|
Russians In The United Kingdom
Russians in the United Kingdom are Russians, or the persons born in the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union or the Russian Federation, who are or were citizens of or residents of the United Kingdom. Settlement and population numbers The 2001 UK census recorded 15,160 residents born in Russia. The 2011 census recorded 36,313 people born in Russia resident in England, 687 in Wales, 2,180 in Scotland and 349 in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics estimates that 73,000 people born in Russia were resident in the UK in 2020. Estimates published by ''The Guardian'' suggest that the resident population of London born in Russia was over 150,000 in 2014. The rise in population has led to jocular nicknames for London such as "Londongrad" and "Moscow-on-the-Thames". Education In London, in particular Notting Hill Gate there are a number of Russian schools aimed at transmitting Russian language and culture to the children of Russian immigrant parents. The Russian Embassy School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Organisation For Economic Co-operation And Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a Forum (legal), forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. The majority of OECD members are High income economy, high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index, Human Development Index (HDI), and are regarded as Developed country, developed countries. Their collective population is 1.38 billion. , the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of List of countries by GDP (nominal), global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
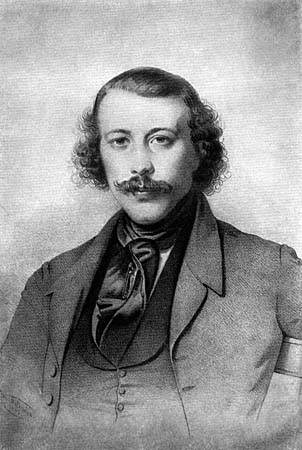 |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutionary socialist and social anarchist tradition. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing The Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. In 1849, he was arrested in Dresden for his participation in the Czech rebellion of 1848 and deported to Russian Empire, where he was imprisoned fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Peter Kropotkin
Pyotr Alexeyevich Kropotkin (; russian: link=no, Пётр Алексе́евич Кропо́ткин ; 9 December 1842 – 8 February 1921) was a Russian anarchist, socialist, revolutionary, historian, scientist, philosopher, and activist who advocated anarcho-communism. Born into an aristocratic land-owning family, Kropotkin attended a military school and later served as an officer in Siberia, where he participated in several geological expeditions. He was imprisoned for his activism in 1874 and managed to escape two years later. He spent the next 41 years in exile in Switzerland, France (where he was imprisoned for almost four years) and England. While in exile, he gave lectures and published widely on anarchism and geography. Kropotkin returned to Russia after the Russian Revolution in 1917, but he was disappointed by the Bolshevik state. Kropotkin was a proponent of a decentralised communist society free from central government and based on voluntary association ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Kolokol (newspaper)
''Kolokol'' (russian: Колоколъ, lit. 'bell') was the first Russian censorship-free weekly newspaper in Russian and French languages, published by Alexander Herzen and Nikolai Ogaryov in London (1857–1865) and Geneva (1865–1867). It had a circulation of up to 2500 copies. Despite being banned in Russia, it was well known and had a significant influence on the reformist and revolutionary movements of the 1860s. Initially the publishers viewed ''Kolokol'' as a supplement (прибавочные листы) to a literary and socio-political almanac '' Polyarnaya Zvezda'' (Polar Star), but it soon became the leader of the Russian censorship-free press. The newspapers '' Pod sud'' (To Trial; 1859–1862) and '' Obshcheye veche'' (General Veche; 1862–1864) were published as supplements to ''Kolokol''. At ''Kolokols base was a theory of Russian peasant socialism, elaborated by Herzen. Its political platform included democratic demands for liberation of peasants with land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Nikolai Ogarev
Nikolay Platonovich Ogarev (Ogaryov; ; – ) was a Russian poet, historian and political activist. He was deeply critical of the limitations of the Emancipation reform of 1861 claiming that the serfs were not free but had simply exchanged one form of serfdom for another. Ogarev was a fellow-exile and collaborator of Alexander Herzen on ''Kolokol'', a newspaper printed in England and smuggled into Russia. In the summer of 1827, during a walk in the Sparrow Hills above Moscow, Herzen and Ogarev made an oath not to rest until their country was free; the oath reportedly sustained them and their friends throughout many crises of their lives at home and abroad and was described in E. H. Carr's ''The Romantic Exiles''. Biography Nikolay Ogaryov was born in Saint Petersburg into a family of wealthy Russian landowners. Having lost his mother early, Nikolay spent his childhood years in his father's estate nearby Penza. In 1826 he met and became a close friend of his distant relative A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_title_page_1855.jpg) |
Free Russian Press
The Free Russian Press (russian: Вольная русская типография, also: Вольная русская книгопечатня) was a printing company and a publishing house launched in 1853 in London by Alexander Hertzen with a view to becoming the 'uncensored voice of free Russia'. History On 21 February 1853, Hertzen issued a statement, published under the title "Free Russian Press in London. For Brothers in Russia" in which he informed "all the free-thinking Russians" of the new publishing house with its own printing facilities to be opened on 1 May and promising 'free tribune to all'. "Send me whatever you will, and everything written in the spirit of freedom will be published, from the scientific articles or pieces on statistics and history, to novels, novellas or poems... If you haven't got anything of your own, sent hand-written copies of the banned poems by Pushkin, Ryleyev, Lermontov, Polezhayev or Pecherin... Since I am yet to maintain my links with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg) |
Socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the economic, political and social theories and movements associated with the implementation of such systems. Social ownership can be state/public, community, collective, cooperative, or employee. While no single definition encapsulates the many types of socialism, social ownership is the one common element. Different types of socialism vary based on the role of markets and planning in resource allocation, on the structure of management in organizations, and from below or from above approaches, with some socialists favouring a party, state, or technocratic-driven approach. Socialists disagree on whether government, particularly existing government, is the correct vehicle for change. Socialist systems are divided into non-market and mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(1830s%2C_GIM).jpg) |
Alexander Herzen
Alexander Ivanovich Herzen (russian: Алекса́ндр Ива́нович Ге́рцен, translit=Alexándr Ivánovich Gértsen; ) was a Russian writer and thinker known as the "father of Russian socialism" and one of the main fathers of agrarian populism (being an ideological ancestor of the Narodniki, Socialist-Revolutionaries, Trudoviks and the agrarian American Populist Party). With his writings, many composed while exiled in London, he attempted to influence the situation in Russia, contributing to a political climate that led to the emancipation of the serfs in 1861. He published the important social novel ''Who is to Blame?'' (1845–46). His autobiography, '' My Past and Thoughts'' (written 1852–1870), is often considered one of the best examples of that genre in Russian literature. Life Herzen (or Gertsen) was born out of wedlock to a rich Russian landowner, Ivan Yakovlev, and Henriette Wilhelmina Luisa Haag from Stuttgart. Yakovlev supposedly gave his son t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Jewish Emancipation In The United Kingdom
Jewish emancipation in the United Kingdom was the culmination in the 19th century of efforts over several hundred years to loosen the legal restrictions set in place on England's Jewish population. Advocates of each stage of this process, in and out of Parliament, sought and eventually won the passage of laws that placed male Jews in the United Kingdom on an equal legal footing with the kingdom's other emancipated males. Freedom for Catholics bodes well for Jews When in 1829 the Roman Catholics of the United Kingdom were freed from all their civil disabilities, the hopes of the Jews rose high; and the first step toward a similar alleviation in their case was taken in 1830 when William Huskisson presented a petition signed by 2,000 merchants and others of Liverpool. This was immediately followed by a bill presented by Robert Grant on 15 April that year which was destined to engage the British legislature in one form or another for the next thirty years. Thomas Macaulay, later a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Catholic Emancipation
Catholic emancipation or Catholic relief was a process in the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland, and later the combined United Kingdom in the late 18th century and early 19th century, that involved reducing and removing many of the restrictions on Roman Catholics introduced by the Act of Uniformity, the Test Acts and the penal laws. Requirements to abjure (renounce) the temporal and spiritual authority of the pope and transubstantiation placed major burdens on Roman Catholics. The penal laws started to be dismantled from 1766. The most significant measure was the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829, which removed the most substantial restrictions on Roman Catholicism in the United Kingdom. The Act of Settlement 1701 and the Bill of Rights 1689 provisions on the monarchy still discriminate against Roman Catholics. The Bill of Rights asserts that "it hath been found by experience that it is inconsistent with the safety and welfare of this Protestant Kingdom to be governe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg) |
Abolitionism In The United Kingdom
Abolitionism in the United Kingdom was the movement in the late 18th and early 19th centuries to end the practice of slavery, whether formal or informal, in the United Kingdom, the British Empire and the world, including ending the Atlantic slave trade. It was part of a wider abolitionism movement in Western Europe and the Americas. The buying and selling of slaves was made illegal across the British Empire in 1807, but owning slaves was permitted until it was outlawed completely in 1833, beginning a process where from 1834 slaves became indentured "apprentices" to their former owners until emancipation was achieved for the majority by 1840 and for remaining exceptions by 1843. Former slave owners received formal compensation for their losses from the British government, known as compensated emancipation. Origins In the 17th and early 18th centuries, English Quakers and a few evangelical religious groups condemned slavery (by then applied mostly to Africans) as un-Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |