|
ROV KIEL 6000
The ROV KIEL 6000 is a remotely operated vehicle built by Schilling Robotics, Davis, California. It's in the possession of the German GEOMAR - Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel. The ROV has been designed for certain scientific tasks with a max. operational depth of 6,000 m (19,685 feet). The ROV is electrically powered and directly linked to the operating ship via a deep-sea glass fiber cable. It can be operated from ships of opportunity which fulfill certain requirements such as deck space and stability, power supply, dynamic positioning and crane/winch capacities. ROV KIEL 6000 is used within multidisciplinary scientific projects such as the Cluster of Excellence "The Future Ocean The Future Ocean is a Cluster of Excellence founded in November 2006 in line with the German excellence initiative by the Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel (CAU), the Muthesius Kunsthochschule (MKHS), the Institut für Weltwirtschaft (I ..." and for the installation and maintenance o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remotely Operated Vehicle
A remotely operated underwater vehicle (technically ROUV or just ROV) is a tethered underwater mobile device, commonly called ''underwater robot''. Definition This meaning is different from remote control vehicles operating on land or in the air. ROVs are unoccupied, usually highly maneuverable, and operated by a crew either aboard a vessel/floating platform or on proximate land. They are common in deepwater industries such as offshore hydrocarbon extraction. They are linked to a host ship by a neutrally buoyant tether or, often when working in rough conditions or in deeper water, a load-carrying umbilical cable is used along with a tether management system (TMS). The TMS is either a garage-like device which contains the ROV during lowering through the splash zone or, on larger work-class ROVs, a separate assembly which sits on top of the ROV. The purpose of the TMS is to lengthen and shorten the tether so the effect of cable drag where there are underwater currents is minimize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFM-GEOMAR
The GEOMAR - Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), former ''Leibniz Institute of Marine Sciences'' (German: ''Leibniz-Institut für Meereswissenschaften'', IFM-GEOMAR), is a research institute in Kiel, Germany. It was formed in 2004 by merging the Institute for Marine Science (Institut für Meereskunde Kiel, (IFM)) with the Research Center for Marine Geosciences (GEOMAR) and is co-funded by both federal and provincial governments. It was a member of the Leibniz Association till 2012 and is coordinator of the FishBase Consortium. Since 2012 it is member of the Helmholtz Association and named ''GEOMAR - Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel''. The institute operates worldwide in all ocean basins,Leibniz Institute of Marine Sciences (IFM-GEOMAR) ''German Marine Research Consortium''. Retri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
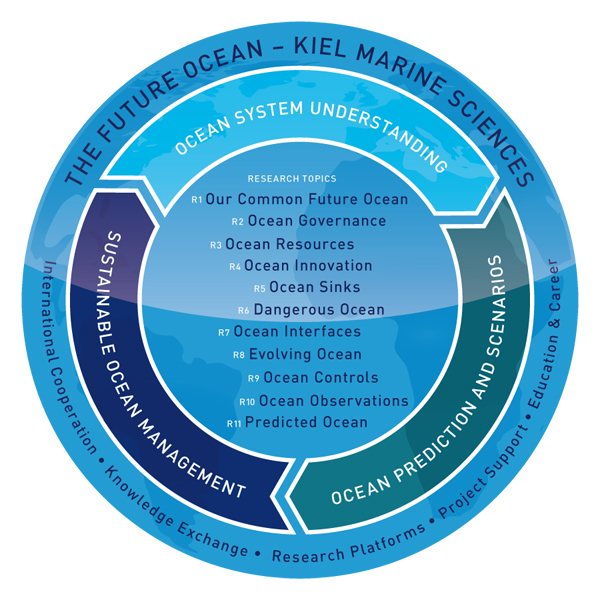
The Future Ocean
The Future Ocean is a Cluster of Excellence founded in November 2006 in line with the German excellence initiative by the Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel (CAU), the Muthesius Kunsthochschule (MKHS), the Institut für Weltwirtschaft (IfW) and the Helmholtz-Zentrum für Ozeanforschung (GEOMAR). It is an interdisciplinary marine research group and it is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG). Part of the cluster is the Integrated School of Ocean Sciences (ISOS) which is a post graduate school for ocean sciences in Kiel. Goals The ocean plays an important role in the global climate, holds dangers, but simultaneously provides opportunities not just in the form of exploitable resources but also in many different fields of research. With that in mind the scientists in the cluster "The Future Ocean" have one common goal: to reassess the opportunities and risks of global change for the ocean and to allow a sustainable management of its resources based on these insi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotic Submarines
Robotics is an interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrates fields of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, Information engineering (field), information engineering, mechatronics, electronics, bioengineering, computer engineering, control engineering, software engineering, mathematics, etc. Robotics develops machines that can substitute for humans and replicate human actions. Robots can be used in many situations for many purposes, but today many are used in dangerous environments (including inspection of radioactive materials, bomb detection and bomb disposal, deactivation), manufacturing processes, or where humans cannot survive (e.g. in space, underwater, in high heat, and clean up and containment of hazardous materials and radiation). Robots can take any form, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |