|
RIPEMD
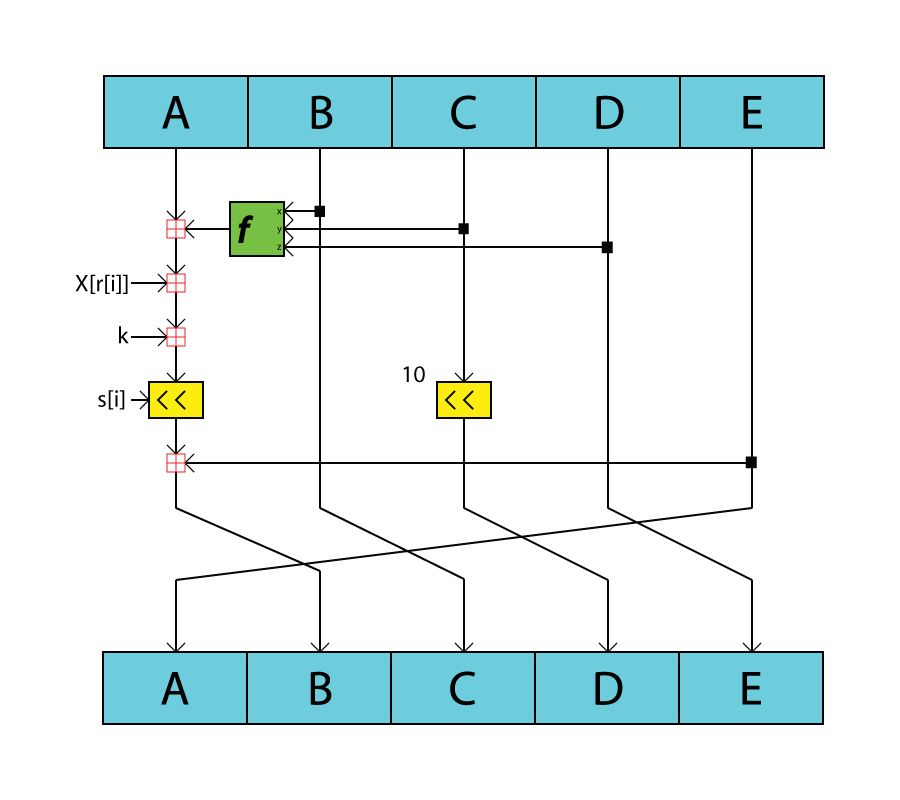
RIPEMD (RIPE Message Digest) is a family of cryptographic hash functions developed in 1992 (the original RIPEMD) and 1996 (other variants). There are five functions in the family: RIPEMD, RIPEMD-128, RIPEMD-160, RIPEMD-256, and RIPEMD-320, of which RIPEMD-160 is the most common. The original RIPEMD, as well as RIPEMD-128, is not considered secure because 128-bit result is too small and also (for the original RIPEMD) because of design weaknesses. The 256- and 320-bit versions of RIPEMD provide the same level of security as RIPEMD-128 and RIPEMD-160, respectively; they are designed for applications where the security level is sufficient but longer hash result is necessary. While RIPEMD functions are less popular than SHA-1 and SHA-2, they are used, among others, in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies based on Bitcoin. History The original RIPEMD function was designed in the framework of the EU project RIPE (RACE Integrity Primitives Evaluation) in 1992. Its design was based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RIPEMD 160 2
RIPEMD (RIPE Message Digest) is a family of cryptographic hash functions developed in 1992 (the original RIPEMD) and 1996 (other variants). There are five functions in the family: RIPEMD, RIPEMD-128, RIPEMD-160, RIPEMD-256, and RIPEMD-320, of which RIPEMD-160 is the most common. The original RIPEMD, as well as RIPEMD-128, is not considered secure because 128-bit result is too small and also (for the original RIPEMD) because of design weaknesses. The 256- and 320-bit versions of RIPEMD provide the same level of security as RIPEMD-128 and RIPEMD-160, respectively; they are designed for applications where the security level is sufficient but longer hash result is necessary. While RIPEMD functions are less popular than SHA-1 and SHA-2, they are used, among others, in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies based on Bitcoin. History The original RIPEMD function was designed in the framework of the EU project RIPE (RACE Integrity Primitives Evaluation) in 1992. Its design was based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptographic Hash Function
A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm (a map of an arbitrary binary string to a binary string with fixed size of n bits) that has special properties desirable for cryptography: * the probability of a particular n-bit output result (hash value) for a random input string ("message") is 2^ (like for any good hash), so the hash value can be used as a representative of the message; * finding an input string that matches a given hash value (a ''pre-image'') is unfeasible, unless the value is selected from a known pre-calculated dictionary (" rainbow table"). The ''resistance'' to such search is quantified as security strength, a cryptographic hash with n bits of hash value is expected to have a ''preimage resistance'' strength of n bits. A ''second preimage'' resistance strength, with the same expectations, refers to a similar problem of finding a second message that matches the given hash value when one message is already known; * finding any pair of different messa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hash Function Security Summary
This article summarizes publicly known cryptanalysis, attacks against cryptographic hash functions. Note that not all entries may be up to date. For a summary of other hash function parameters, see comparison of cryptographic hash functions. Table color key Common hash functions Collision resistance Chosen prefix collision attack Preimage resistance Length extension *Vulnerable: MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA512 *Not vulnerable: SHA384, SHA-3, BLAKE2 Less-common hash functions Collision resistance Preimage resistance Attacks on hashed passwords Hashes described here are designed for fast computation and have roughly similar speeds. Because most users typically choose short passwords formed in predictable ways, passwords can often be recovered from their hashed value if a fast hash is used. Searches on the order of 100 billion tests per second are possible with high-end graphics processors. Special hashes called key derivation functions have been created to sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bart Preneel
Bart Preneel (born 15 October 1963 in Leuven, Belgium) is a Flemish cryptographer and cryptanalyst. He is a professor at Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, in the COSIC group. He was the president of the International Association for Cryptologic Research in 2008-2013 and project manager of ECRYPT. Education In 1987, Preneel received an electrical engineering degree in applied science from the Katholieke Universiteit, Leuven. In 1993, Preneel received a PhD from the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. His dissertation in computer science, entitled ''Analysis and Design of Cryptographic Hash Functions'', was advised by Joos (Joseph) P. L. Vandewalle and René J. M. Govaerts. Career Along with Shoji Miyaguchi, he independently invented the Miyaguchi–Preneel scheme, a complex structure used in the hash function Whirlpool. He is one of the authors of the RIPEMD-160 hash function. He was also a co-inventor of the stream cipher MUGI which would later become a Japanese standard, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptlib
cryptlib is an open-source cross-platform software security toolkit library. It is distributed under the Sleepycat License, a free software license compatible with the GNU General Public License. Alternatively, cryptlib is available under a proprietary license for those preferring to use it under proprietary terms. Features cryptlib is a security toolkit library that allows programmers to incorporate encryption and authentication services to software. It provides a high-level interface so strong security capabilities can be added to an application without needing to know many of the low-level details of encryption or authentication algorithms. It comes with an over 400 page programming manual. At the highest level, cryptlib provides implementations of complete security services such as S/MIME and PGP/OpenPGP secure enveloping, SSL/TLS and SSH secure sessions, CA services such as CMP, SCEPRTCS and OCSP, and other security operations such as secure timestamping. Since cryptlib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Dobbertin
Hans Dobbertin (April 17, 1952 – February 2, 2006) was a German cryptographer who is best known for his work on cryptanalysis of the MD4, MD5, and original RIPEMD hash functions, and for his part in the design of the new version of the RIPEMD hash function. He was a member of the German Federal Office for Information Security (Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik, BSI) and professor at the Ruhr University in Bochum Bochum ( , also , ; wep, Baukem) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia. With a population of 364,920 (2016), is the sixth largest city (after Cologne, Düsseldorf, Dortmund, Essen and Duisburg) of the most populous Germany, German federal state o .... External linksIACR obituary* {{DEFAULTSORT:Dobbertin, Hans 1952 births 2006 deaths Modern cryptographers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mbed TLS
Mbed TLS (previously PolarSSL) is an implementation of the TLS and SSL protocols and the respective cryptographic algorithms and support code required. It is distributed under the Apache License version 2.0. Stated on the website is that Mbed TLS aims to be "easy to understand, use, integrate and expand". History The PolarSSL SSL library is the official continuation fork of the XySSL SSL library. XySSL was created by the French "white hat hacker" Christophe Devine and was first released on November 1, 2006, under GNU GPL v2 and BSD licenses. In 2008, Christophe Devine was no longer able to support XySSL and allowed Paul Bakker to create the official fork, named PolarSSL. In November 2014, PolarSSL was acquired by ARM Holdings. In 2011, the Dutch government approved an integration between OpenVPN and PolarSSL, which is named OpenVPN-NL. This version of OpenVPN has been approved for use in protecting government communications up to the level of Restricted. As of the release o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libgcrypt
Libgcrypt is a cryptography library developed as a separated module of GnuPG. It can also be used independently of GnuPG, but depends on its error-reporting library Libgpg-error. It provides functions for all fundamental cryptographic building blocks: Libgcrypt features its own ''multiple precision arithmetic'' implementation, with assembler implementations for a variety of processors, including Alpha, AMD64, HP PA-RISC, i386, i586, M68K, MIPS 3, PowerPC, and SPARC. It also features an ''entropy gathering'' utility, coming in different versions for Unix-like and Windows machines. Usually multiple, stable branches of Libgcrypt are maintained in parallel; since 2022-03-28 this is the Libgrypt 1.10 branch as stable branch, plus the 1.8 branch as LTS ("long-term support") branch, which will be maintained at least until 2024-12-31. See also * Comparison of cryptography libraries The tables below compare cryptography libraries that deal with cryptography algorithms and have A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypto++
Crypto++ (also known as CryptoPP, libcrypto++, and libcryptopp) is a free and open-source C++ class library of cryptographic algorithms and schemes written by Wei Dai. Crypto++ has been widely used in academia, student projects, open-source, and non-commercial projects, as well as businesses.* J. Kelsey, B. Schneier, D. Wagner, C. Hall (1998)"Cryptanalytic Attacks on Pseudorandom Number Generators". ''Fast Software Encryption, 5th International Proceedings''http://www.schneier.com/paper-prngs.pdf. Retrieved 2010-08-10. * C. Adjih, D. Raffo, P. Mühlethaler (2004)"OLSR: Distributed Key Management for Security". ''Independent Research''http://www2.lifl.fr/SERAC/downloads/attacks-olsr-dkm.pdf. Retrieved 2010-08-10. * X. Yinglian, M. K. Reiter, D. O'Hallaron (2006)"Protecting Privacy in Key-Value Search Systems" ''Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC)''https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~ylxie/papers/report03.pdf Retrieved 2010-08-10. * T. Zidenberg (2010). ''Technion, Israel Institute o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenSSL
OpenSSL is a software library for applications that provide secure communications over computer networks against eavesdropping or need to identify the party at the other end. It is widely used by Internet servers, including the majority of HTTPS websites. OpenSSL contains an open-source implementation of the SSL and TLS protocols. The core library, written in the C programming language, implements basic cryptographic functions and provides various utility functions. Wrappers allowing the use of the OpenSSL library in a variety of computer languages are available. The OpenSSL Software Foundation (OSF) represents the OpenSSL project in most legal capacities including contributor license agreements, managing donations, and so on. OpenSSL Software Services (OSS) also represents the OpenSSL project for support contracts. OpenSSL is available for most Unix-like operating systems (including Linux, macOS, and BSD), Microsoft Windows and OpenVMS. Project history The OpenSSL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nettle (cryptographic Library)
Nettle is a cryptographic library designed to fit easily in a wide range of toolkits and applications. It began as a collection of low-level cryptography functions from lsh in 2001. Since June 2009 (version 2.0) Nettle is a GNU package. Features Since version 3, nettle provides the AES block cipher (a subset of Rijndael) (with assembly optimizations for x86 and sparc), the ARCFOUR (also known as RC4) stream cipher (with x86 and sparc assembly), the ARCTWO (also known as RC2) stream cipher, BLOWFISH, CAMELLIA (with x86 and x86_64 assembly optimizations), CAST-128, DES and 3DES block ciphers, the ChaCha stream cipher (with assembly for x86_64), GOSTHASH94, the MD2, MD4, and MD5 (with x86 assembly) digests, the PBKDF2 key derivation function, the POLY1305 (with assembly for x86_64) and UMAC message authentication codes, RIPEMD160, the Salsa20 stream cipher (with assembly for x86_64 and ARM), the SERPENT block cipher (with assembly for x86_64), SHA-1 (with x86, x86_64 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WolfSSL
wolfSSL is a small, portable, embedded SSL/TLS library targeted for use by embedded systems developers. It is an open source implementation of TLS (SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and DTLS 1.0, 1.2, and 1.3) written in the C programming language. It includes SSL/TLS client libraries and an SSL/TLS server implementation as well as support for multiple APIs, including those defined by SSL and TLS. wolfSSL also includes an OpenSSL compatibility interface with the most commonly used OpenSSL functions. A predecessor of wolfSSL, yaSSL is a C++ based SSL library for embedded environments and real time operating systems with constrained resources. Platforms wolfSSL is currently available for Win32/64, Linux, macOS, Solaris, Threadx, VxWorks, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, embedded Linux, Yocto Project, OpenEmbedded, WinCE, Haiku, OpenWrt, iPhone, Android, Nintendo Wii and Gamecube through DevKitPro support, QNX, MontaVista, Tron variants, NonStop OS, OpenCL, Micrium's MicroC/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |