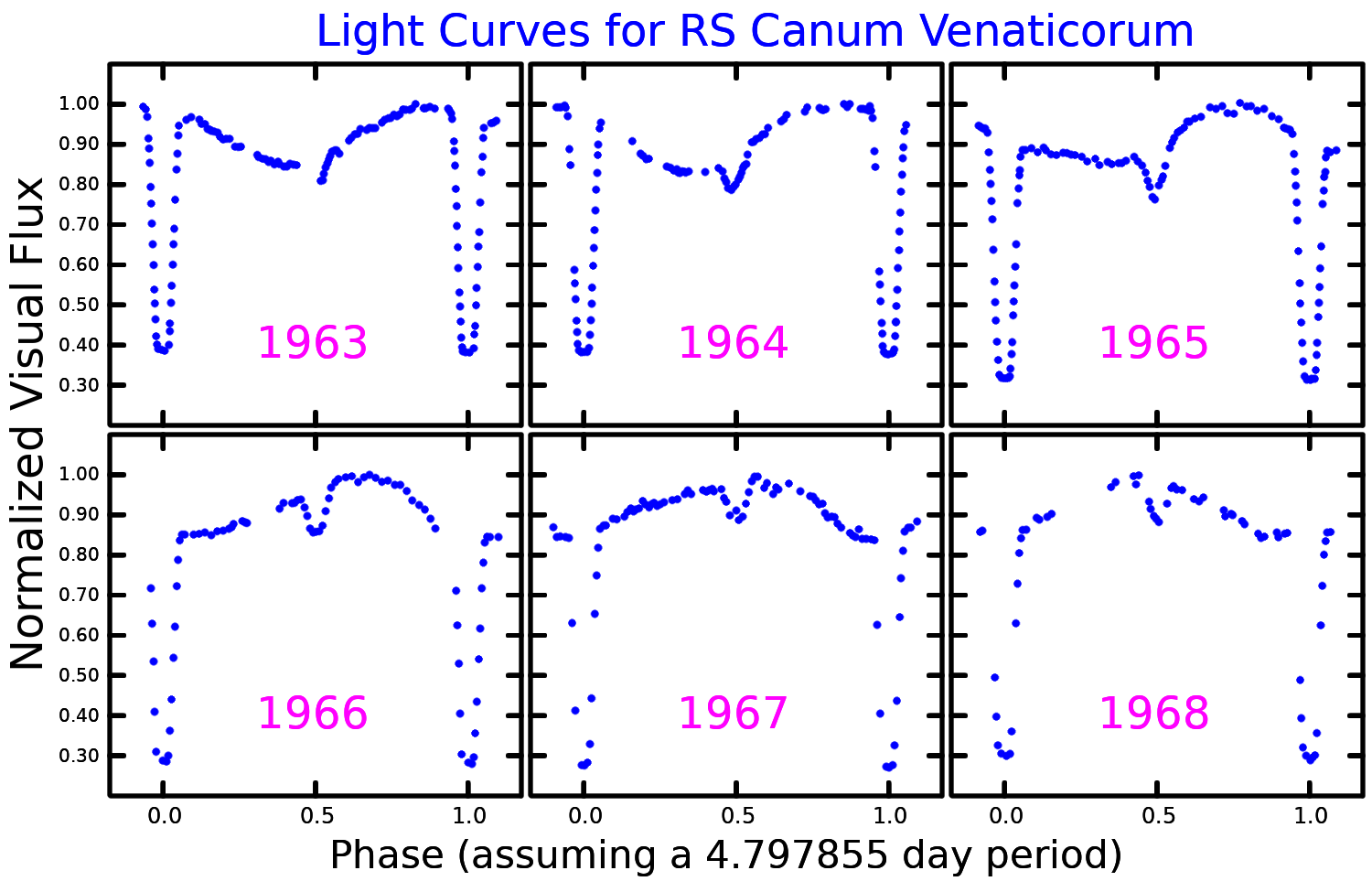
RS Canum Venaticorum Variable
An RS Canum Venaticorum variable is a type of variable star. The variable type consists of close binary stars having active chromospheres which can cause large stellar spots. These spots are believed to cause variations in their observed luminosity. Systems can exhibit variations on timescales of years due to variation in the spot surface coverage fraction, as well as periodic variations which are, in general, close to the orbital period of the binary system. Some systems exhibit variations in luminosity due to their being eclipsing binaries. Typical brightness fluctuation is around 0.2 magnitudes. They take their name from the star RS Canum Venaticorum (abbreviated RS CVn). Otto Struve (1946) first called attention to the group, but it was Oliver (1974) who was the first to formally propose a set of observational characteristics to define the RS CVn criteria. The working definition, as it is used today, was that set down by Hall (1976). Berdyuginabr>2.4 RS CVn stars/ref> The RS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iota Trianguli
Iota Trianguli, Latinized from ι Trianguli, is a quadruple star system in constellation of Triangulum. The pair have a combined apparent magnitude of 4.95 and are approximately 290 light years from Earth. Both components of ι Trianguli are spectroscopic binaries and the brighter pair is variable. It has been given the variable star designation TZ Trianguli. The variations are due to the ellipsoidal shape of the stars as they rotate, and also it is classified as an RS Canum Venaticorum variable An RS Canum Venaticorum variable is a type of variable star. The variable type consists of close binary stars having active chromospheres which can cause large stellar spots. These spots are believed to cause variations in their observed luminosi .... Together with 10 Trianguli and 12 Trianguli, it forms part of the obsolete Triangulum Minus. References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Iota Trianguli F-type main-sequence stars Rotating ellipsoidal varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |