|
RHOT2
Mitochondrial Rho GTPase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RHOT2'' gene. As a Miro (protein), Miro protein isoform, the protein facilitates mitochondrial transport by attaching the mitochondria to the motor/adaptor complex. Through its key role in mitochondrial transport, RHOT2 is involved in mitochondrial homeostasis and apoptosis, as well as Parkinson’s disease (PD). Structure In mammals, RHOT2 is one of two Miro isoforms. Both isoforms share a structure consisting of two EF-hand motifs linking two GTP-binding domains and a C-terminal transmembrane domain that attaches the protein to the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM). The EF-hand motifs serve as binding sites for the adaptor protein Milton and the KIF5B, kinesin heavy chain. These domains can also bind calcium ions, and the binding results in a conformational change that dissociates the mitochondrial surface from kinesin. Function RHOT2 is a member of the Rho family of GTPases, Rho GTPase family and one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miro (protein)
The Ras superfamily, derived from "Rat sarcoma virus", is a protein superfamily of small GTPases. Members of the superfamily are divided into families and subfamilies based on their structure, sequence and function. The five main families are Ras, Rho, Ran, Rab and Arf GTPases. The Ras family itself is further divided into 6 subfamilies: Ras, Ral, Rap, Rheb, Rad and Rit. ''Miro'' is a recent contributor to the superfamily. Each subfamily shares the common core G domain, which provides essential GTPase and nucleotide exchange activity. The surrounding sequence helps determine the functional specificity of the small GTPase, for example the 'Insert Loop', common to the Rho subfamily, specifically contributes to binding to effector proteins such as WASP. In general, the Ras family is responsible for cell proliferation: Rho for cell morphology, Ran for nuclear transport, and Rab and Arf for vesicle transport. Subfamilies and members The following is a list of human proteins belon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RHOT1
Mitochondrial Rho GTPase 1 (MIRO1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RHOT1'' gene on chromosome 17. As a Miro (protein), Miro protein isoform, the protein facilitates mitochondrial transport by attaching the mitochondria to the motor/adaptor complex. Through its key role in mitochondrial transport, RHOT1 is involved in mitochondrial homeostasis and apoptosis, as well as Parkinson's disease (PD) and cancer. Structure In mammals, RHOT1 is one of two Miro isoforms. Both isoforms share a structure consisting of two EF-hand motifs linking two GTP-binding domains and a C-terminal transmembrane domain that attaches the protein to the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM). The EF-hand motifs serve as binding sites for the adaptor protein Milton and the KIF5B, kinesin heavy chain. These domains can also bind calcium ions, and the binding results in a conformational change that dissociates the mitochondrial surface from kinesin. Function RHOT1 is a member of the Rho family of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- or bursa-derived cells) are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, whereas B cells are primarily responsible for humoral immunity (relating to antibodies). The function of T cells and B cells is to recognize sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
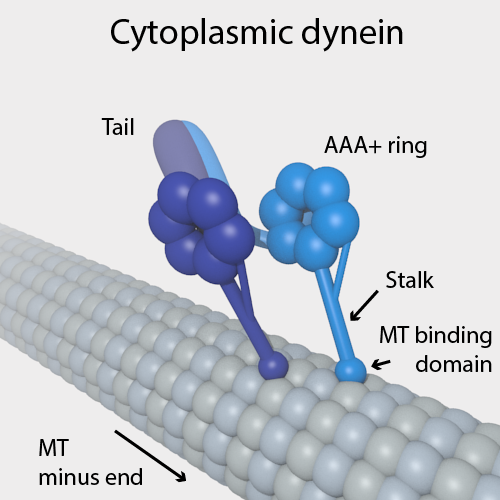
Dynein
Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical work. Dynein transports various cellular cargos, provides forces and displacements important in mitosis, and drives the beat of eukaryotic cilia and flagella. All of these functions rely on dynein's ability to move towards the minus-end of the microtubules, known as retrograde transport; thus, they are called "minus-end directed motors". In contrast, most kinesin motor proteins move toward the microtubules' plus-end, in what is called anterograde transport. Classification Dyneins can be divided into two groups: cytoplasmic dyneins and axonemal dyneins, which are also called ciliary or flagellar dyneins. * cytoplasmic ** heavy chain: DYNC1H1, DYNC2H1 ** intermediate chain: DYNC1I1, DYNC1I2 ** light intermediate chain: DYNC1LI1, DYNC1LI2, DYNC2LI1 ** light chain: DYNLL1, DYNLL2, DYNLRB1, DYNLRB2, DYNLT1, DYNLT3 * axo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DISC1
Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DISC1'' gene. In coordination with a wide array of interacting partners, DISC1 has been shown to participate in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, neuronal axon and dendrite outgrowth, mitochondrial transport, fission and/or fusion, and cell-to-cell adhesion. Several studies have shown that unregulated expression or altered protein structure of DISC1 may predispose individuals to the development of schizophrenia, clinical depression, bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. The cellular functions that are disrupted by permutations in DISC1, which lead to the development of these disorders, have yet to be clearly defined and are the subject of current ongoing research. Although, recent genetic studies of large schizophrenia cohorts have failed to implicate DISC1 as a risk gene at the gene level, the DISC1 interactome gene set was associated with schizophrenia, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARMCX3
Armadillo repeat-containing X-linked protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARMCX3'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the ALEX family of proteins which may play a role in tumor suppression. The encoded protein contains a potential N-terminal transmembrane domain and a single Armadillo repeat. Other proteins containing the arm repeat are involved in development, maintenance of tissue integrity, and tumorigenesis. This gene is closely localized with other family members on the X chromosome The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-d .... Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * {{gene-X-stub Armadillo-repeat-containing proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitophagy
Mitophagy is the selective degradation of mitochondria by autophagy. It often occurs to defective mitochondria following damage or stress. The process of mitophagy was first described over a hundred years ago by Margaret Reed Lewis and Warren Harmon Lewis. Ashford and Porter used electron microscopy to observe mitochondrial fragments in liver lysosomes by 1962, and a 1977 report suggested that "mitochondria develop functional alterations which would activate autophagy." The term "mitophagy" was in use by 1998. Mitophagy is key in keeping the cell healthy. It promotes turnover of mitochondria and prevents accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria which can lead to cellular degeneration. It is mediated by Atg32 (in yeast) and NIX and its regulator BNIP3 in mammals. Mitophagy is regulated by PINK1 and parkin proteins. In addition to the selective removal of damaged mitochondria, mitophagy is also required to adjust mitochondrial numbers to changing cellular metabolic needs, for stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |