|
RDoc
RDoc, designed by Dave Thomas, is an embedded documentation generator for the Ruby programming language. It analyzes Ruby source code, generating a structured collection of pages for Ruby objects and methods. Code comments can be added in a natural style. RDoc is included as part of the Ruby core distribution. The RDoc software and format are successors to the Ruby Document format (with associated software RD). RDoc can produce usable documentation even if the target source code does not contain explicit comments as it will still parse the classes, modules, and methods, and list them in the generated API An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build ... files. RDoc also provides the engine for creating Ruby ri data files, providing access to API information from the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Comparison Of Documentation Generators
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of documentation generators. Please see the individual products' articles for further information. Unless otherwise specified in footnotes, comparisons are based on the stable versions without any add-ons, extensions or external programs. Note that many of the generators listed are no longer maintained. General information Basic general information about the generators, including: creator or company, license, and price. Supported formats The output formats the generators can write. Other features See also * Code readability * Documentation generator * Literate programming Literate programming (LP) is a programming paradigm introduced in 1984 by Donald Knuth in which a computer program is given as an explanation of how it works in a natural language, such as English, interspersed (embedded) with snippets of macr ... * Self-documenting code Notes References {{DEFAULTSORT:Compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ruby Document Format
RD (Ruby Document) is a lightweight markup language for writing Ruby-related documents. It can be embedded in Ruby source code. RD is a traditional format. In modern Ruby, developers tend to write documents in RDoc instead of RD. Use Originally, most documentation in the Ruby world, including for Ruby itself, had been written in RD. Then in 2002, much of it was converted to RDoc format. Although, the Japanese version of the ''Ruby Reference Manual'' still remains in RD format. RD is designed to be written by hand and easily read in its raw form. Most end-users however experience it after it has been converted into HTML or man pages. RD can be embedded in Ruby code, and pure RD files usually have the extension .rd. Sample RD document This document is syntactically correct RD, which attempts to follow the major conventions on section naming as well. See also * Markdown * Plain Old Documentation Plain Old Documentation (pod) is a lightweight markup language used to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dave Thomas (programmer)
Dave Thomas (born 1960) is a computer programmer, author and editor. He has written about Ruby and together with Andy Hunt, he co-authored ''The Pragmatic Programmer'' and runs The Pragmatic Bookshelf publishing company. Thomas moved to the United States from England in 1994 and lives north of Dallas, Texas. Thomas coined the phrases 'Code Kata' and ' DRY' (Don't Repeat Yourself), and was an original signatory and author of The Manifesto for Agile Software Development. He studied computer science at Imperial College London. Works * ''The Pragmatic Programmer'', Andrew Hunt and David Thomas, 1999, Addison Wesley, . * '' Programming Ruby: A Pragmatic Programmer's Guide'', David Thomas and Andrew Hunt, 2000, Addison Wesley, * ''Pragmatic Version Control Using CVS'', David Thomas and Andrew Hunt, 2003, The Pragmatic Bookshelf, * ''Pragmatic Unit Testing in Java with JUnit'', Andrew Hunt and David Thomas, 2003, The Pragmatic Bookshelf, * ''Pragmatic Unit Testing in C# with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Modular Programming
Modular programming is a software design technique that emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent, interchangeable modules, such that each contains everything necessary to execute only one aspect or "concern" of the desired functionality. A module interface expresses the elements that are provided and required by the module. The elements defined in the interface are detectable by other modules. The implementation contains the working code that corresponds to the elements declared in the interface. Modular programming is closely related to structured programming and object-oriented programming, all having the same goal of facilitating construction of large software programs and systems by decomposition into smaller pieces, and all originating around the 1960s. While the historical usage of these terms has been inconsistent, "modular programming" now refers to the high-level decomposition of the code of an entire program into pieces: structured progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Free Software Programmed In Ruby
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, the ability to act or change without constraint or restriction * Emancipate, attaining civil and political rights or equality * Free (''gratis''), free of charge * Gratis versus libre, the difference between the two common meanings of the adjective "free". Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment *, an emoji in the Enclosed Alphanumeric Supplement block. Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media personality * Free, a pseudonym for the activist and writer Abbie Hoffman * Free (active 2003–), American musician in the band FreeSol Arts and media Film and television * ''Free'' (film), a 2001 American dramedy * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ruby Programming/RubyDoc
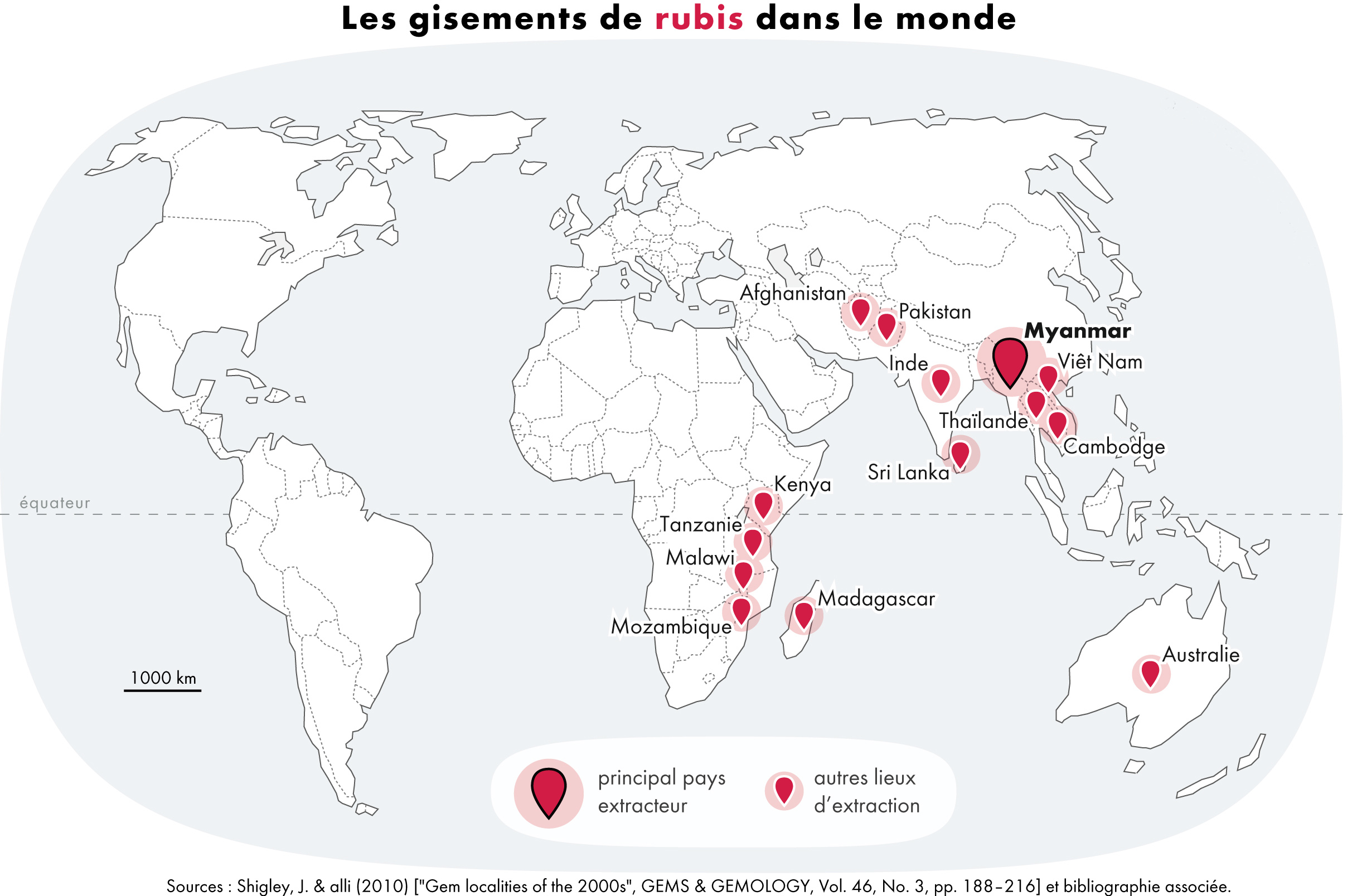
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum (aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires; given that the rest of the corundum species are called as such, rubies are sometimes referred to as "red sapphires". Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the presence of chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large prem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Markdown
Markdown is a lightweight markup language for creating formatted text using a plain-text editor. John Gruber created Markdown in 2004 as an easy-to-read markup language. Markdown is widely used for blogging and instant messaging, and also used elsewhere in online forums, collaborative software, documentation pages, and readme files. The initial description of Markdown contained ambiguities and raised unanswered questions, causing implementations to both intentionally and accidentally diverge from the original version. This was addressed in 2014 when long-standing Markdown contributors released CommonMark, an unambiguous specification and test suite for Markdown. History Markdown was inspired by pre-existing conventions for marking up plain text in email and usenet posts, such as the earlier markup languages setext (), Textile (c. 2002), and reStructuredText (c. 2002). In 2002 Aaron Swartz created atx and referred to it as "the true structured text format". G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Command-line Interface
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternative to the non-interactive mode available with punched cards. For a long time, a CLI was the most common interface for software, but today a graphical user interface (GUI) is more common. Nonetheless, many programs such as operating system and software development utility software, utilities still provide CLI. A CLI enables automation, automating computer program, programs since commands can be stored in a scripting language, script computer file, file that can be used repeatedly. A script allows its contained commands to be executed as group; as a program; as a command. A CLI is made possible by command-line interpreters or command-line processors, which are programs that execute input commands. Alternatives to a CLI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parsing
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a String (computer science), string of Symbol (formal), symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar by breaking it into parts. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning Part of speech, part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional Sentence (linguistics), sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject (grammar), subject and predicate (grammar), predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Class (computer Programming)
In object-oriented programming, a class defines the shared aspects of objects created from the class. The capabilities of a class differ between programming languages, but generally the shared aspects consist of state ( variables) and behavior ( methods) that are each either associated with a particular object or with all objects of that class. Object state can differ between each instance of the class whereas the class state is shared by all of them. The object methods include access to the object state (via an implicit or explicit parameter that references the object) whereas class methods do not. If the language supports inheritance, a class can be defined based on another class with all of its state and behavior plus additional state and behavior that further specializes the class. The specialized class is a ''sub-class'', and the class it is based on is its ''superclass''. Attributes Object lifecycle As an instance of a class, an object is constructed from a class via '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |